What is Electrical PPE?
Electrical PPE stands for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for the electrical sector. It refers to a variety of specialized gear as well as equipment designed to protect individuals from electrical hazards who labor with or around electricity.
The use of electrical PPE is an essential component of electrical safety protocols & must always be accompanied by appropriate work procedures and adherence to applicable safety regulations and standards.
PPE’s Importance in Electrical Safety
According to Safety & Health Magazine, the (ESFI) – Electrical Safety Foundation International – noticed that workers in the extraction and construction sectors were responsible for 40% of electrical fatalities caused by risks and hazards, while those working in installation, maintenance, and repair work were responsible for 20% of these fatalities.
When performing operations such as electrical installation, maintenance, troubleshooting, or repair, there is a risk of electric shock, burns, arc blasts, and flashes, which are abrupt, powerful energy releases caused by electrical faults or short circuits.
To minimize or lessen the effects of potential risks, PPE should be used appropriately and safely to function as an interruption between the worker & electrical energy.
PPE for electrical safety needs to be given top priority for the following reasons, in addition to its essential function in ensuring worker safety:
Protection Against Electrical Shock: Tools with voltage ratings and insulated gloves are examples of personal protective equipment (PPE) that is made to resist and insulate against the high voltages found in electrical systems.
Preventing Burns and Arc Flashes: Arc flash suits and flame-resistant apparel can help prevent arc flash incidents by preventing ignition, minimizing the severity of burns, and provide thermal protection.
Decrease of Electrical Contact Injuries: The use of electrical protective equipment (PPE), such as non-conductive safety shoes and insulating mats, offers insulation and stops electric current from passing through the worker’s body, lessening the severity of injuries in the event of an electrical malfunction.
Respect for Safety Regulations: In order to keep the workplace safe, employees and employers should make sure that all applicable national and state laws are followed.
Risk Mitigation: By providing a further level of safety, electrical personal protective equipment (PPE) lowers the possibility of mishaps, injuries, and the total risk involved in electrical work.
Different PPE Types for Electrical Work
It’s essential to choose the electrical personal protective equipment (PPE) that will be employed according to the particular electrical risks and voltage levels that exist in the workplace. Some significant PPE types for electrical work are as follows:
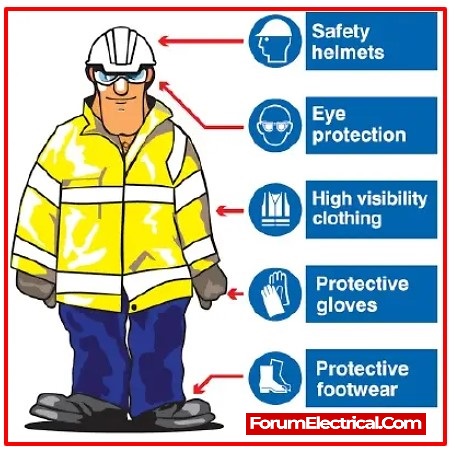
1). Helmet – Head Protection
Hard helmets have electrical insulating qualities that guard against impact risks, electrical shock, and falling objects.
Helmets are usually needed only when working on outdoor switchgear to protect from falling materials & impacts with solid objects at head height. Outdoor substations must always be designated as safety helmet’ zones, with helmet use made mandatory.
2). Safety Glass & Face Shield – Eye & Face Protection
Safety glasses that guard the eyes from flying sparks, debris, and other hazards are known as goggles or side shields.
Face shields provide further defense for the face & eyes against more serious risks including chemical splashes and arc flashes.
3). Ear Plugs – Hearing Protection
When using loud electrical equipment, earplugs made of foam or other materials can be worn to safeguard the ears from high noise levels.
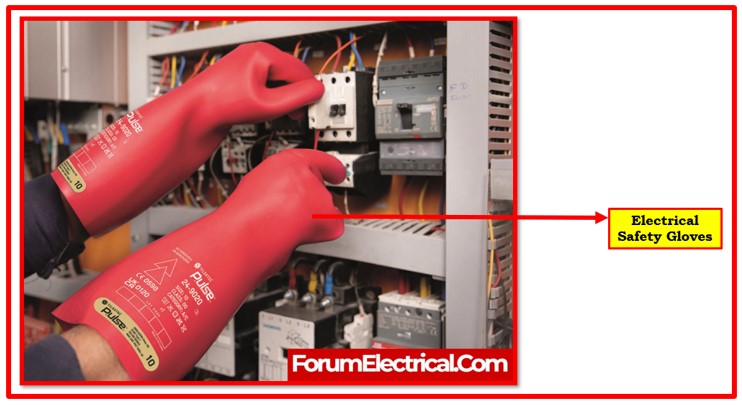
4). Gloves – Hand & Arm Protection
When working on live electrical circuits, wear insulated gloves made of rubber (or) other insulating materials to prevent electric shock.
Rubber lineman gloves give electrical workers doing high-voltage jobs more protection and insulation.
Sleeves that are made of insulating layers covering the arms providing further defense against electrical contact
5). Protection for Legs and Feet
Safety shoes that insulate the feet and have non-conductive bottoms to prevent electrical shock
Relativistic Overshoes are non-conductive shoes that may be worn over other shoes to give another layer of protection against electrical currents.
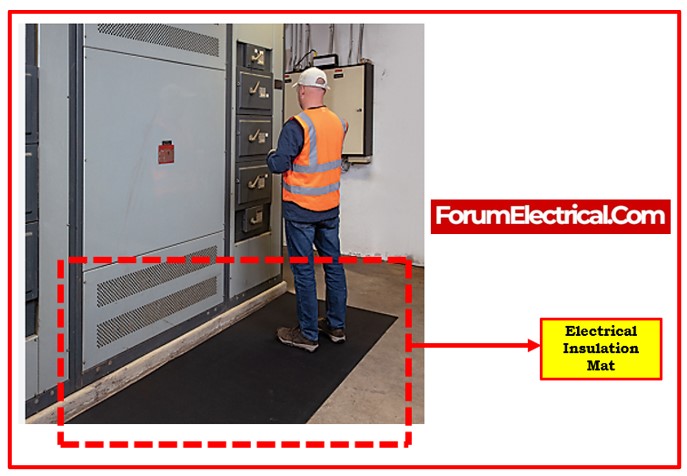
Insulating rubber matting is used to protect personnel from electrical shock when working live LV-HV switchgear, switchboards, substations, transformers, and electrical workstations. It accomplishes this by absorbing the power that could result from an electrical leak or short circuit.
6). Body Protection
Clothing that resists flames is made of non-conductive materials, like cotton, to lower the chance of burns from electrical fires or arc flashes.
Arc flash suits are made out of face shields or hoods, leggings, and jackets that withstand flames to shield wearers from the heat of arc flashes.
Furthermore, there are other options that can enhance an organization’s labor-protective measures. One method allows qualified personnel not wearing insulating personal protective equipment (PPE) to enter the minimum approach distance by covering (or) guarding exposed live electrical parts.
However, due to the low protective potential of IPE (Insulating Protective Equipment), it is still recommended to wear the minimum required level of electrical PPE.
7). Voltage Detector
In the electrical and power sectors, voltage detectors are frequently used to check for live wires (or) electrical circuits that are actively energized. When performing maintenance on electrical equipment (or) in locations where there are electrical hazards, this is an essential tool.
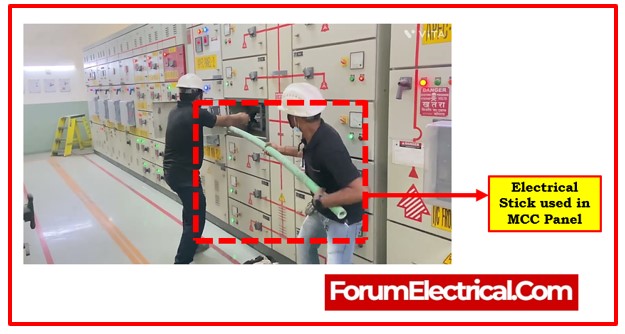
8). Electrical Stick
It is long enough to allow lineman to work safely away from electrically charged machinery. The fiberglass construction of the stick prevents it from conducting electricity. Additionally, a lineman can avoid the hazardous arc zone by staying 6–10 feet away from electrically charged equipment.
Considerations for Choosing the Perfect Electrical PPE
When choosing the suitable electrical PPE, many factors must be considered to ensure worker protection and safety.
The following are some important considerations:
- Determine the most appropriate types of PPE required by identifying potential risks such as arc flashes, electric shock, arc explosions, burns, and exposure to flying debris or chemicals.
- Identify the voltage levels required in the electrical work, as different voltage levels necessitate varying levels of insulation and safety. Determine that the PPE chosen has an appropriate rating for the voltage levels required in order to give suitable protection.
- Familiarize with the applicable electrical safety standards & regulations in the location. To ensure compliance & maximum safety, ensure that the PPE chosen meets (or) exceeds these criteria.
- Examine the characteristics & features of the different PPE alternatives. Choose those that adequate protection while still being functional for the work at the moment.
- Consider the size & fit options available for various PPE equipment and make the selection accordingly to ensure maximum protection and comfort.
- Examine the individual work to be performed as well as the PPE requirements for each, as some tasks may necessitate additional (or) specialized PPE.
- Select trusted vendors who provide dependable & high-quality electrical PPE. Check that the PPE fulfills established safety standards & has been properly tested and certified.
Electrical PPE Safety Guidelines
When utilizing electrical PPE, it is important to follow best practices to ensure optimal effectiveness, safety, & ability to limit the risk of electrical accidents by taking the following essential measures into consideration:
- Workers should get comprehensive training on the proper selection, usage, care, & maintenance of electrical PPE. Determine that they are aware of the specific hazards, restrictions, and procedures for utilizing each type of PPE.
- Inspect all electrical PPE on a regular basis for indicators of corrosion, wear, or degradation. Inspect for cuts, tears, fraying, (or) other problems that may affect the protective properties of the PPE and replace any damaged or defective PPE as soon as possible.
- Choose the appropriate PPE based on the particular risks present & the voltage levels in the work area. To ensure compliance & sufficient protection, follow safety standards and guidelines.
- When necessary, wear numerous layers of PPE. Wearing safety glasses with a face shield, for example, or combining insulated gloves with rubber sleeves, gives further protection against electrical risks.
- To reduce contamination and maintain cleanliness, use proper procedures for donning (putting on) & doffing (taking off) PPE.
- Clean & maintain electrical PPE on a regular basis according to the manufacturer’s specifications. For maintenance of non-electrical components, apply mild detergent and water, and follow particular cleaning and inspection methods for insulated components.
- To ensure the longevity and availability of electrical PPE, keep it in a clean, dry, and conveniently accessible location. PPE should be kept away from direct sunlight, harsh temperatures, chemicals, and other elements that could compromise its quality.
- Encourage employees to report any difficulties or concerns they have about the effectiveness (or) comfort of their PPE. Use their comments to enhance the selection & use of PPE & to develop a safety culture.
Conclusion
Electrical Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is an important tool for reducing the risk of injury and protecting electrical workers against potential hazards.
Electrical workers can make their workplace safe for themselves by using safety shoes, rubber matting, insulated hand gloves, face shields/goggles, helmets, and other PPEs. PPEs must be inspected every day to verify their dependability and efficiency in preventing electrical risks.
Improving safety & security in the field of electrical engineering can be achieved partially by making PPE use and maintenance a priority.