- What is the definition of electrical engineering?
Electrical engineering is a fundamental concept of mechanical physics and one of the most fundamental electrical interview questions that cover the study and application of electromagnetism and electricity in a variety of appliances. A.C. and D.C. are important concepts in electrical engineering. & D.C. Electric traction, current, transformers, and so on.
- What’s the difference between a capacitor, a resistor, and an inductor?
Capacitor: A capacitor is an electrical component that serves as a passive element by opposing current flow. When a potential is applied, it also stores some type of electrical charge.
Resistor: A resistor is an electrical component that obstructs the flow of current. It is a two-terminal component that is mostly used to minimise current flow.
Inductor: An inductor is an electrical component that stores energy in the form of a magnetic field and is used to build electrical circuits. It is also known as a choke or a coil.

- What is the distinction between capacitance and inductance?
Capacitance: Capacitance is defined as the amount of charge stored inside a capacitor at a fixed voltage.
Inductance: Inductance is a coil’s ability to resist changes in the electric current running through it. Mutual inductance occurs when the current change in the primary coil is opposed by a secondary coil.
- What is the difference between a generator and an alternator?
Both the generator and the alternator operate on the same principle, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Generator: It converts induced emf (Electro Motive Force) into direct current using a stationary magnetic field and a revolving conductor that rolls on the armatures with slip rings and brushes riding against each other.
Alternator: It has a spinning magnetic and stationary armature for high voltage and a rotating armature for low voltage, as well as a stationary magnetic field.
- What is the motor principle?
An electric motor operates on the idea of a conductor that carries current and generates a magnetic field around it. Rotatory movements are caused by placing a conductor perpendicular to a magnetic field (known as torque).
- What exactly is electric traction?
Electric traction refers to the use of electric power in a traction system (i.e., for railways, trams, trolleys etc).
Electric traction refers to the use of electricity for all of the aforementioned equipment. Magnetic traction is now employed for bullet trains, while electric traction systems are primarily powered by dc motors.
- What is an RLC circuit?
An RLC circuit is an electrical circuit that has a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C) that are linked in parallel or series. A second order circuit is one in which every voltage or current in the circuit can be represented by a second order differential equation.
- What is the MARX CIRCUIT?
It is used with generators to charge and discharge a number of capacitors in parallel. It is utilised when the voltage required for testing is greater than the available voltage.
- What are the benefits of thyristor-based speed control?
Faster switching than MOSFET, BJT, and IGBT
Low price
More precise.
- What exactly is armature reaction?
The reaction of armature flux to main flux is known as armature reaction. The armature flux can either assist or oppose the main flux.
- What is ACSR cable and how is it used?
ACSR stands for Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced, and it is utilised in transmission and distribution.
- What exactly is an automatic voltage regulator (AVR)?
AVR is an abbreviation for Automatic Voltage Regulator. It is an important component in Synchronous Generators since it manages the generator’s output voltage by adjusting its excitation current. As a result, it can control the Generator’s output Reactive Power.
- What exactly is a stepper motor? What are its applications?
A stepper motor is an electrical mechanism that responds to an input pulse. It is a sort of synchronous motor that works in steps in either direction rather than in a whole cycle, and it is utilised in automation parts.
- What’s the distinction between earth and neutral?
Neutral is a return current path for equipment, while earthing is human protection. Earth is a neutral support. If neutral is not present, the machine will enter full phase and we will receive a shock. To avoid such shocks, earthing is used.
- What exactly is Form Factor?
The ratio of the RMS (Root Mean Square) value to the average value is the form factor of an alternating current waveform (signal) (mathematical mean of absolute values of all points on the waveform)
- What exactly is slip?
Slip is the difference between the synchronous speed Ns and the actual speed N of the rotor.
- What exactly are dummy coils?
These are utilised with wave winding and are employed when the standard armature punching does not meet the requirements of the windings. They simply provide mechanical balance for the armature because an armature with some slots but no windings would be mechanically out of balance.
- What exactly is Voltage Regulation?
It is the voltage shift caused by reducing the load from its rated value to zero, represented as a percentage of the rated load voltage.
- What are the applications of interpoles?
Because the polarity of the interpoles is the same as that of the main pole ahead, they create an emf in the coil (due to commutation), which aids in current reversal. Another role is to counteract the armature reaction’s cross magnetising effect.
- What exactly is a two-phase motor?
A two-phase motor is one that features a phase split between the starting and running windings. Example: AC servo motor with a 90-degree phase separation between the auxiliary and control windings.
- Why are synchronous generators used to generate electricity?
Synchronous machines can work on different power factors (or different imaginary powers) by altering the field EMF, and are thus utilised to generate electricity.
- What exactly is an Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)?
The term AVR stands for Automatic Voltage Regulator. It is a key component in Synchronous Generators; it controls the generator’s output voltage by adjusting its excitation current. As a result, it can regulate the Generator’s reactive power output.
- What exactly is Eddy Current Loss?
The rate of change in an induced magnetic field causes this phenomenon. The relative motion generates a circulating flow of electrons or current within the conductor, resulting in a loss of efficiency.
- What exactly is a ground line?
The ground line’s function is to provide a continuous, uninterrupted channel for a circuit fault current to return to the distribution panel and trip the circuit’s over current device.
- How does one increase the number of parallel routes in an armature?
One can increase the parallel paths in an armature by increasing the number of magnetic poles.
- In a DC generator, how are the brushes connected?
Typically, all positive brushes are linked together, and all negative brushes are linked together.
- How is field distortion corrected?
Using compensatory windings inserted in the pole-shoe holes and coupled in series with the armature
- What causes the brushes to spark?
It is caused by the self-induction of the commutating coil.
- What is the standard rotational direction of DC generators?
When viewed from the other end to the driving end, clockwise
- What is meant by a generator’s voltage buildup?
It refers to the steady increase in generator voltage to its maximum value once the generator is started from a standstill.
- How do you start a generator?
It is normally brought up to speed with the assistance of a driving engine known as a prime mover.
- What is the distinction between synchronous and asynchronous generators?
Synchronous generators provide both active and reactive power, whereas asynchronous generators (induction generators) provide only active power while observing reactive power for magnetising. This form of generator is utilised in windmills.
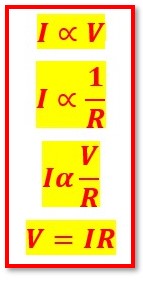
- Define Ohm’s law?
Ohm’s law defines a relationship between the three essential concepts of voltage, current & resistance. It states that the electric current in a circuit is directly proportional to voltage and to the resistance it is inversely proportional.
- What is the primary usage of a transistor in an electric circuit?
Transistors are primarily used to amplify current so that the output power exceeds the input power.
- What if the series current doubles?
When the series current doubles, the resistance is half.
- Explain what a series of resistors will do.
When a sequence of resistors is connected in series, the source voltage is divided in proportion to their values.
- What is a Zener diode?
When exposed to adequate voltage, a Zener diode permits current to flow in the opposite direction.
- What is the purpose of a series of resistors?
When we add a series of resistors, they divide the source voltage into the amount that corresponds to their values.
- What does an ideal transformer look like?
If no losses occur, a transformer is said to be an ideal transformer. In other words, in an ideal transformer, the transformer input authority should be equal to the transformer output authority, i.e., they have 100% competence.
- What is reverse polarity, and how can it be corrected?
Reverse polarity occurs when one or more of your receptacles are wired incorrectly. Check the wire connection at the outlet and verify your receptacle to correct the reverse polarity. A receptacle with reverse polarity will have the white wire screwed to the hot side and the black wire screwed to the neutral side; if this is the case, swap the wires and the problem will be resolved. If the problem persists, a qualified electrician will be required.
- What exactly do you mean by reversal polarity? What is the procedure for repairing it?
Reverse polarity happens when the wires are not properly connected. For instance, suppose the white wire is connected to the hot side and the black wire is connected to the neutral side. You can resolve this issue by inspecting the wire connection from the outlet or the receptacle. By exchanging this entanglement, you can solve the reverse polarity.
- What exactly are laser diodes?
Laser diodes are transistor-like small packages with two or more electrical lines. Lasing happens when stimulated emission leads in photon amplification in the lasing mode. These photons collide between the rear and front mirrors, resulting in a diverging beam from the laser diode packages.
- What is the RLC current?
RLC is an abbreviation for Resistor (R), Inductor (L), and Capacitor (C). The term RLC refers to three circuit elements: resistor (R), inductor (L), and capacitor (C). This circuit can supply direct current to the entire circuit. A differential equation of the second order characterizes this talent. That is why it is also referred to as a second-order circuit.
- What is the function of a circuit breaker?
A device intended to safeguard a circuit from harm caused by a short circuit.
- What are the principles underlying the operation of a circuit breaker?
A circuit breaker functions as a switch that can be used to interrupt the flow of current. The protection layers (indicators) indicate circuit rupture due to overloading or other issues, which prevents the circuit from breaking.
- What are the many types of networks utilised to construct an electrical circuit?
Passive and Active Networks are the two primary types of networks used to construct an electrical circuit. A passive network is one that comprises passive elements like as resistance, capacitance, and inductance. An Active Network, on the other hand, is a network that comprises active elements such as Current or Voltage Sources.
- What is the definition and function of an exciter?
An exciter is a device (a generator/battery) that provides power to another generator or motor. This electric current is then employed in the other circuit to generate the magnetic field.
- What are the various kinds of semiconductors?
In electronics, there are two types of semiconductors: intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. Extrinsic semiconductors are divided into two types: N-type semiconductors and P-type semiconductors.
- What do you mean by a laser diode?
A laser diode is a small transistor with two or more electrical connections. It is a semiconductor device comparable to a light-emitting diode in which a diode directly pumped with an electrical current can produce lasing conditions at the diode’s junction. Laser diodes may transform electrical energy directly into light.
- Why can’t a series motor be started with no load?
Because of the large starting torque, a series motor cannot be started without a load. Series motors are used in trains, cranes, and other applications.
- What do you mean by a transistor?
A transistor is a semiconducting device constructed entirely of semiconducting materials. Electrical signals and power are interpreted by transistors. An external circuit should link a transistor to at least three terminals. It is sometimes referred to as a mixture of numerous n-type and p-type semiconductors.
- In distribution lines, where should the lighting arrestor be installed?
Near distribution transformers, 11kv outgoing feeders, 33kv incoming feeders, and power transformers in substations.
- What exactly do you mean by reversal polarity, and how can you rectify it?
The state of reverse polarity occurs when one or more receptacles are misconnected. To correct the reverse polarity, check the wire connection at the outlet and inspect the receptacle. The white wire is connected to the hot side and the black wire is connected to the neutral side by a receptacle with reverse polarity. You may quickly solve the problem by swapping the wires.
- What is the permissible rise of temperature in a well-designed generator?
270C above the surrounding air is the permissible rise of temperature in a well-designed generator.
- What are the primary applications of a transistor?
A transistor’s principal function is to increase the input current, which in turn increases the output current. To put it another way, transistors are utilised to improve electric and electrical power.
- What exactly is IDMT relay?
It is a relay with an inverse definite minimum time. The operation of an IDMT relay is inversely proportional, and it also has a minimum time after which it runs. It is inverse in the sense that as the amplitude of the fault current increases, the tripping time decreases.
- Why is temperature rise carried out in bus bars and isolators?
Bus bars and isolators are designed for continuous power flow, which means they carry high currents, raising their temperature. As a result, these devices must be tested for temperature rise.
- What are HRC fuses and where it is used?
HRC stands for “high rupturing capacity” fuse and is utilised in electrical transformer distribution systems.
- Why do most analogue o/p devices have an o/p range of 4 to 20 mA rather than 0 to 20 mA?
4-20 mA is a typical range for indicating measurable quantities for any process. The reason 4mA was chosen over 0mA is for fail safe operation. A pressure instrument, for example, outputs 4mA to signify 0 psi and up to 20 mA to indicate 100 psi or full scale. If there is a problem with the instrument (for example, a broken wire), the output is reduced to 0 mA. So, if the range is 0-20 mA, we can tell whether it is due to a broken wire or 0 psi.
- What is knee point voltage?
Knee point voltage is computed for electrical current transformers and is a critical component in selecting a CT. The voltage at which a CT becomes saturated








