RCCB
RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
- RCCB
- What is a RCCB used for?
- Test Procedure
- RCCB Test Button (Before Test)
- Tripping Time Test
- ½ I Test (Non-Trip Test)
- I Test (Trip Test)
- 5I Trip Test
- RCCB Test Button (After Test)
- RCCB Ramp Test
- Earth Fault Loop Impedance Test
- Checklist
- Difference Between RCD and RCCB
- RCD vs RCCB
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
It is the full form of RCCB.
Residual Current Circuit Breakers are designed to protect individuals from the dangers of electrical shocks, electrocution, and fires caused by faulty wiring or ground faults.
The Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB), often known as a circuit breaker, is an electrical safety device that switches off the power supply quickly when it detects leakage that may result in an electric shock.
Current leaks can be caused by aging or exposed cables, malfunctioning electrical appliances, or broken insulation.
RCCB is very effective in cases where there is an unexpected earth fault in the circuit.
If the circuit is protected with an RCCB, it will trip within a fraction of a second, preventing that individual from receiving an electrical shock.
Therefore, it is a smart & safe practice to mount an RCCB in the electrical circuit.
What is a RCCB used for?
The Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB), often known as a circuit breaker, is an electrical safety device that switches off the power supply quickly when it detects leaks that could cause an electric shock.
Test Procedure
RCCB Test Button (Before Test)
Tripping Time Test
Use a testing instrument to determine the RCCB’s tripping time. This metric measures how soon the RCCB acts to a fault.
½ I Test (Non-Trip Test)
A test at ½ 50% of the RCCB’s recommended tripping current for 2 seconds.
This serves as a ‘no-trip’ test, & the RCCB should not trip. This is meant to ensure that the RCCB does not trip when false ‘nuisance’ current appears in circuit being protected.
I Test (Trip Test)
Test the RCCB at 100% of its rated tripping current.
This acts as a ‘trip’ test, requiring the RCCB to break the circuit within 300ms.
Choosing polarity (0⁰ or 180⁰) allows for correct measurement of trip duration, as some RCCBs function differently at the start of a positive or negative cycle.
5I Trip Test
This test is mostly for RCCBs rated at no more than 30mA (i.e. 30mA and 10mA).
The RCCB should break the circuit within 40ms, with a residual current of 5IΔn.
Choosing polarity (0⁰ or 180⁰) allows for accurate trip measurement, as some RCCBs function differently at the start of a positive or negative cycle.
RCCB Test Button (After Test)
RCCB Ramp Test
This test measures the trip current of an RCCB. The current level gradually increases from half of the rated tripping current (0.5 x IΔn) of RCCB.
When the RCCB trips, actual trip current (milliamps) is displayed. Very effective in diagnosing undesirable RCCB tripping. IEC 61008-compliant RCCBs can operate between 0.5 and 1.0 times their rated tripping current. If the RCCB trips at less than 0.5 times the rated tripping current, replace it.
Earth Fault Loop Impedance Test
Perform an earth fault loop impedance test to make sure a low impedance transmit for fault currents. This demonstrates the RCCB’s efficacy in the occurrence of a fault.
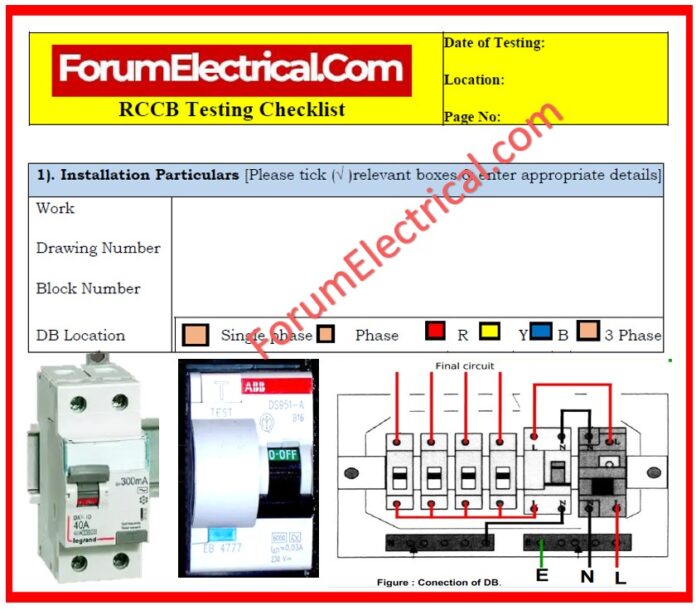
Checklist
Important Note
This Test Form is for RCCB without time-delayed operation according to IEC 61008.
This Test Form is for testing 2 Pole-RCCBs & is not applicable to 4 Pole-RCCBs.
Difference Between RCD and RCCB
RCD vs RCCB
| RCD | RCCB |
| RCDs not only detect current imbalances, but also guard against overcurrent. | RCCB mainly protects against residual currents. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1). What does an RCCB detect?
Residual Current Circuit Breaker, or RCCB, is a device that detects current and disconnects any low voltage (uneven current) circuit when a failure occurs.
The primary reason for installing a RCCB is to protect individuals from electric shocks, which can be fatal.
2). Where should the RCCB be checked in the circuit?
Although the tests can be performed right away on the RCCB’s load side, it is best to perform them at the protected circuit’s extremity (final point).
When testing the RCCB, the load switch should be turned off or the load should be unplugged from the circuit.
3). What causes the RCCB to trip?
A large number of appliances connected to a single circuit might generate power fluctuations, which could trip the RCCB. To prevent overload, distribute appliances across many circuits. Don’t overload sockets (or) extension cords.