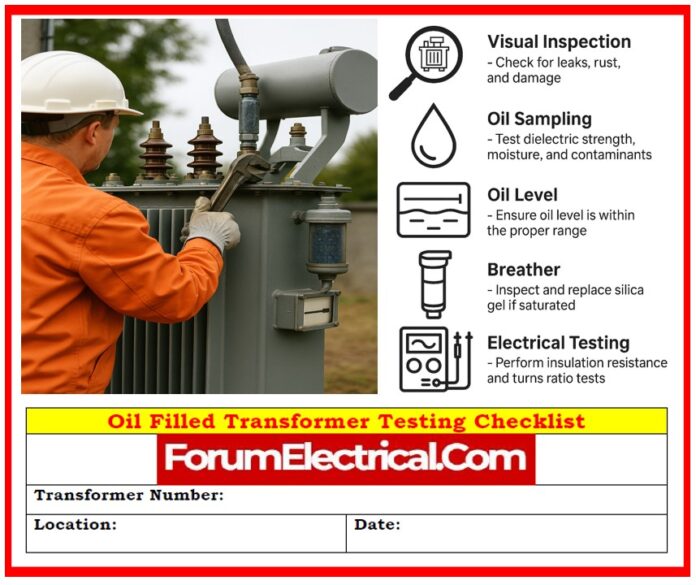
Oil-filled transformers are essential components of power systems, enabling voltage transformation & electrical isolation.
Regular testing of these transformers assures peak performance, increased dependability, reduced downtime, and avoids catastrophic failures.
- Transformer Identification & Nameplate Details
- Transformer Information
- Nameplate Details
- Routine Testing Activities
- Visual & Physical Inspection
- Breather & Bushing Check
- Protection & Monitoring Devices
- Oil Sampling & DGA
- Other Key Components
- Electrical Test
- Insulation Resistance Test (IR)
- Earth Resistance Test
- Dielectric Strength (BDV) Test for Oil
- Checklist
- Observations
This checklist guides technicians, engineers, & testing supervisors through extensive inspections, common diagnostic tests, and the recording of critical operational information.
This testing checklist is appropriate to be utilized during routine inspections, scheduled preventive testing activities, and condition-based monitoring. It helps to:
- Detect and address early indicators of wear & tear.
- Maintain safety and regulatory standards.
- Improve the transformer’s performance and efficiency.
- Reduce unwanted downtime and expensive repairs.
Transformer Identification & Nameplate Details
Before initiating testing, record the fundamental identification information to ensure traceability & documentation accuracy.
Transformer Information
- Transformer Number: A unique identifier for tracking.
- Location: Substation or location name.
- Inspection Date: The date on which the testing operation occurred.
Nameplate Details
Capture the specs listed on the transformer nameplate for inspection and comparison with test findings.
| Parameter | Details |
| Capacity (kVA/MVA) | |
| Make/Manufacturer | |
| Serial Number | |
| Commissioning Year | |
| Manufacturing Year | |
| HV Voltage Rating | |
| LV Voltage Rating | |
| HV Current Rating | |
| LV Current Rating | |
| Vector Group | |
| Impedance (%) | |
| Cooling Type (ONAN/ONAF) |
Routine Testing Activities
The following routine checks must be done with each testing cycle:
Visual & Physical Inspection
- Complete a visual assessment of the transformer’s body, surroundings, & fittings.
- Inspect for oil leaks, corrosion, dirt accumulation, & paint condition.
- Check the oil levels in the main tank & conservator.
Breather & Bushing Check
- Examine the silica gel breather for discolouration, which indicates moisture saturation.
- Check the level of oil in the breather cup.
- Examine the transformer bushings for cracks, flashover marks, & contaminants.
Protection & Monitoring Devices
- Clean and test the operation of the relays & alarm contacts.
- Check the functionality of thermometers.
- Check for free movement of the indicator points.
Oil Sampling & DGA
- Collect oil samples for Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA), which can detect thermal or electrical issues.
Other Key Components
- Evaluate the performance of the Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) & Pressure Relief Vent.
- Inspect the conservator tank for oil levels, rust, and blockages.
- Inspect the general paint condition for rust (or) blockage.
Electrical Test
Insulation Resistance Test (IR)
This test determines the insulation level between various transformer windings & ground. It assists in detecting moisture intrusion, insulation breakdown, or contamination.
| Test Description | 1 Min IR (MΩ) | 10 Min IR (MΩ) | Polarization Index (PI) |
| HV to Earth | |||
| LV to Earth | |||
| HV to LV |
Important Note: A PI value of > 2.0 indicates good insulating conditions.
Earth Resistance Test
Make sure that all earthing connections provide a low resistance path for the fault current dissipation.
| Test Point | ER (Ω) |
| Neutral Earth to Ground | |
| Body Earth to Ground |
Important Note: Earth resistance should normally be less than 1 Ohm for proper grounding.
Dielectric Strength (BDV) Test for Oil
BDV testing measures the dielectric quality of transformer oil. Low BDV could suggest contamination or moisture infiltration.
| Sample | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | Average (kV) | Remarks |
| Transformer Main Tank Oil |
Important Note: A BDV of ≥ 30 kV is regarded suitable for continuous operation.
Checklist
Observations
Record for documenting any anomalies, corrective measures done, or other recommendations.
Regular testing of the oil-filled transformers is essential for their operational reliability and asset longevity.
This checklist establishes a standardized format for evaluating transformer health via inspections and diagnostic tests.
It supports testing professionals in early fault detection, improves safety, and minimizes the likelihood of unexpected equipment failures.