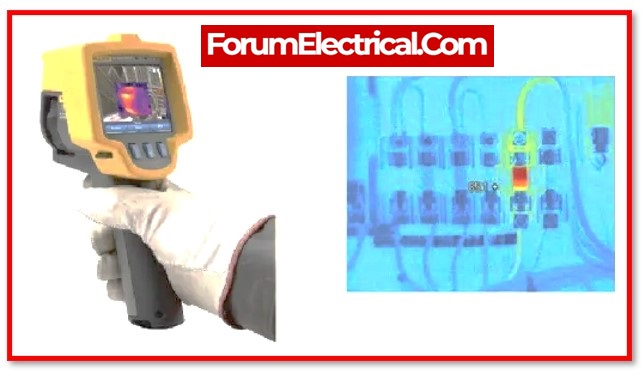
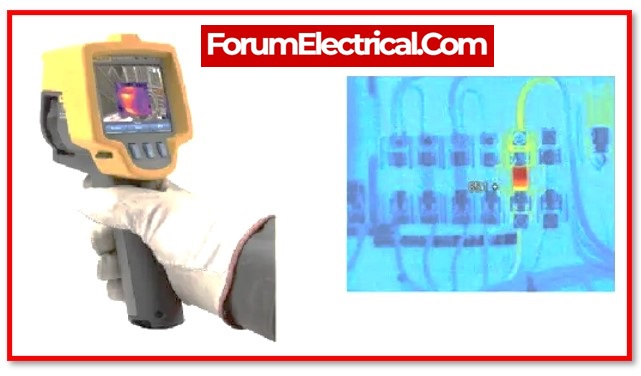
1). LV Intrusive Switchboard
Low-voltage intrusive switchboards regulate and distribute power in buildings and facilities. Power distribution & circuit protection depend on it.
LV intrusive switchboards accept power from the utility & generator & distribute it to building circuits. Multiple circuit breakers or fuses safeguard each circuit against over-loads, short-circuits, & other types of electrical failures. The switchboard makes power separation and control simple.
Safety
- Before shutting down, verify that all power meters are working.
- Verify the lights and indicators work.
- Check locking mechanisms for signs of wear or damage.
Maintenance
- All LV switchboards should be completely cleaned, vacuumed, and given a thorough visual check on the inside and out.
- Verify that any installed electronic surge protection is still functional.
- Be sure to check the rating as well as the continuity of the fuse in the control circuit.
- As needed, inspect and torque-test bolted electrical connections to the required values.
- Arc chute secondary injection, check contacts, withdrawable or fixed ACB maintenance, etc.
- Visual examination for overheating or degradation indicators.
- A final visual check once the work is finished to ensure everything is in order.
- Examining each panel for rust and evidence of paintwork deterioration.
- Examine battery integrity, battery tripping packs, flaws, etc.
2). LV Non-Intrusive Switchboard
In low-voltage electrical systems, LV non-intrusive switchboards control and distribute power. It protects, controls, and monitors building electrical circuits.
Non-intrusive means the switchboard can monitor and operate the electrical system without directly interference with the electrical wiring connections. Communication interfaces, electronic trip units, and sophisticated metering devices perform functionality.
Attention: No shutdowns are necessary for these maintenance operations.
Safety
- Before shutting down, verify that all power meters are working.
- Verify the lights and indicators work.
- Check the locking mechanisms to look for any signs of wear or damage.
Maintenance
- Completely clean, hoover and check the outside simply visually.
- Control wires, relays, power supplies, timers, and fuse carriers may all be visually inspected.
- Verify that any installed electronic surge protection is still functional.
- Visual examination for overheating or degradation indicators.
- Examining each panel for rust and evidence of paintwork deterioration.
- Examine the battery’s integrity, tripping, and any symptoms of faults.
3). Chassis for ACB: Rack out ACB
A rack out Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) is an Air Circuit Breaker that can be readily removed (or) “racked out” from the chassis for the purposes of maintenance or replacement. The chassis of a rack out ACB is constructed such that it may safely house the ACB unit while also facilitating its removal in a way that is user-friendly.
- Vacuum or clean the interior chassis.
- Verify the safety shutters’ shutting functionality.
- Verify the integrity of the shutter locking mechanisms.
- Verify the contacts’ location and functionality.
- Use the locking system.
- If necessary, grease clusters.
4). ACB’s overall condition
ACBs safeguard electrical circuits against overcurrent & short circuit failures. When abnormal circumstances exist, it immediately interrupts electric current to avoid circuit or device damage.
Industrial and commercial low-voltage electrical distribution networks employ ACBs. They protect more significant circuits and manage more currents. ACB’s “air” is arc extinction medium.
- Check the ACB’s overall condition, ACBs.
- Vacuum ACB and clean with Henkel 273471 diluents.
- Clean up filters and hoover the arc-chutes.
- Look for signs of contact wear.
- Examine the insulation of the auxiliary wire.
- Verify the ACB locking mechanisms.
- Manually open and shut.
- Manually recharge the electronic device.
- Trip curve data from secondary injection using FFT kit.
- Inspect the earth fault/earth leakage protection.
- In case it’s required, grease the contacts.
- Trip test of the MCCB with report.
5). Busbar & Accessories
Busbars, commonly referred to as bus bars, distribute electrical power in electrical systems. It transfers electricity between many circuits or devices. Copper or aluminium busbars carry electricity well.
Switchgear, distribution boards, panelboards, & electricity distribution systems in commercial, industrial,& residential environments use busbars. They reduce power losses & voltage drops to distribute electricity efficiently.
- Visual observation of every Power bar runs
- Supports should be checked, as well as straight runs, alignment, joint packs, and directional change components.
- Verify earth continuity, panel flanges, etc.
- Complete full thermal image survey
6). Meters
Current transformers (CTs) measure and monitor AC currents in electrical power networks. It reduces high currents for measurement and protection. Industrial, electricity, and distribution systems employ CTs.
An instrument transformer called a potential transformer (PT) or voltage transformer (VT) steps down high voltages for monitoring and protection. It measures AC voltage instead of current, like a current transformer (CT).
- CT connections
- Voltage connections
- Modbus connections
7). Check MCCB
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker is known as MCCB. It is a type of circuit breaker that safeguards electrical systems against overcurrents & short circuits. In order protect circuits and electrical equipment from harm caused by high current, MCCBs are often employed in low voltage electrical distribution systems & industrial applications.
- Motor operation
- Release under voltage
- Power source unit
- Relay controls
- Fuse holders and fuses
8). Power Distribution Unit (PDU)
A PDU is a device that distributes electrical power to several devices or components of equipment in industries, server rooms, and other IT locations. It acts as a centralised system for managing and distributing power, offering organised and practical power connection.
- Completely clean the interior and exterior PDU switchboards.
- Verify the operation of each power meter.
- Check the rating and continuity of the control circuit fuse.
- Verify the lights and indicators are working.
- Inspect & torque test (TT) bolted electrical connections to the appropriate levels as required.
- Verify the tightness and torque of all cable connections’ terminals.
- Visual examination for overheating or degradation indications
- Examination of all panels for corrosion and evidence of paintwork deterioration
- Prior to installing coverings, inspection is performed to ensure that everything is in order.
- Every label is affixed correctly and firm in place.