What is an Earth Pit?
In an earthing system, a Concrete Earth Pit is a construction used to give access to earth conductors & other components for maintenance and inspection.
Usually built from reinforced concrete, it is a type of underground box placed where the earthing system is found.
Purpose
To outline regular maintenance of Earth pit working procedure.
Scope
This procedure applies to preventive maintenance of earth pits.
Equipment Required
- Basic PPE
- Fall Protection Harness
- Lifting Equipment
- Ladders
Roles & Responsibilities
- Manager
- Engineer
- Supervisor
- Technicians
Tools Required
Megger
Reference
Maintenance Checklist
Safety
Verify that testing uses calibrated instruments and that safety criteria are followed.
Functioning
Factors affects Earthing:
- Soil resistivity
- Soil condition
- Moisture
- Dissolved salts
- Climate condition
- Location of the earth pit.
Permissible Values of Earth Resistance
- Major power station – 0.5 Ω
- Major Sub-stations – 1.0 Ω
- Minor Sub-station – 2 Ω
- Neutral Bushing – 2 Ω
- Service connection – 4 Ω
- Medium Voltage Network – 2 Ω
- L.T Lightening Arrestor – 4 Ω
- L.T Pole – 5 Ω
- H.T Pole – 10 Ω
- Tower – 20 Ω
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
- Excavation on ground for a standard soil pit size is 1.5M x 1.5M x 3.0 M.
- Utilize 500 mm x 500 mm x 10 mm GI Plate or Greater Size to lower Earth Resistance and increase Contact of Earth.
- Combine Wood Coal Powder Salt and Sand in equal weight.
- Rust confirms for GI Plate for long life; wood coal powder is a good conductor of electricity and anti-corrosive.
- Coal and salt help to permanently moist the ground.
- Coal absorbs water and the salt percolates to maintain the moist soil.
- Watering earth pits in summer should always be done with care to ensure the pit soil will be wet.
- Carbon, the component of coal, is a good conductor reducing the earth resistance.
- Use salt as electrolyte to generate conductivity between GI Plate Coal & Earth under dampness.
- Porosity formed from sand allows water and humidity to cycle around the combination.
- Place a 500 mm x 500 mm GI Plate ( EARTH PLATE) with 10 mm in the middle of the mixture.
- Connect GI Plate to the system earthing using Double GI Strip size 30 mm x 10 mm.
- Covering GI Strip from earth plate to top flange with GI Pipe of size 2.5″ diameter with a flange on top will be more preferable.
- Use water time sometimes via this GI pipe to bottom of soil plate and cover top of the GI pipe with the T joint to avoid jamming of the pipe with dust and mud.
- Using another conductor dip on the Earth at least 500 mm deep, keep less than one Ohm Resistance from earth pit from a distance of 15 Meters surrounding the earth pit.
- Verify the check voltage across earth pit conductors and neutral of mains. Given 220V AC 50 Hz, it must be < 2.0 V.
Maintenance Procedure
Engineer conveys Powerhouse and allocates Technicians according the Preventive Maintenance plan.
- Request Engineer for your work authorization.
- PM activities call for specific PPE.
- Arrange 2 electrode for the earth pit checking.
- Check tightness of the Connection & clean Earth Pit.
- Connect the equipment as per Fall of Potential method.
- Obtain Earth Resistance Value when the grid connected (< 2Ω).
- Taken Earth Resistance Value when grid disconnected.
Fill all data in checklist; if earth resistance value is low, add water and salt in the Pit; after completion of preventive maintenance (PM) work, the same must be communicated to respective area Engineer; this preventive maintenance shall be carried out once in year as per schedule.
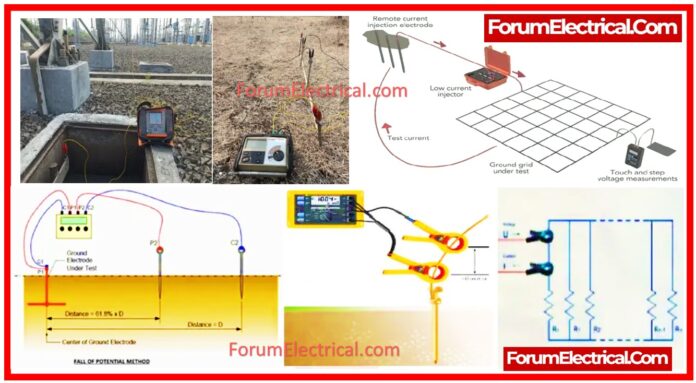
Testing Procedure
- The frequency of testing the earth pit will be once per year. (Megger)
- The Earth Tester is utilized to measure soil resistivity. It is also known as the “MEGGER“.
- The instrument has a voltage source, a meter for measuring resistance in ohms, switches to adjust the range, wires to connect terminals to the earth electrode, and spikes.
- Measured with a 4 terminal earth tester instrument.
- Wires are used to connect the terminals.
P = Potential Spike, C = Current Spike. The distance across the spikes might be 1M, 2M, 5M, 10M, 35M, (or) 50M.
- Spikes are evenly spaced and in a straight line to ensure electrical continuity. Take measurements in multiple directions.
Soil Resistivity = 2πLR
Where
R – Earth resistance in (Ω) ohms.
L – Measure the distance between spikes in cm.
π = 3.14
P – Earth resistivity in (Ω-cm) ohm-cm.
- Earth resistance values are proportional to soil resistivity values.
Conventional Earth Pit Maintenance Procedure
- Pour water twice (in week) via the Pit Funnel & around the Earth Pit Pipe to moist the pit.
- The correct operation of the earth pit depends thoroughly on its being wet at all times.
- One is advised a permanent drip kind of watering system. For this application, a container of five liters in capacity filled with water with a little tube outlet from it can be quite beneficial opening into the soil pit watering funnel & water dripping out of it.
- Small amounts of water daily are required instead of continuously pouring additional water at intermittent intervals.
- Let the Earth Pit never get dry.
- Not connect any other device (or) equipment either to copper wire from earth pit or the plug mains set for VSAT.
- Apply cement plastering not above the soil pit. Let the surface of the soil pit show.
- Dig nowhere else for any other reason near the earth pit. To be left from the earth pit outside edge at least a clearance of around three feet.
- Plant no plants or shrubs over or very near the earth pit.
- At all costs, do not cut or break the copper wire connecting to plug mains (wherein the modem is connected) or the antenna.
- No waste should be allowed to flow over or very close to the earth pit; this will rust earthing electrodes & lower the conductivity, therefore impairing the regular operation of the earth pit for its intended use.
- Customer should once a week verify the E-N voltage and record the same at site itself. This will enable one to grasp the state of the grounding system & implement necessary corrections.
- Once in every month, check the continuity of the copper wire going from the earth pit to the antenna and modem plug mains; if there is any cut, discontinuity (or) damage to running wire, conduct the necessary modifications. A logbook to be maintained by consumer at site.
The maintenance of earth pit is actually essential. Hence, the activities stipulated need to be carried out without fail for human safety and protection from electrocution at any cost. Improved life and performance from every equipment.