- What are the room design requirements for UPS?
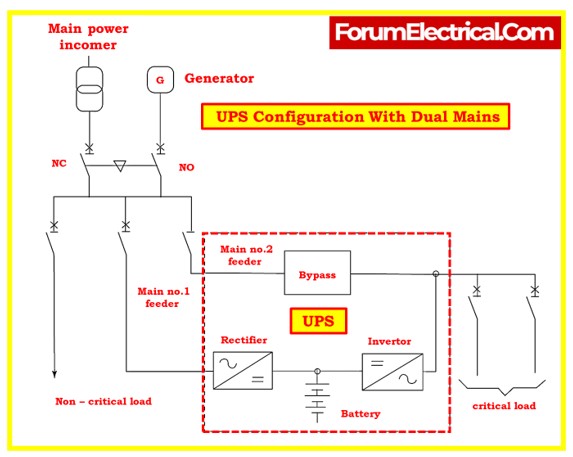
- What is the general arrangement of UPS system?
- Cable Sizing & Installation
- General guidelines for cable routing & laying
- What are the safety requirements and rules for UPS?
- What are the room design requirements for UPS?
- Battery protection
- Connection of the Load
- External Protection
What are the room design requirements for UPS?
Location
- Care should be taken in selecting the UPS installation location. Depending on the precise position and how close it is to the connected load, different types and amounts of site preparation may be necessary. The UPS should ideally be installed close to the loads.
- If the distance between the load and the UPS is greater, we must take into account the voltage drop based on the length of the cable and take appropriate measures, such as oversizing the cable.
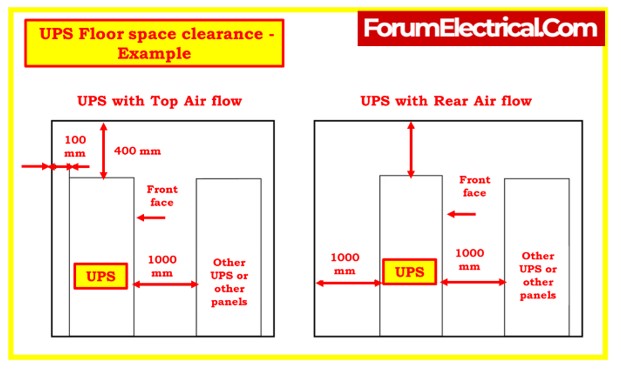
Floor Space and Clearance
- Ensure there is enough floor space for the UPS system, as specified in the manufacturer’s data sheets.
- If rear access is not needed, the UPS can be installed against a wall.
- It’s beneficial to maintain both side and rear access for service requirements. Rear clearance depends on the UPS’s construction, with modular units requiring rear clearance.
- Keep at least 1 meter of clear area in front of the unit for service personnel.
- Confirm that the floor can support the UPS and batteries, considering the unit’s weight, which varies based on capacity and type.
What is the general arrangement of UPS system?
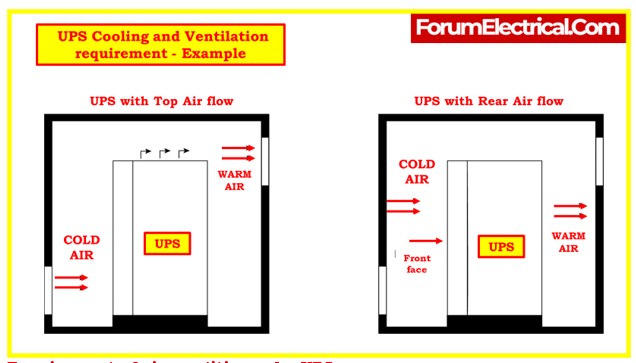
Ventilation and Temperature
- Most UPS units operate optimally at temperatures below 40°C (104°F). Ensure the room has proper ventilation to dissipate heat generated by the UPS.
- Ventilation can be achieved through cross ventilation (using air exchangers and fans) or air conditioning.
- Consider installing a duct to remove heat from the UPS.
- Maintain at least 1000mm of clearance on the top or rear side of the UPS to ensure effective ventilation.
- Keep the area around the bottom front of the equipment clear for airflow since cooling air enters from there.
- While UPS systems can operate in a range of temperatures and humidity, maintaining a temperature of 25-35°C (77-95°F) is ideal for extended equipment life.
- High temperatures can reduce the lifespan of electronic components, so it’s important to control the room temperature effectively.
- Ensure the UPS room is free from excessive dust and contaminants to maintain cooling efficiency.
- Adjust temperature control to prevent condensation on the UPS, especially in high-humidity areas, and consider using dehumidifiers or precision air conditioning if needed.
Requirement of air conditioner for UPS
Selecting the right air conditioner for a UPS room is essential to maintain a suitable temperature and prevent overheating. Here are the factors that need to be considered when choosing an air conditioner for a UPS room:
- Know UPS Heat: Understand how much heat your UPS generates, usually measured in BTUs or Watts.
- Room Size: Consider the room’s size. Bigger rooms with more equipment need more cooling.
- People: Think about the number of people in the room; they also produce heat.
- Other Heat Sources: Identify any other heat sources, like lights or additional electronics.
- Insulation: Room insulation matters. Well-insulated rooms need less cooling, poorly insulated ones need more.
- Climate: Local weather conditions can affect cooling needs.
- Backup: Decide if you need backup cooling in case of a failure.
Cable Sizing & Installation
- Choosing the right cables for UPS installations is critical. Incorrect cable selection can lead to problems like overheating, fire risks, and early failure.
- It’s also important to pick the best installation method and routing.
- Use the same cable size for input and output, ensuring it can handle the thermal current continuously.
- A site survey will determine the cable length needed and how much voltage drop is allowed in the project. It’ll also specify the lug size required.
General guidelines for cable routing & laying
Here are simplified general guidelines for cable routing and laying:
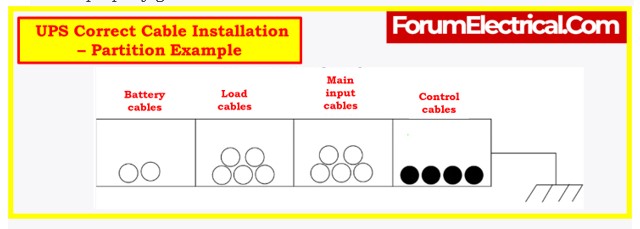
- Group power cables (input, output, battery) together with at least 10 cm clearance between cable groups.
- Separate control cables (e.g., UPS paralleling, communication, EPO) to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI/EMC) issues. Place control cables in a separate cable tray.
- Ensure that all cable trays, including those for power and control cables, are properly grounded.
Cable termination
To connect input, output, and battery cables to the UPS system:
- Terminals are typically located at the bottom, and many UPS units have provisions for bottom cable entry.
- Due to limited space and bending requirements, it’s best to use single-core flexible copper cables.
- If armored aluminum cables are used, elevate the UPS system to ensure the required cable bending radius.
Electrical protection
Using breakers or switch fuse units (SFU) is essential for two reasons:
- Protecting Connected Loads and Isolating Faults: These devices safeguard other connected loads on the same distribution bus and can isolate faults to prevent further damage.
- Protecting Cables: They also protect the cables that connect the power source to the loads.
For proper protection:
- Install breakers or SFUs with semiconductor fuses at the input of the UPS.
- Use devices like MCCBs, MCBs, or fuses in the downstream circuit.
- Implement an isolator at the output of the UPS.
For added reliability, consider:
- Employing split mains with dedicated input breakers for the rectifier and bypass mains. This prevents a single point of failure.
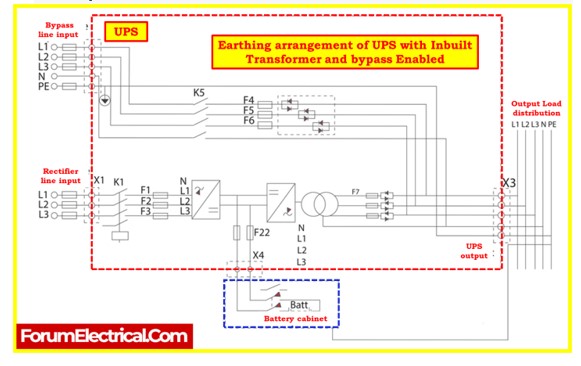
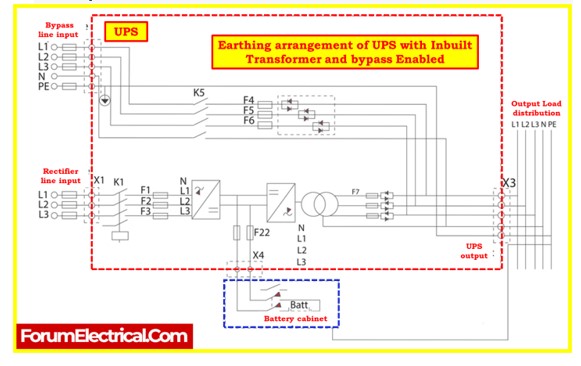
Earthing
- Earthing is critical for UPS systems because it directs fault currents to the earth, activating the protection system.
- When multiple UPS units are used or UPS units are configured in parallel, it’s essential to connect all of them to the same earthing system. This ensures the effective and safe operation of the UPS setup.
What are the safety requirements and rules for UPS?
Requirements for battery installation
When installing batteries in a UPS system, especially SMF VRLA batteries, follow these simple steps to ensure safety:
- Battery Type: Use SMF VRLA batteries designed to recombine hydrogen gas safely.
- Hydrogen Gas: Manage hydrogen gas to prevent escape. Follow safety standards like IEEE-1187.
- Ventilation: Ensure good airflow in the installation area to disperse any gas.
- Prevent Overcharging: Avoid overcharging batteries to reduce the risk of excess gas.
- Safety Vents: Keep safety vents unblocked for safe gas release.
- Monitoring: Regularly check the battery system for issues and follow maintenance schedules.
- Safety Equipment: Have safety gear and equipment on hand in case of emergencies.
What are the room design requirements for UPS?
Battery room consideration
When setting up a battery room, consider the following recommendations:
Safety Measures:
- Use flame retardant doors for added safety.
- Limit electrical installations to lighting, ventilation, and safety equipment.
Safety Equipment:
- Install smoke and hydrogen detectors in the battery room.
- Interlock fan operation with hydrogen detector activation.
- Connect fan operation and hydrogen detection to the Emergency Power Off (EPO) of the UPS system. This ensures that if hydrogen gas accumulates, the UPS can be switched off, and charging can stop.
Room Design:
- Maintain a flat ceiling to prevent pockets of trapped hydrogen gas, reducing the risk of explosive gas accumulation.
- Position light fittings on walls or suspend them at least 50 cm from the ceiling, avoiding placement directly above batteries or charging units.
- Use closed-type light fittings and equipment to prevent gas accumulation
Battery rack consideration
It’s best to install batteries in an open rack rather than a closed cabinet for several reasons:
- Open racks are better than closed cabinets for battery installation.
- Open racks offer easy access for installation, maintenance, and inspections.
- They simplify connection checks and torque verification.
- Battery terminals are readily accessible for readings and visual checks.
- Replacing faulty battery blocks is straightforward in open racks.
- Open racks minimize heat-related problems from nearby equipment, restricted airflow, and charging heat.
- Open racks enhance personnel safety compared to closed cabinets.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation in a battery room is crucial for safety:
- Inadequate ventilation can lead to hydrogen gas buildup, which poses a fire risk.
- Ventilation requirements for VRLA batteries are defined in EN 50272-2.
- The goal of ventilation is to keep hydrogen concentration below 4%vol Hydrogen Lower Explosion Limit (LEL). This ensures safety by preventing explosive conditions in battery locations or enclosures.
Battery protection
Battery protection and cable
To protect batteries and their associated cables, follow these guidelines:
- Install battery protection devices close to the battery, ideally in the battery rack or in a nearby enclosure.
- If multiple battery banks are used, it’s recommended to have a common isolator with a fuse or an MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) and an individual battery isolator for each battery string. This setup enhances safety and control.
Connection of the Load
When connecting the load to a UPS system, ensure the following:
- Connect load cables based on the maximum allowable load, staying within the UPS system’s rated capacity.
- Confirm that the load’s power factor (cos phi) is within specified limits.
- For three-phase UPS systems, consider that the load might be single-phase, meaning it’s connected between a phase and neutral.
- If connecting non-linear loads to a three-phase UPS system, check that the neutral current doesn’t exceed the rated ampacity of the conductor.
- Recommended: Connect the output neutral to earth for added safety and stability.
- In some cases, consider using a bypass transformer with galvanic isolation.
- This allows you to connect the output neutral to earth.
- The decision to use such a transformer should align with local legal provisions.
- Always follow local regulations and guidelines for electrical installations.
External Protection
- Limit the maximum fuse nominal current at the load output to ensure selectivity with internal fuses.
- Refer to the “Technical data” for conditions related to the rectifier incoming feeder fuse (mains).
- When using circuit breakers between the busbar and the consumer: Choose a circuit breaker with a rated current not exceeding 15% of the nominal current.