Introduction
Electric motors are essential components in many industrial, commercial, and household applications.
These motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is then used to power machinery, appliances, and equipment in various industries.
Given their importance, guaranteeing their dependability and endurance is essential to avoiding operating downtime, costly maintenance, and potential safety risks.
Protecting electric motors against failure requires careful selection, installation, maintenance, & the use of protective measures.
This comprehensive method addresses a variety of elements that can contribute to motor failure, such as electrical problems, mechanical wear and tear, climatic conditions, and operating stress.
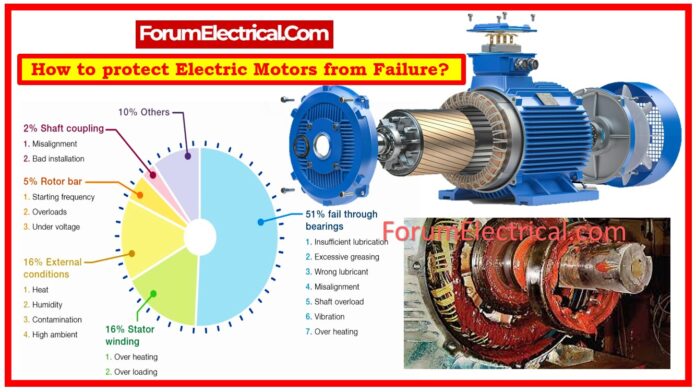
Causes of Motor Failure
To successfully protect electric motors, you must first understand the most common reasons of motor failure. These causes are broadly classified as
- Electrical failures,
- Mechanical failures,
- Thermal overloads,
- Environmental variables, and
- Operational stress.
If not maintained effectively, any of these elements might lead to motor dysfunction or damage.
Electrical Failures
- Phase Imbalances: Phase Imbalances arises when the voltage (or) current in a three-phase electrical source is not equal, resulting in unequal torque and possible overheating.
- Overvoltage & Undervoltage: Excess voltage might lead to insulation breakdown & overheating, whereas insufficient voltage can result in low torque and excessive current consumption.
- Insulation Breakdowns: The breakdown of the motor’s insulation system may lead to short circuits, grounding failures, and, eventually, motor failure.
Mechanical Failures
- Bearing Failure: Bearings are essential for smooth spinning. Lubrication difficulties, contamination, (or) misalignment can all result in premature bearing wear or failure.
- Misalignment: Improper alignment of the motor and driven equipment can result in excessive vibration & stress on the motor shaft & bearings.
- Imbalances: Imbalances in the motor shaft can cause inconsistent rotation, increased vibration, &possibly damage to motor components.
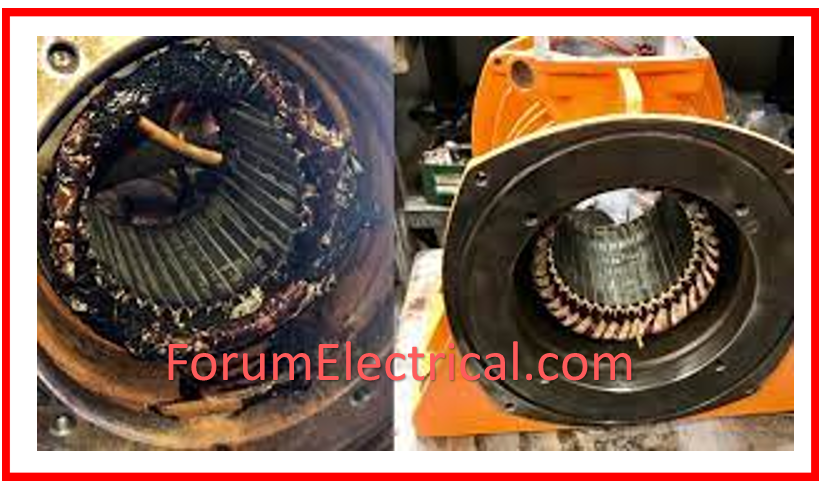

Thermal Overloads
- Overloading: Operating the motor above its rated capacity produces excessive heat, resulting in insulation breakdown & component degradation.
- Poor Ventilation: If the airflow is restricted or insufficient, the motor will overheat.
- High Ambient Temperatures: High ambient temperatures can worsen thermal stress and shorten motor life.
- Environmental Factors
- Moisture: Water and extreme humidity can lead to rust, corrosion, & electrical short circuits.
- Dust and Contaminants: Dust & contaminants can obstruct cooling channels, interfere with moving parts, and cause insulation damage.
- Corrosive Chemicals: Chemicals can deteriorate motor materials, resulting in structural and electrical integrity failure.
- Excessive Temperatures: Both high & low temperatures can have an impact on motor performance or durability, with extreme cold leading to brittleness and excessive heat leading to thermal stress.
Operational Stress
- Frequent Starting & Stopping: Frequent starting & stopping of the motor can produce heat cycling, resulting in component fatigue and wear.
- Incorrect Duty Cycles: Operating the motor outside of its specified duty cycle can result in overheating and excessive wear.
- Mechanical Shocks: A sudden collision or jolt may result in physical damage to the motor’s internal & external components.
Proper Installation & Routine Maintenance for Electric Motors
The proper mounting of electric motors is essential to avoiding numerous problems that might lead to motor failure.
To prevent excessive stress on shafts & bearings, ensure that the motor is precisely aligned with the driving equipment.
Furthermore, employing proper foundations and solid mounting reduces vibrations that can otherwise cause mechanical wear & damage.
Adhering to the manufacturer’s wiring, grounding, & insulation specifications is also important to preventing electrical failures and ensuring the motor functions safely.
Routine maintenance and inspections are essential for spotting possible issues before they become significant failures.
Essential maintenance procedures include
- Keeping bearings properly lubricated to decrease friction & wear, that improves the motor’s life.
- It is also essential to keep the motor & its surroundings clean to avoid dust & debris from impairing performance.
- Periodic checks should be performed to look for indications of wear, overheating, & electrical problems, allowing for prompt interventions and repairs.
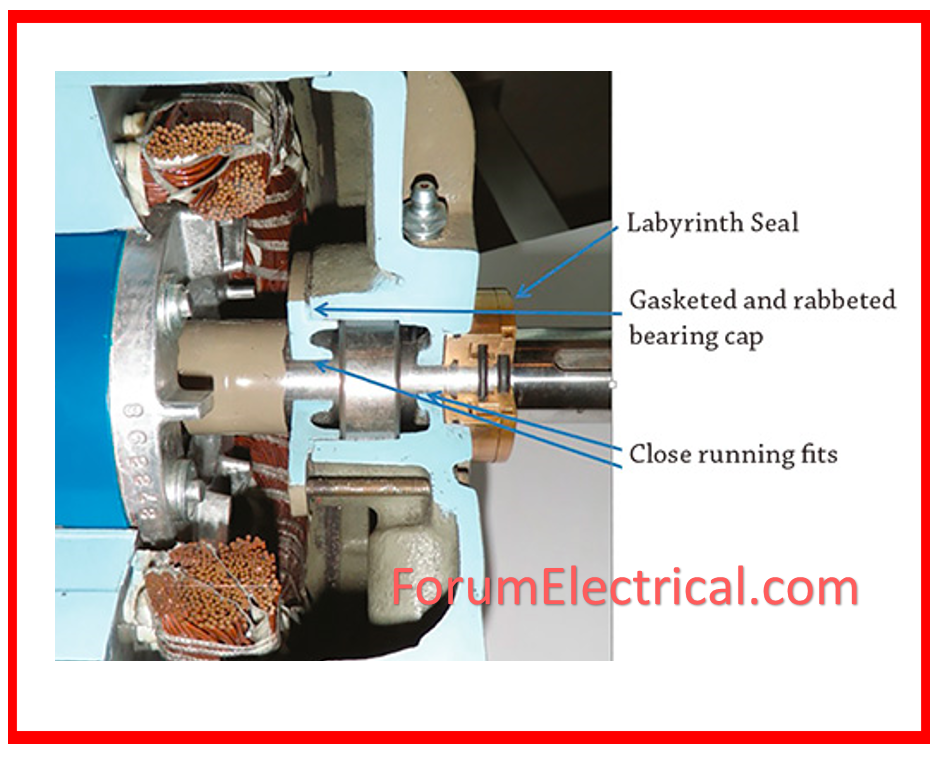
Alignment: Ensures exact alignment with driven equipment, reducing stress on shafts and bearings.
Foundation & Mounting: Utilize proper foundations and safe mounting to reduce vibrations.
Electrical Connections: To avoid electrical failures, follow the manufacturer’s wiring, grounding, & insulation requirements.
Lubrication: Ensures that bearings are properly lubricated to decrease friction and wear.
Cleaning: Maintains the motor & surrounding area clean to avoid dust and dirt from impairing performance.
Inspections: Performs periodic inspections to look for symptoms of wear, overheating, & electrical problems.
Installing Protective Devices for the Electric Motors
Various protection devices are required to protect electric motors from any possible harm, assuring their longevity and consistent operation. These devices prevent electrical, thermal, & mechanical failures by reacting automatically to abnormal conditions.
- Thermal Overload Relays: These components protect against excessive current by terminating the circuit when overload conditions are identified, thus preventing overheating & possible motor damage.
- Time Overcurrent Relays: A Time Overcurrent Relay (TOC Relay) protects when current surpasses a preset value for a specified time. It prevents short circuits and overloads from damaging electrical circuits. To accommodate surges, the relay checks circuit current and begins a time-delayed response if it exceeds a threshold. To protect equipment and maintain safety, the relay will trip & isolate the problematic part if the excessive current persists.
- LodtrakIV Relay: Advanced monitoring & protection features distinguish the LodtrakIV digital relay. Overcurrent protection, load profiling, fault recording, & smart grid communication interfaces are included. This relay optimizes electrical network performance and reliability with precise readings and diagnostics. Its digital nature makes it vital in modern power systems for quick configuration, real-time data analysis, & remote control.
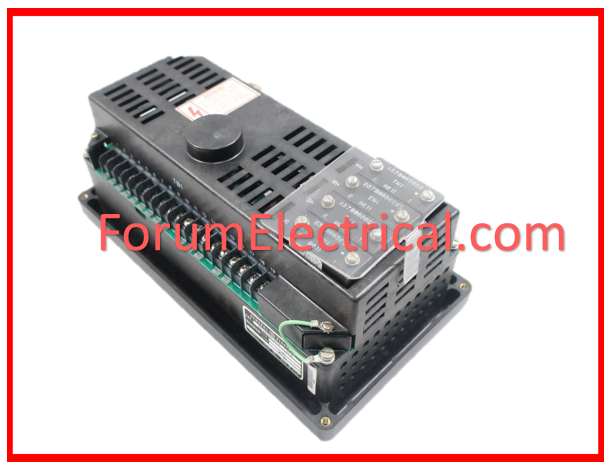

- Digital Relay: A Digital Relay protects and controls electrical connections using digital technology. Digital relays are more accurate, reliable, and flexible than electromechanical ones. They execute complicated algorithms to detect defects, offer thorough diagnostics, and interface with power system units. Digital relays can be programmed to alter protective settings and integrate with automated systems, improving power distribution network efficiency and safety.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Circuit breakers and fuses provide fundamental protection from short circuit & over-current, which can lead to motor failure (or) fire dangers.
- Thermal Protectors: Thermal protectors avoid overheating by turning off electricity when temperatures rise above safe limits. This helps to prevent excessive heat from damaging the motor windings & other components.
- Surge Protectors: Surge protectors protect against voltage spikes, which can damage motor windings & insulation. By absorbing and channeling excess voltage, they shield the motor from electrical surges resulting from lightning, power outages, (or) other transient occurrences.
Conclusion
Understanding typical motor failure causes and executing a comprehensive protection method will improve electric motor dependability and longevity.
Prevention of motor failures and uninterrupted functioning of important systems and machinery requires proper selection, installation, maintenance, and protective devices.