Electric distribution networks provide quality and reliable electricity to users. Due to increasing distribution service quality standards and electrical network technology, efficient maintenance procedures are essential to meeting both criteria.
Thus, effective program development has many possibilities and criteria, making decision-making difficult.
This post discusses electrical distribution system maintenance planning using economic and reliability factors. In particular, an integrated framework based on predictive, preventive, and corrective maintenance summarizes the work.
Developing Maintenance Schedules
The essential condition for safety during maintenance is de-energizing the electrical system.
It is advisable to anticipate and arrange for maintenance in advance and to shut down the entire facility during a holiday season or another time where the operational disturbance can be reduced, if feasible, because de-energizing by its very existence interferes with continuous facility operations.
Preparation planning & budgeting are important for anticipating the need for maintenance shutdowns because they are expensive and need careful preparation.
Routine Maintenance
Electrical systems require routine maintenance in order to ensure that they are in continuing accordance with the regulations. This maintenance will prevent failures in both the system and the equipment, as well as ensuring the highest possible levels of both safety & efficiency in the use of the facilities.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
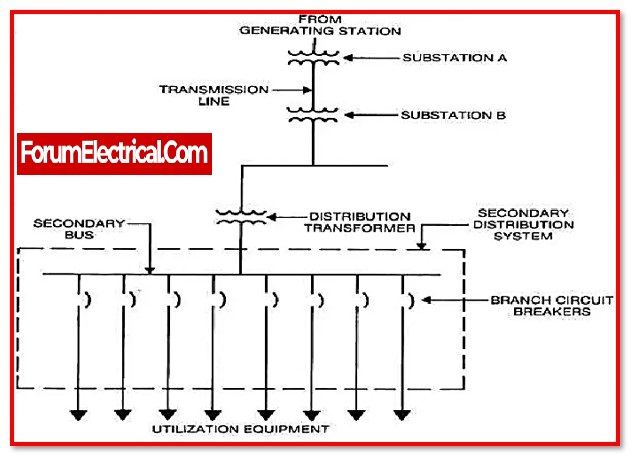
When it pertains to routine maintenance, the distribution system is separated into two main parts:
(a) Distribution networks, and
(b) Switchgear and switchyard equipment.
The recommended electrical maintenance for each of the above components is discussed below:
a). Distribution Networks
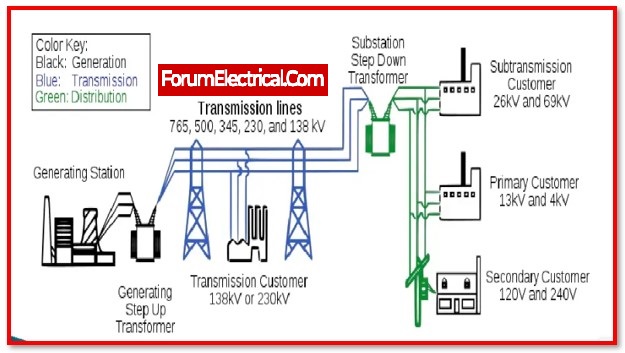
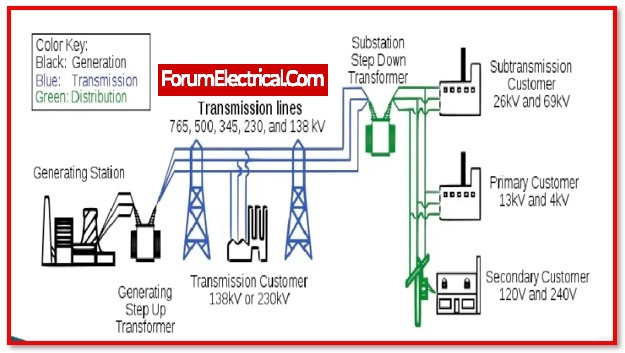
Distribution systems are essential section of electrical grids, and electrical corporations of about 40% of their capital investments to them, with the remaining allocation going to generation & transmission (40% generation and 20% transmission).
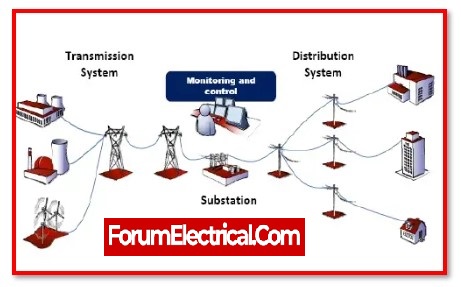
For an electrical utility, the distribution system is essential for two reasons:
1. Because of its proximity to the customers, any distribution problems directly impact the customer. For example, breaks in service to consumers may result from faults in the transmission and generation sections.
2. Its high-priced investment costs
Distribution networks connect power supply providers and LT and medium-voltage users. Consumers receive uninterrupted power from a functioning distribution network.
Long, complicated distribution network systems that haven’t been maintained in years cause low voltage at consumers’ properties and frequent power outages. Distribution networks need frequent maintenance monitoring.
Electrical maintenance in this area saves lives and helps the supply provider to be better. Distribution network electrical maintenance includes the following:
- Calculate the load for each phase on a regular basis, and maintain load balance throughout the three phases by moving the load from the phase that is strongly loaded to the phase that is lightly loaded.
- Examine the voltage regulation at the customer location. The appropriate preparations should be taken to reduce drop-in-voltage by installing additional distribution transformers if voltage dip exceeds the permitted value.
- Whenever practicable, install 11KV/440V transformers positioned on HT (11 KV) line supports to provide LT-less service to a limited number of consumers.
- Whenever possible, replace the traditional overhead, weatherproof house or commercial (enterprise) service connection wires with underground cables with conductors made of the same material as LT distribution line conductors.
- Verify the vertical alignment of all supporting structures for lines.
- Verify the integrity of the stay insulators and the tightness of the stay wires. Replace line insulators with cracks or breaks.
- Keep line conductors & other live parts away from the ground, structures, and buildings. Clean bird nests, darts, and poisons off of cross arms and insulators. Clean creepers growing along stays & supports. Check earth resistance.
- Examine the conductors, C.I. blocks, earth wires, clamps, bolts, nuts, supports, cross arms, etc. for mechanical strength.
- Use anticorrosive paint on all metallic parts.
- Verify the AB switches’ alignment and stability.
- Verify that the lighting arresters and horn gaps are operating properly.
- Verify the dielectric strength (BDV) of the oil in the distribution transformers.
- Inspect the HT & LT fuse carriers and replace them if necessary.
b). Switchgear and Switchyard Equipment
- Maintain line conductors & other live parts free of the ground, structures, and buildings.
- Clear the switchyard floor of all debris, including grass, dirt, and oil.
- The preventive maintenance procedures advised for electrical line conductors apply to bus bars if they are constructed of flexible conductors.
- The preventative maintenance procedures recommended for suspension/strain insulators and switchyard hard goods are likewise relevant to those for distribution line insulators and hard goods.