1). What is the term under-voltage protection?
It protects the breaker from being accidentally closed, or the generator from coming on load during the parallel operation. It also protects against voltage loss when machinery is connected to switchboard.
2). What makes steering gear overload safety unique?
Short circuit protection and, when applicable, single-phase protection are installed. Furthermore, instead of overcurrent protection, an Overload alarm is installed, which is programmed to activate at no less than twice the typical running current.
3). What is the criterion for alternator paralleling?
The following requirements must be accomplished in order for alternators to be properly synchronised.
The incoming machine’s terminal voltage must be about equivalent to the bus-bar voltage.
The incoming machine frequency must be the same as the frequency of the bus-bar.
An additional criterion for 3-phase alternators is that the incoming machine voltages – phase sequence match that of the bus-bars.
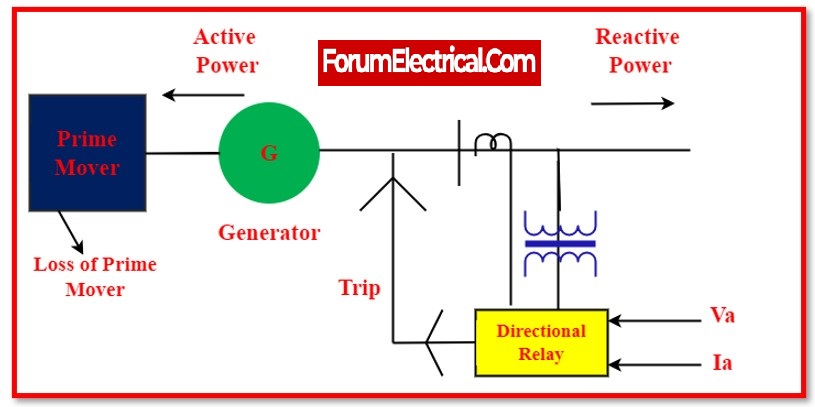
4). When does the power flow reverse?
Created from the Free App Electrical Diagram
A generator is supplying a system through switchgear, and numerous generators are linked in parallel with one generator. When the system is operational, current flows from generators to switchgear.
If one generator fails & its terminal voltage falls under the system voltage, the generator will behave similarly to a motor, & current will flow from switchgear to generator. This is known as reverse power. In the case of a full mechanical failure of generator, effects might range from minor to severe.
5). How is protection from reverse power provided?
Anti-motoring employs reverse power protection. The purpose of this function is to protect the prime mover, not the generator. It has the ability to cut off the prime mover and shut off the fuel supply.
6). What does “preferential trip” mean? Why is it obtainable?
In the event of a partial failure (or) overload of the main supply, a preferred trip is a type of electrical system aboard a ship that is intended to separate the non-essential circuit, or non-essential load, from the main bus bar. As a safety measure, it trips the non-essential loads (like the galley and air conditioning) while allowing the necessary loads to operate (like the steering gear).
7). What is the function of the earth fault indicator that is displayed on the switch board?
It finds faults in the phase to earth connection on a circuit and provides an indication of such faults.
8). Why is reverse power employed in alternators instead of reverse current?
Although reverse current is exceedingly difficult to detect in an alternating current (AC) system, reverse power may be recognised and protected by a reverse power relay.
9). What does the term “excitation” in an alternator mean?
An electric generator (or) electric motor is made out of a rotor that spins in a magnetic field. Permanent magnets or field coils can generate the magnetic field. In cases of a machine with field coils, a current has to flow through the coils to produce the field; otherwise, no power is delivered to or from the rotor. Excitation is the technique of creating a magnetic field using an electric current.
10). What does residual magnetism mean?
Residual magnetism is a characteristic in which some excitation persists in the conductor after the magnets are removed.
11). How does the speed of a three-phase induction motor change?
The frequency of voltage being supplied determines the speed of a standard three-phase induction motor. Changing such motor speed necessitates the construction of a three-phase power frequency converter. This can be accomplished by employing power MOSFETs (or) IGBTs that are capable of high voltages with fast switching speeds.
12). What is the function of a self-monitoring alarm circuit?
It checks the alarm circuit’s health on itself. That is, it determines if the power supply to alarm circuit is in good working order and whether all of the relays and contacts are operational.
13). How does emergency generator start automatically?
It is actuated by an undervoltage relay. When there is a power outage, the undervoltage relay detects the loss of voltage and activates the emergency generator. Similarly, when electricity is restored, the relay shuts down the emergency generator.
14). What is the function of a shaft generator?
The primary engine is powered by a shaft generator. It consists of a frequency converter (thyristor operated) that transforms the variable engine speed into a near constant speed and generates electrical power. It can only be used at full speed at sea (not at manoeuvring speed).
15). What excitation methods are utilised in an alternator?
- Rotary: This method employs rotating diode rectifiers, a primary exciter, and a main exciter.
- Static :Brushes and slide rings provide static excitation.
16). What are the main electrical power sources within the ship?
Batteries and generators are the main sources of electrical power within the ship. Batteries stores electrical energy for the immediate use, whereas generators generate power when batteries are depleted.
17). What is the function of a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) in a maritime electrical system, and where should be installed?
A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is used to prevent against electrical shocks by immediately shutting power when it identifies a ground fault (current leakage). It should be fitted in locations where there is a risk of water exposure, such as galley & bathroom outlets.
18). Explain why correct cable size and voltage drop concerns are important in maritime electrical systems.
The proper size of cables assures that electrical circuits are capable of carrying the appropriate current without experiencing excessive voltage drop. Voltage drop may affect device performance and cause wire to overheat.
19). How do you calculate a maritime circuit breaker’s capacity (ampacity) for a certain application?
The maximum current that a circuit breaker may safely sustain determines its ampacity. It is determined by the wire size, insulation type, & component temperature rating. NEC (National Electrical Code) guidelines are often used.
20). What is the function of a ship’s emergency power system (EPS), and how is it usually configured?
An EPS delivers backup power in condition that the primary power system fails. It is equipped with separate generators, distribution panels, & key loads to make certain that important systems like as navigation and safety continue to function.
21). What are the primary distinctions between land-based and marine-based electrical systems?
To prevent galvanic corrosion, marine electrical systems require consideration for the corrosive effects of seawater, vibration, and the necessity for isolation. Because of the potentially dangerous surroundings, they also demand additional safety procedures.
22). Discuss the significance of harmonic distortion analysis in the maritime electrical systems and how to reduce it.
Harmonic distortion analysis is essential for protecting sensitive equipment. Among the techniques for mitigation include the use of
- Harmonic filters,
- Proper grounding, and
- Use of equipment constructed
to manage harmonic loads.
23). What are the basic components of the marine electrical system?
- Generators,
- Batteries,
- Switchboards, and
- Wiring
are the essential components of a maritime electrical system.
Generators generate power, batteries store it, switchboards transmit it to various areas of the vessel, and cabling connects each of the components.
24). What are the most frequently occurring problems with marine electrical systems, and how do diagnose them?
- Corrosion,
- Vibration, and
- Moisture
are some of the most typical problems that occur with maritime electrical systems.
- Corrosion may harm electrical connections & wiring,
- Vibration and moisture might cause wires to break.
A range of instruments and procedures, including as voltage testers, continuity testers, & circuit diagrams, can be used to diagnose marine electrical problems.
25). Why does galvanic corrosion occur in maritime electrical systems, and how can it be avoided?
When different metals get into electrical contact with one another in a salt-water atmosphere, galvanic corrosion can occur which damages the metal. Use
- Sacrificial anodes,
- Separate dissimilar metals, &
- Installing corrosion-resistant parts
in requirements to prevent it.