What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is a device that switches off the inappropriate or fault current. It is a mechanical switch that also interrupts the transfer of the high fault (magnitude) current. The circuit breaker is primarily intended to close or open an electrical circuit, thereby protecting the electrical system from the damage.
- What is a Circuit Breaker?
- What needs to be accomplished by the Circuit Breaker (CB)?
- Circuit Breaker Types
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker Overload (RCBO)
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
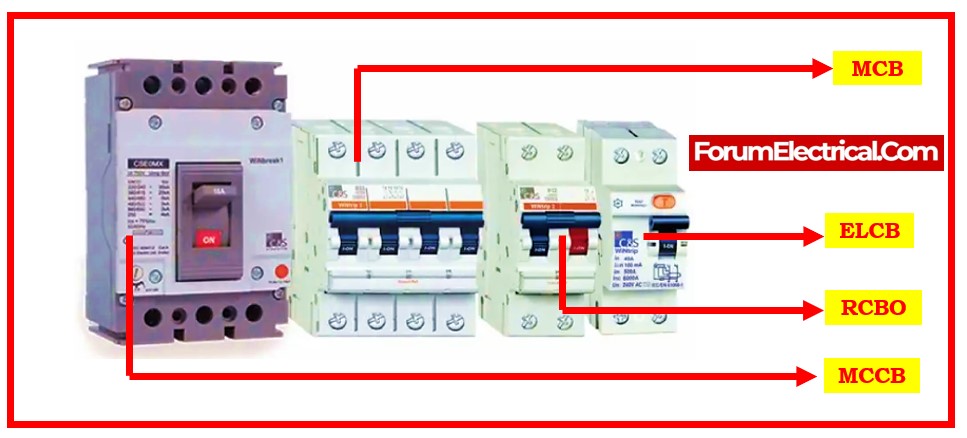
- Difference between MCB, MCCB, RCCB & ELCB
- MCB Vs MCCB Vs RCCB Vs ELCB
What needs to be accomplished by the Circuit Breaker (CB)?
A circuit breaker’s primary objective is to open the circuit in safe way.
- It is capable of sustaining short-term fault current resistance.
- Ideally, the circuit should be safely opened.
- After breaking, its terminals need to be able to bear the voltage.
- It should stop the arc from striking again.
- The circuit breaker temporarily resists the fault current while allowing other circuit breakers to correct the fault.
- The CB is made to withstand a certain range of the fault current without harming its terminals.
Circuit Breaker Types
Circuit breakers are primarily categorized according to their application and voltage.
1). Low Voltage Circuit Breaker
2). Medium Voltage Circuit Breaker and
3). High Voltage Circuit Breaker
In this post, discuss in detail about various types of low voltage circuit breaker as follows:
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker Overload (RCBO)
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
An electromagnetic device that is completely encased in a moulded insulating (insulation) material is a miniature circuit breaker, or MCB.
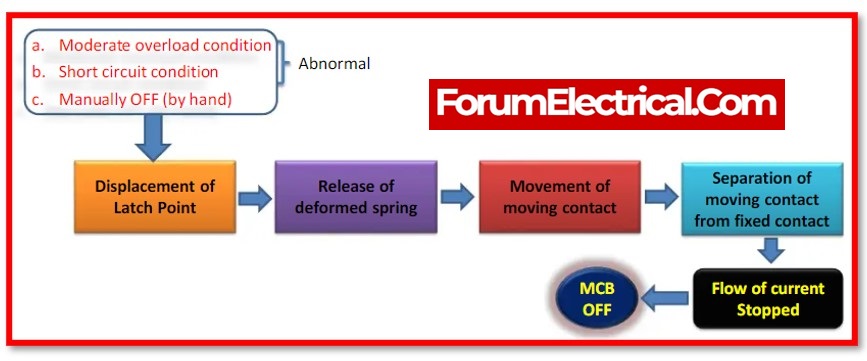
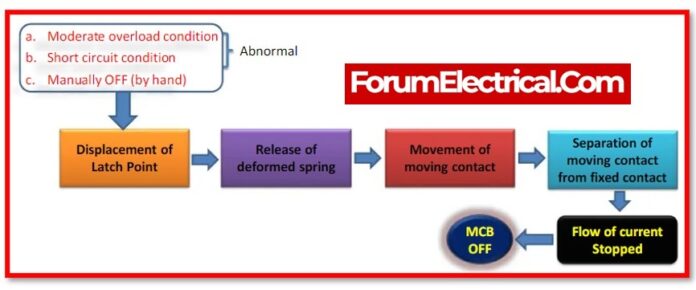
An MCB’s primary function is to automatically switch the circuit, or open the one that is linked to it, when the current flowing through it exceeds the limit for which it is set, It is able to manually turned ON & OFF, just like a standard switch, if necessary.
MCBs are time-delay tripping devices, and the amount of overcurrent that occurs determines how long they stay operational. This indicates that they are activated whenever overloads persist long enough to endanger the circuit they are intended to protect.
MCB Symbol
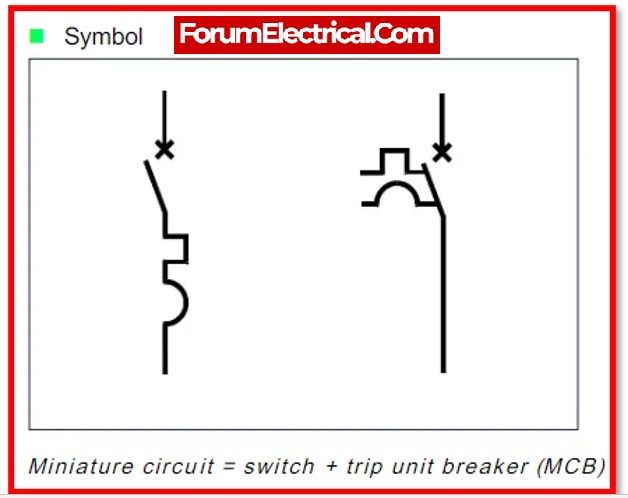
As a result, transient loads like switch surges & motor starting currents are neglected by MCBs. These are often made to function in short circuit faults at less than 2.5 ms and in overload faults at 2 seconds to 2 minutes (depending on the degree of current).
In the majority of circuits, MCB’s are generally employed as a fuse switch replacement. Currently, a wide range of MCB’s with breaking capacities ranging from 10 ka to 16 KA are used in all types of home, commercial, & industrial applications as a dependable form of protection.
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
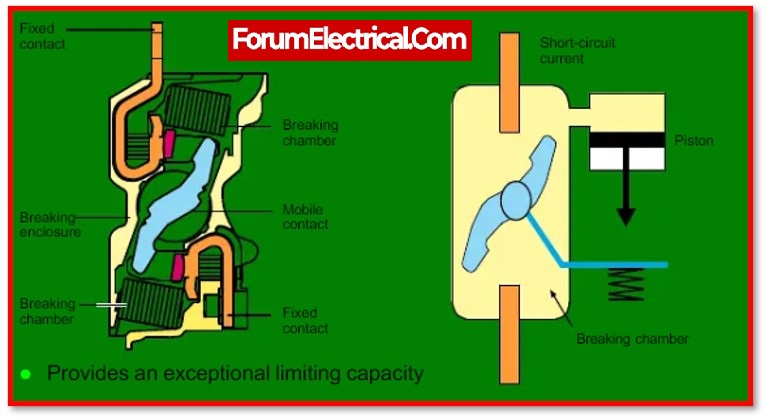
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker, also known as MCCB, is a type of circuit breaker that is enclosed in a moulding or enclosure made of a moulded material. It is often utilized for fault levels up to 150 KA and current ratings up to 1600 A. Due to the speedy operation of its electronic type release, microprocessor based MCCB’s have become extremely common. They provide protection against overload and short circuits using bimetal and solenoids.
Air is used as the dielectric medium by MCCB, to interrupt a circuit. Air is utilized for protection in the low voltage circuits because it has a lower dielectric strength than other mediums.
MCCB, often known as circuit breakers, are automatic electrical devices.
Since it functions like a small circuit breaker, it is a better version of the MCB. However, it has other capabilities that make it a better circuit breaker, like remote closing and configurable trip settings, which allow to change the current settings & time settings according to requirements.
Motor Protection Circuit Breaker (MPCB)
Specifically for motor protections, MPCB are used. MPCB is utilized primarily for motor applications since it provides protection against overload, short circuit, and single phasing as a stand-alone device.
MPCB are a particular type of electrical protection device designed specifically for electric motors.It is essential to efficiently protect electric motors with MPCB since they are used to operate mechanical devices of various types and have a wide range of applications.
It can provide motors an uninterrupted electrical supply due to several of its features, including:
- Protection against electrical failures such line-to-ground, line-to-line, and short-circuit faults. Any electrical problem that is less severe than its breaking capability can be stopped by the MPCB.
- When a motor consumes more electric current than its nameplate value for a prolonged length of time, motor overload protection is triggered. MPCB typically have overload protection that is programmable.
- Protection from phase imbalances & phase loss. A three-phase motor can be severely damaged in any condition, so the MPCB will get disconnect the motor as soon as the malfunction is identified.
- To provide the motor time to cool down after an overload, thermal delay prevents the motor from being switched back on immediately. If a motor has overheated, restarting it could result in irreparable damage.
- MPCBs typically have buttons (or) dials for the purpose of switching the motor circuit.
- The majority of motor protection circuit breakers include an LED display that glows whenever the MPCB trips. For adjacent professionals, this serves as a visible indication that a malfunction has occurred and that the electric motor should not be reconnected until the problem is fixed.
- Automatic Reconnection: In the condition of an overload, some MPCB types allow the input of a cooling off period, after which the motor restarts automatically.
- The MPCB serves as an essential part since electric motors are expensive parts of machinery. It can be essential to perform costly maintenance or possibly replace the equipment entirely if a motor is not properly protected. An electric motor will last much longer if it is properly protected with an MPCB.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)
Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) provide protection from earth leakage. Depending on the level of current sensitivity needed for the application, it is utilized in houses, offices, and companies. It detects current leakage and trips when it occurs, protecting the circuit and people from shock and the negative effects of the current leakage.
Kirchhoff’s law, which states that the current flowing into a circuit must be equal to the current flowing out of it, is the fundamental principle upon which RCCB is based. The RCCB analyzes the variations in current that are present between the live wires and the neutral wires.
The current coming into the circuit from live wire should ideally be the same as the current flowing through the neutral wire. When a fault occurs, the current from the neutral wire is lowered, and the difference between the two is known as residual current. The RCCB is activated to trip the circuit when a residual current is detected.
- Protects against earth faults as well as leakage currents.
- The circuit will be immediately disconnected if the rated sensitivity is exceeded.
- Provides the possibility of the dual termination for cable & busbar connections.
- It provides voltage fluctuation protection by including a filtering component that protects against the transient voltage levels.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker Overload (RCBO)
Residual Current Circuit Breaker Overload (RCBO)devices are intended to maintain electrical circuits safe by initiating disconnection if a problem is detected. They are typically utilized for combination overload protection & short-circuiting against the earth leakage currents.
The RCBO protects against the 2 types of electrical faults.
- The first fault is residual current, sometimes known as earth leakage. This occurs when there is an unintentional break in the circuit, which can occur as a result of wiring faults or DIY incidents (for example, cutting through a cable with an electric hedge cutter). If the electricity supply is not interrupted, the subject will receive a potentially lethal electric shock.
- Overcurrent is another type of electrical fault that may appear as an overload or a short circuit. In the initial stage, the circuit will be overloaded with the too many electrical components, resulting in power transmission that exceeds the capacity of the cable. Short-circuiting can also occur as a result of the insufficient circuit resistance & high-level amperage multiplication. This carries a higher level of risk than overloading.
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
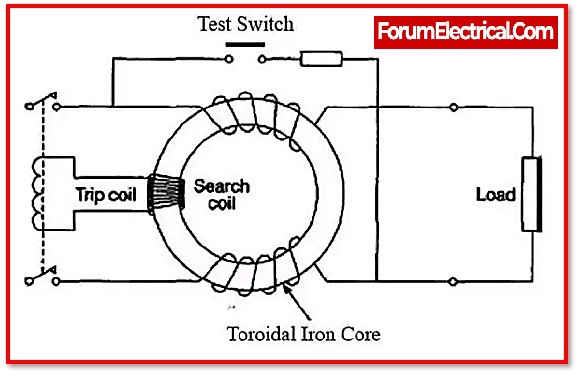
Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCB), are circuit breakers supposed to protect devices against leakage current. When it detects a leakage current, it breaks the circuit and breaks down the power supply to the load. Earth leakage can result in lethal electrical shocks.
ELCBs are primarily used to protect against electrical shock. They don’t provide protection against short circuits or overloads. Because of this, they have to be utilized in combination with an MCB.
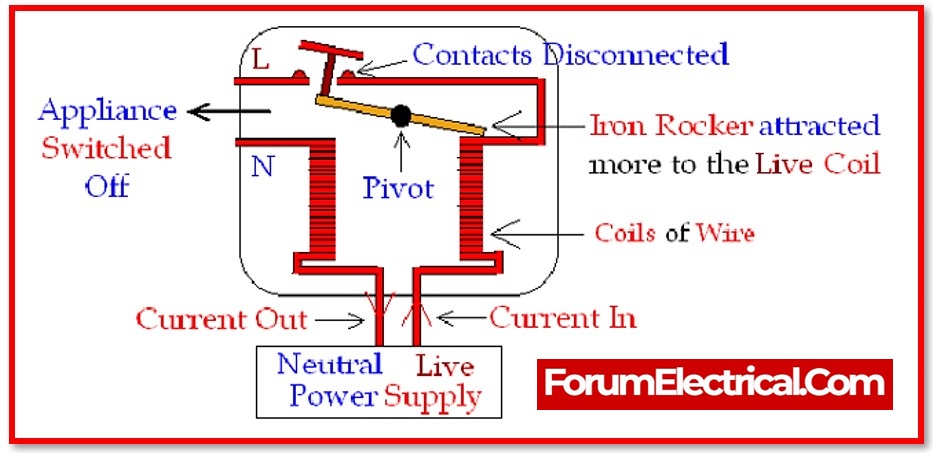
The primary function of an ELCB is to avoid electrical shock. It maintains record of the leakage current that circulates out of the circuit along any unexpected direction. It is not capable of protecting against overloading (or) short circuit current.
Under normal conditions, current flows from the source into the load across the live wire and out across the neutral wire. However, the magnitude of both currents is the same. The difference between the live and neutral wires occurs if current leaks through any not desired path. Using a current transformer, the ELCB can detect the imbalance and break the contacts with an electromagnetic relay.
Difference between MCB, MCCB, RCCB & ELCB
MCB Vs MCCB Vs RCCB Vs ELCB
| MCB | MCCB | RCCB | ELCB |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCB represents Miniature Circuit Breaker. | MCCB represents Moulded Case Circuit Breaker. | RCCB represents Residual Current Circuit Breaker. | ELCB represents Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker. |
| According to their power capacities, MCBs are mostly employed in residences where small breaking capacities are needed. | MCCB is primarily utilized for industrial applications that require both low & high breaking capacities. | It provides 100% leakage current detection and can detect both AC and DC leakage current. | Based on the earth leakage current, the ELCB operates. If the voltage measured by these devices on the ground conductor was not zero, a current leak to earth was occurred. |
| Since they primarily correspond to low circuits, its trip characteristics are typically not customizable. | Its trip current can be fixed or modified for an overload or magnetic setting. | RCCB can trip when the both currents (phase & neutral) are different & can endure both currents being the same because it has no connection to the ground wire. | Since it is able to identify current flowing back through the primary earth wire, it is not preferred. |