In electrical terms, what does MOCP Mean?
MOCP – Maximum Over-Current Protection
MOCP is the highest (maximum) current rating that an electrical device’s over-current protection devices (such fuses or circuit breakers) are permitted to handle (e.g., a motor or air conditioner).
The maximum allowed rating (or) size of the circuit breaker is known as MOCP, and it determines how effectively the circuit or equipment will be disconnected in the case of any consequential fault condition.
If the protective devices are enormous, they could not be able to function in a fault state, which might lead to overheating that could damage the wire or other equipment.
Hence it follows that protective equipment must be the right size.
The MOCP value helps to determine the largest possible over-current protection device, such as a fuse or circuit breaker, and its maximum capacity.
When there is a possibility of a fault occurring, MOCP may be employed to safeguard the wire and equipment.
How to calculate MOCP?
The MOCP is the measured value (calculated value) that is used to determine the maximum (highest value) size of the over-current protection devices, such as
- Circuit breaker or
- Fuse,
that are used to protect the wire and equipment in the circumstance of fault conditions. These devices include circuit breakers & fuses.
The minimum current amps must be greater than the value of the circuit breaker (or) fuse in order for them to be acceptable (MCA).
As a result of this, the value of MOCP is also always higher than the value of MCA.
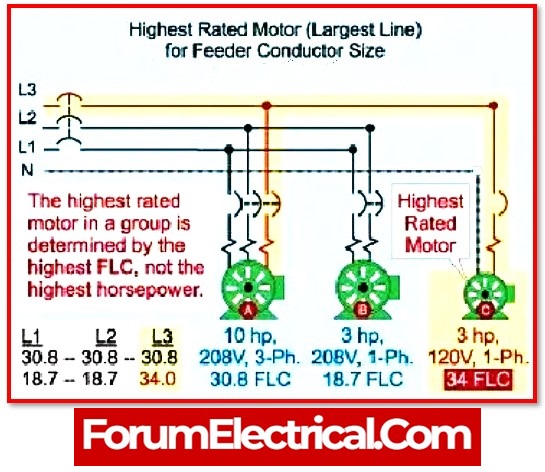
MCA and MOCP are crucial numbers that govern the minimum wire (or) conductor size and the maximum fuse (or) circuit breaker size that are permitted in order to lessen the possibility of over-current and, as a result, the possibility of a fire.
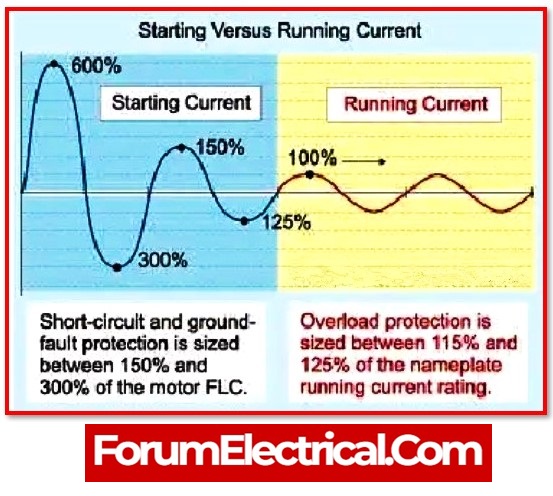
When all additional loads of 1 A or more that are capable of being in operation (function) at the same time are factored in, the value of MOCP is calculated to be 2.55 times the FLA of the biggest(heavy) motor.
MOCP = (2.25 x FLA of the Largest Motor) + (Other Motor Loads) + (Other resistive electrical load Ex: Heater Load)
Steps to compute (calculate) MOCP
1) Determine the FLA of the motor (or) compressor. The FLA is the full load Current when the motor or compressor is operating at its rated voltage and load.
2) Locate the load from the heater; this is a resistive electrical load.
3) After calculating the value of MOCP, choose the value of MOCP depending on the three requirements that are mentioned further below:
a) If MOCP is not a multiple of 5, the value of MOCP is rounded down to the closest standard fuse or circuit breaker size. This occurs when the estimated value of MOCP is not an even multiple of 5.
b). If MOCP is Lower Than MCA (MOCP < MCA) – If the value of MOCP is estimated to be less than the value of MCA, then the value of MOCP is assumed to be equal to the value of MCA, and it is rounded up to the closest standard fuse (or) circuit breaker size, which is normally a multiple of 5. Because of this, the value of MOCP does not fall below the value of MCA.
MCA
MCA – Minimum Current Ampacity (or) Minimum Circuit Ampacity
The minimum current ratings for a supply wire (or) conductor in an electrical circuit are referred to as the minimum current ratings (MCA).
To further explain, the minimum current ratings (low current ratings) that the wires (or) conductors should be able to safely carry under typical working circumstances are referred to as the MCA.
The minimum current ampacity is the amount of current that the conductor should be capable of carrying; hence, it refers to the conductor’s or wire’s ability to carry current.
The value of the MCA supports in determining the minimum wire size required to guarantee that the wire will not overheat under typical circumstances of operation.
The value of MCA is determined by multiplying the motor’s FLA by 1.25 and then adding all of the additional resistive loads, such as the heater load.
MCA = 1.25 x (Motor FLA + Heater Current)
FLA
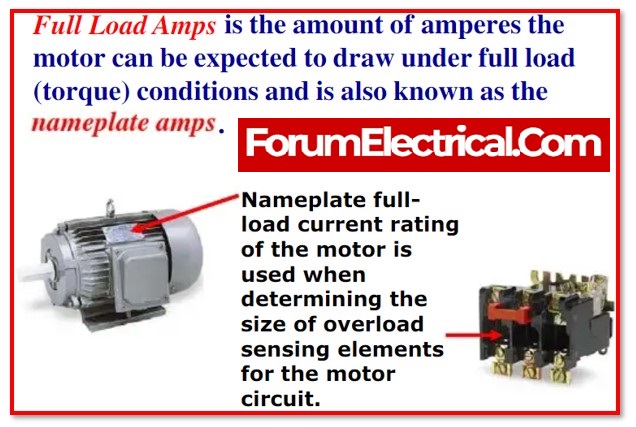
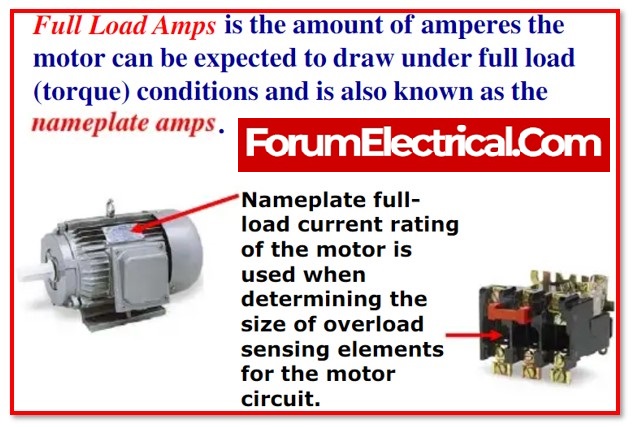
FLA – Full Load Ampere
The amount of continuous current that a machinery component or equipment is able to draw while it is operating at its maximum load is referred to as its full load ampere, or FLA .
The full load current (FLA) is the amount of current that the motor will draw when operating at the specified voltage and load in order to deliver the stated amount of horsepower.
The value of FLA is more relevant than the value of MCA and MOCP since FLA is utilised to calculate MCA and MOCP values. So, it is used in an indirectly to estimate the size of the conductors, the equipment, and the over-current protection devices such as the fuse, the MCB, the circuit breaker, and so on.
FLA = 0.80 x MCA
and
FLA = 0.44 x MOCP
LRA
LRA – Locked Rotor Ampere
The amount of current that the motor is able to draw while it is in a locked rotor state is denoted by locked rotor ampere or LRA. The starting (initial) current of the motor may be virtually equal to the value of LRA, which can be around eight times the value of the full load current.
LRA = 8 x FLA
The value of LRA is what is utilised to determine the maximum voltage drop that will occur when the motor is started under its starting conditions.
If the voltage loss is more than 80–85 percent, the motor may fail to start, and once it does, it may start vibrating.
What is the major difference between the LRA and the FLA?
Full Load Amps, often known as FLA, refer to the amount of current that is drawn by the motor (or) compressor while it is operating at its rated output. Load Running Amps, or LRA measure the steady-state continuous current when the load is operating as expected.
Since the load could be lower than the motor’s rated capacity, the current might be lower than the rating as well.
Does FLA have the same value as MOCA?
When all additional loads of 1 A or more that are capable of being in operation(function) at the same time are factored in, the value of MOCP is calculated to be 2.55 times the FLA of the heaviest motor.