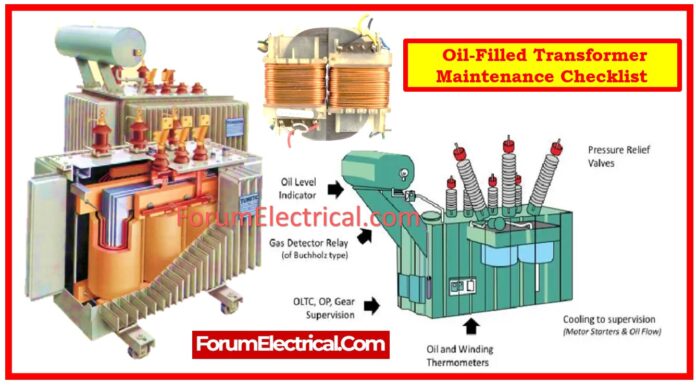
Oil-filled transformers require routine maintenance to ensure their dependability, efficiency, and prolonged operational lifespan.
An organized checklist is provided below, as well as tips for doing maintenance operations properly.
Basic Information
Before starting maintenance, record the following information:
- Location: Enter the installation site.
- Date of Maintenance: Keep track of when the maintenance took place.
- Transformer Label Number: Take note of the unique identity.
Nameplate Details
The nameplate contains essential transformer specifications:
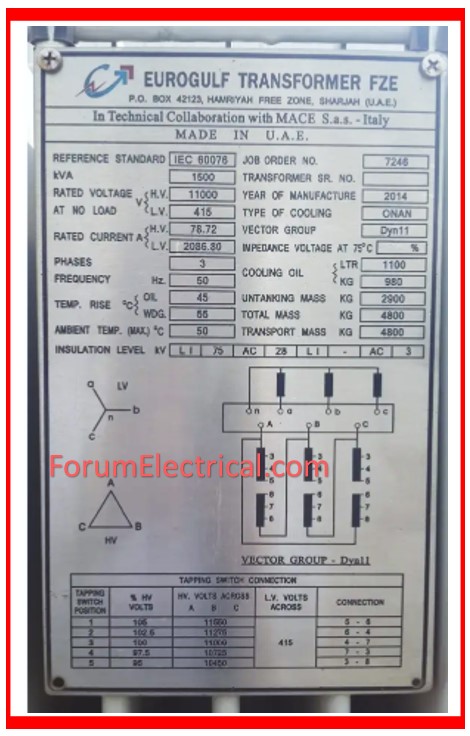
- Capacity: Rated power in kVA (or) MVA.
- Make: The manufacturer’s brand.
- Serial Number: A unique identification number.
- Commissioning Year & Manufacturing Year: Commissioning year & manufacturing year are critical for determining service life.
- HV & LV Voltage: There are high & low voltage ratings in nameplate
- HV and LV Current: HV & LV Current ratings which includes both high & low current ratings.
- Vector Group: Winding connection type is represented by a Vector Group.
- Impedance: Impedance is as indicated by the manufacturer.
- Type of Cooling: Methods for cooling which includes ONAN & ONAF.
Visual and Functional Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the transformer to detect any external damage or irregularities.
- Oil Level Check: Check the oil level with the gauge. Low levels may signal a possible leak.
- Breather Condition: Check the silica gel color and oil level in the breather cup; replace (or) refill as needed.
- Bushing Condition: Look for cracks, chips (or) dirt collection that could compromise insulation.
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Use DGA to discover internal defects and overheating.
- Inspection covers & Gasket Joints: Check for oil leaks & make sure the gaskets are intact.
- Relay & Alarm Contacts: Clean and test the relay & alarm contacts to ensure appropriate functionality.
- Protection Circuits: Test the protection circuits to check that the safety devices work properly.
- Temperature Indicators (OTI & WTI): Ensure that the pointers move freely and that they are properly calibrated.
- Pressure Relief Valve & Vent: Inspect the pressure relief valve and vent for blockages & ensure that they are operating smoothly.
- Oil Conservator Tank: Check for oil level differences or pollution.
- Transformer Painting: Check for flaking or rust and repaint as needed.
Electrical Tests
Insulation Resistance (IR) Measurement
Determine the insulation resistance of windings against the ground and between windings.
Record the following:
- HV to Earth.
- LV to Earth.
- HV to LV.
Calculate the Polarization Index (PI) for insulation evaluation by comparing 1-minute and 10-minute IR values.
Earth Resistance Measurement
Measure and document earth resistance to guarantee appropriate grounding.
- Neutral Earth to Ground
- Body Earth to Ground
Dielectric Strength Test
In order to establish breakdown voltage (BDV) of transformer oil, a dielectric strength tester should be utilized appropriately.
Take three consecutive readings and calculate the average value. This aids in determining oil insulating qualities.
Remarks
Document your observations, test findings, & any corrective actions taken. Additional comments may include suggestions for future maintenance (or) immediate corrections.
Verification
Confirm the checklist is signed by the maintenance professionals.
This systematic approach assures a thorough and effective maintenance process, hence preserving the transformer’s performance and safety.