What is an Earth Pit?
An earth pit is a covered underground chamber that allows inspection, maintenance, & testing of the earthing electrode & other grounding system components.
It’s normally composed of reinforced concrete and provides safe and convenient access to the earthing system.
Purpose
The objective of this Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to establish the standardized technique for doing preventative maintenance on earth pits.
This maintenance ensures that the earthing system performs optimally, which is essential for safety, equipment protection & efficient fault current dissipation.
Scope
The procedure covers all earth pits in the plant and is designed for annual preventive maintenance by the maintenance department.
References
Maintenance Checklist (internal documentation).
IS 3043:1987: Code of Practice for Earthing
Related Documents
Definitions
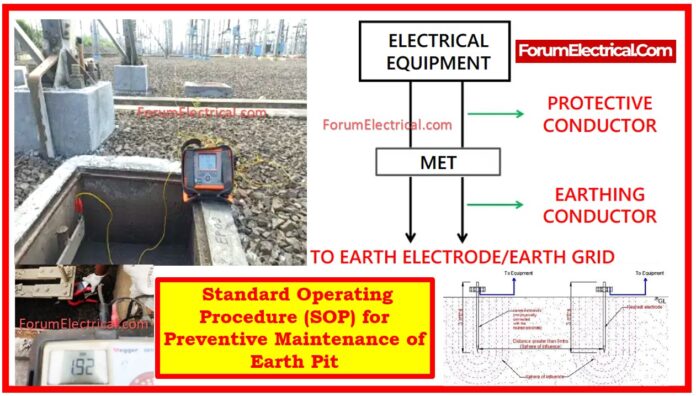
Fall of Potential Method: The Fall of Potential Method is a typical technique for measuring earthing system resistance that involves inserting test electrodes at certain distances from the earth pit.
Maintenance Overview
Schedule of Maintenance
Each earth pit receives preventive maintenance once a year, as specified in the maintenance schedule.
Responsibility
- The maintenance engineer is in charge of scheduling and managing the activities.
- Technicians are personally responsible for carrying out the task in accordance with safety requirements.
Maintenance Procedure
Preparatory Maintenance Activities
Scheduling and Communication
The maintenance engineer will alert the powerhouse & send qualified technicians to the work.
A permit for work should be obtained before starting any maintenance work.
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE)
Ensure that all personnel are wearing proper PPE, such as
- Safety gloves,
- Helmets,
- Safety shoes, &
- Eye protection.
Tool & Equipment Check
Ensure that the Earth Resistance Meter is operational and calibrated.
Prepare the 2 auxiliary electrodes (stakes) needed for the Fall of Potential test procedure.
Earth Pit Inspection & Cleaning
Visual Inspection
Earth Pit Inspection & Cleaning (Visual Inspection)
Open the earth pit cover & check for physical deterioration or corrosion.
Make that the connecting terminals & conductors are intact & undamaged.
Tightening & Cleaning
Tighten every mechanical connection.
Remove any excess soil, trash (or) water & clean the earth pit enclosure as needed.
Earth Resistance Testing
Conduct the Earth Resistance Test utilizing the Fall of Potential Method:
Put the 2 auxiliary electrodes in a straight line at the required distances (per IS 3043).
Connect the equipment using the typical testing configuration.
Measurement Parameters
Measure the resistance value with the grid attached; it must be less than 2Ω.
With the grid unplugged, record the resistance value, which must be less than 5Ω.
Corrective Action
If the earth resistance turns out to be above permissible limits:
- Use water mixed with salt into earth pit to reduce resistance.
- Retest the pit after sometime to confirm the improved values.
Post-Maintenance Activities & Documentation
Use the Earth Pit Maintenance Checklist to record all measured values & observations.
Reporting
Communicate the test findings and the completion of the maintenance work to the site engineer.
Inform the powerhouse of work completion for records.
Safety & Compliance
Ensure that all work is completed in accordance with site-specific safety requirements and ISO 3043:1987.
Maintain a safe distance from live systems and, if necessary, use lock-out/tag-out (LOTO) protocols.
Conclusion
Annual preventive maintenance of the earth pits is essential to ensuring the effective operation of the grounding system.
Proper execution and documentation contribute not just to electrical safety, but also to compliance with Indian standards & internal audit is required.