What is meant by electrical wiring?
Electrical wiring is the process of connecting cables and wires to relevant equipment such as fuses, switches, sockets, lights, fans, and so on to the main distribution board, which is a specific structure connected to the utility pole to ensure continuous power supply.
It is essential to understand the different types of wires and their characteristics as specified by the National Electrical Code (NEC) for varied applications and installations. The following electrical wire factors must be considered while selecting a proper composition,
Size of the Wire – The wire gauge determines the wire size ranges. Some common wire sizes include 10, 12, 14, 18, and so on. And, for roughly 10Amps, 18-gauge wire will be necessary. A 2-gauge cable will be needed for 100Amps.
The Lettering of the Wire – According to the NEC, the insulation of wire types is represented by certain letters. Popular wire insulation combinations include THHN, THWN, THW, and THHN. And the letters stand for:
- H- Heat resistance.
- HH- High heat resistance, which can withstand temperatures of up to 194 degrees Fahrenheit.
- N- Nylon coating for abrasion resistance.
- T- Thermoplastic insulation.
- W- Suitability for wet environments.
- X- Flame resistant synthetic polymer coating.
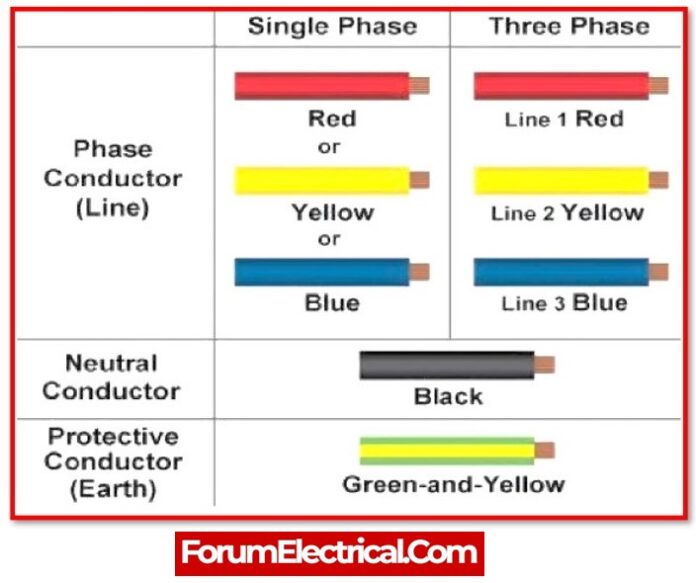
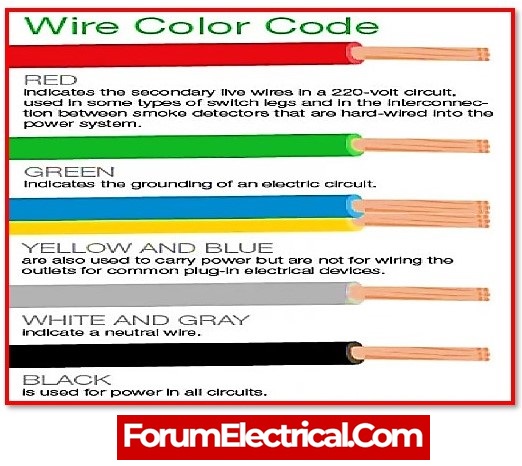
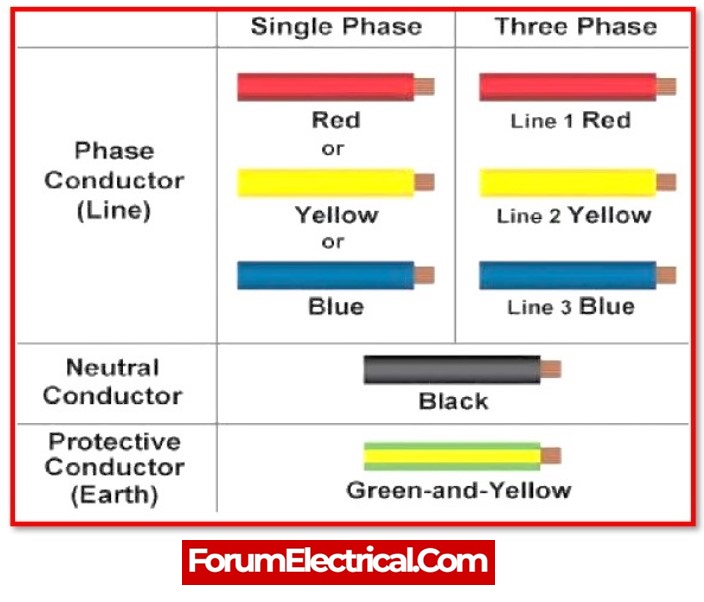
Colour Code for Electric Wires
Different types of wires have different colour codes, which are normally established by national agencies in order to develop a standard operating procedure when working with electrical circuits.

- The live wires that carry current are red.
- White wires are always neutral or neutral wires are also black.
- Green wires are used for earthing or grounding.
- Hot wires, which are symbolised by black, are utilised for outlets and switches.
- Hot wires of blue and yellow colour are utilised for appliances.
Methods of Taking Connection in Electrical Wiring Systems
Electrical wiring is the process of connecting various accessories for the distribution of electrical energy from the supplier’s meter board to home appliances such as lamps, fans, and other domestic appliances which can be accomplished in two ways:
1) Tee system or joint box system
2) Loop – in the system
1). Joint Boxes or Tees Jointing Systems
Connections to appliances are done via joints in this wiring system. These joints are made up in joint boxes using appropriate connectors or joint cut-outs. This wiring solution does not require a large number of cables.
Because this technique of wiring requires less cable, it is less expensive. This method is appropriate for temporary installations and is inexpensive.
2) Loop – in the Systems
This wiring method is widely used in wiring. Lamps and other appliances are linked in parallel so that each can be controlled independently. When a connection is needed at a light or switch, the feed conductor is looped in by carrying it directly to the terminal and then back to the next location to be provided.
The switch and light feeds are routed around the circuit in a series of loops until the last point on the circuit is reached. The phase or line conductors are looped in the switchboard or in the box, and the neutrals are looped in the switchboard or from a lamp or a fan. Never loop a line or phase from a light or fan.

Types of Electrical Wiring
There are various types of wiring, and understanding where they are used is significant.
- Triplex wires,
- Main feeder wires,
- Panel feed wires,
- Non-metallic sheathed wires and
- Single-strand wires
Electrical wiring processes are classified into five types:
- Cleat Wiring,
- Batten Wiring,
- Casing and Caping Wiring and
- Conduit Wiring
- Lead-Sheathed Wiring
1). Cleat Wiring
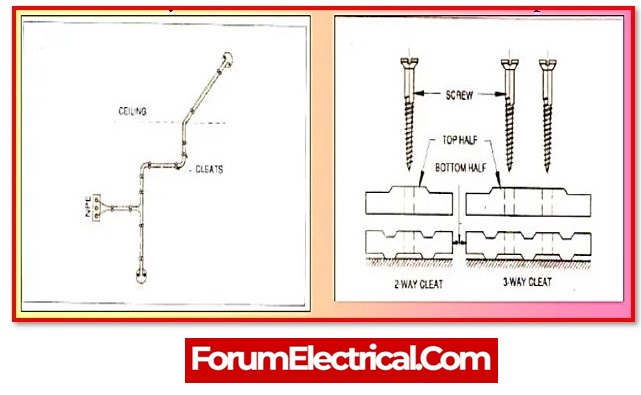
This wiring system consists of standard VIR or PVC insulated wires (rarely sheathed and weatherproof cable) braided and compounded and secured on walls or at 6mm above the walls or ceilings by porcelain cleats, plastic or wood.
Because cleat wiring is a temporary wiring method, it is not ideal for household buildings. The cleat wiring method is no longer in use.
The cleats are divided into two parts. There is one base and one cap. The cables are inserted into groves in the base plate, which is then capped.
However, it is perfectly adequate for establishing a temporary connection in industrial construction activity.
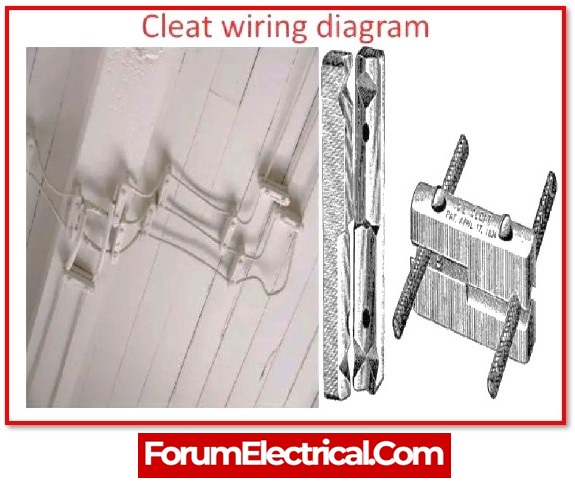
Advantages of Cleat Wiring
- It is a basic and inexpensive wiring system.
- Most appropriate for temporary use, such as under construction buildings or army military camp
- Because the cables and wires of the cleat wiring system are exposed to the elements, faults in the cables can be easily identified and repaired.
- Cleat wiring system installation is simple.
- This wiring system is easily customizable, allowing for changes and additions.
- Inspection is simple and easy.
Disadvantages of Cleat Wiring
- The appearance is not so excellent.
- Cleat wiring should not be used permanently since sagging may occur after a period of time.
- Because the cables and wiring in this wiring system are exposed to the elements like oil, steam, humidity, smoke, rain, chemical, and acidic effects may cause damage to the cables and wires.
- It is not a long-lasting wire system because to weather effects, fire risk, and wear and tear.
2). Batten Wiring
In this type of wiring, single core, double core, or three core TRS cables with round oval forms are employed. Single core wires are typically preferred. TRS cables are chemical, water, and steam resistant, but are marginally impacted by lubricating oil. TRS cables are supported by well-seasoned and straight teak wood battens with a minimum thickness of 10mm.
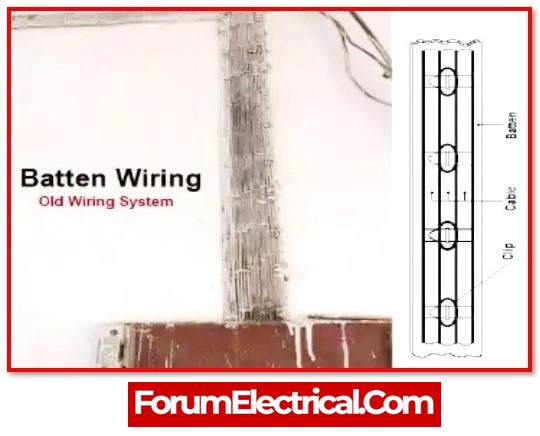
The wires are fastened on the hardwood batten by tinned brass link clips (buckle clips), which are already fixed to the batten with brass pins and spaced at 10cm intervals for horizontal runs and 15cm intervals for vertical runs.
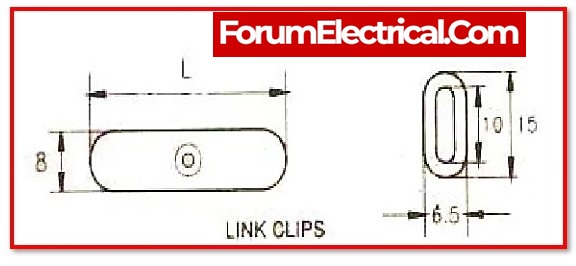
Advantages of Batten Wiring
- Wiring installation is easy and simple.
- When compared to other electrical wiring methods, it is inexpensive.
- It is both good and elegant.
- It is simple to repair
- long-lasting and strong
- This wiring scheme is simple to customise.
- There is less possibility of current leakage with a batten wiring arrangement.
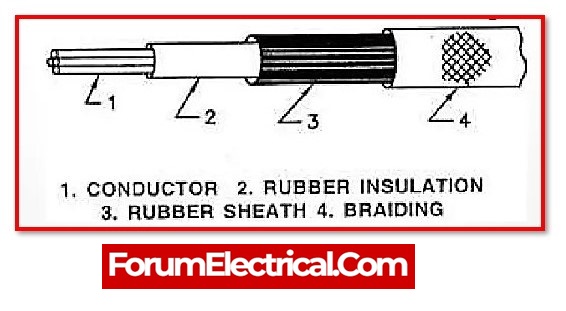
Disadvantages of Batten Wiring
- Cannot be installed in humid, chemically affected, open, or outdoor spaces.
- There is a high risk of fires.
- External wear and tear and weather impacts are not protected (since the wires are exposed to heat, dust, steam, and smoke).
- Heavy cables are not permitted in batten wiring systems.
- Only appropriate for voltages less than 250V.
- More cables and wires are required.
3). Casing and Caping Wiring
Casing and capping wiring systems were widely used in the past, however they are now regarded unnecessary because to the Conduit and sheathed wiring systems. VIR or PVC cables, or any other permitted insulated cables, were utilised in this type of wiring.

The cables were routed via the enclosures made of wood. The enclosure is made of a lengthwise carved strip of wood with parallel grooves to accept VIR cables. The grooves were designed to separate opposing polarities. The capping generally made of wood used to cover the wires and cables inserted and fitted in the casing.
Advantages of Casing and Caping Wiring
- It is a less expensive wiring method than shielded and conduit wiring systems.
- It is a strong, long-lasting wiring system.
- This wiring design lends itself easily to customization.
- Repairing is simple if the Phase and Neutral wires are put in separate slots.
- Because of the strong insulation of the capping and casing, it can stay in the field for an extended period of time.
- It is resistive to oil, steam, smoke, and rain.
- Because of the covered wires and cables in the casing and capping, there is no risk of electric shock.
Disadvantages of Casing and Caping Wiring
- There is a substantial risk of fire in the casing and capping electrical system.
- Not appropriate in acidic, alkaline, or humid conditions.
- Repairing is expensive, and additional material is required.
- Material is difficult to obtain in the contemporary society.
- White ants can cause damage to wood casing and capping.
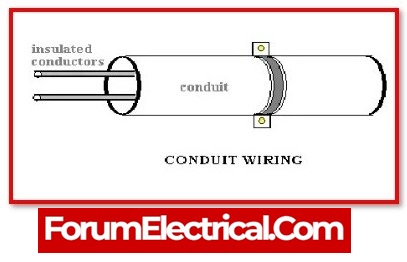
4). Conduit Wiring
The following are the two main forms of Conduit Wiring:
- Surface Conduit Wiring and
- Concealed Conduit Wiring
a). Surface Conduit Wiring
The wiring is certainly done on the outside of the wall, and it is known as Surface Conduit Wiring. This is accomplished by drilling equal-distance holes in the wall and securing them with a GI clamps. And it is delivered to the board and light, fan, or other consumer equipment by pulling the wire through this pipe.
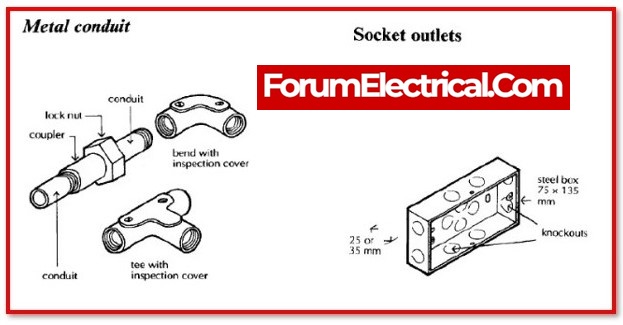
b). Concealed Conduit Wiring
In conduit wiring, steel tubes called conduits are installed on the surface of walls using pipe hooks (surface conduit wiring) or buried in walls under plaster. VIR or PVC cables are then run through the conduits using a GI wire of about 18SWG.
In a conduit wiring system, the conduits should be electrically connected to earth at some suitable points. Conduit wiring is a professional way to wire a building. Most PVC conduits are used in home wiring.
The conduit helps to keep away rodents from chewing on the cables and damaging them. Lead conduits are used in factories and other buildings that are prone to fires. Trunking is more like surface conduit wiring.
It is done by screwing a PVC trunking pipe to a wall and then threading the cables through the pipe. The cables in conduit shouldn’t be too tight. Space needs to be considered.
Conduit Wiring Types
Conduit Wiring are 2 types:
- Metallic Conduit
- Non-metallic conduit
1). Metallic Conduit Wiring
Metallic conduits are made of steel, which is both strong and expensive.
Metallic conduits are classified into two categories:
- Class A Conduit – Low gauge conduit – Thin layer steel sheet
- Class B Conduit – High gauge conduit – Thick sheet of steel conduit
2). Non-Metallic Conduit Wiring
PVC conduit, which is solid rather than hollow, is utilised as a non-metallic conduit because it is flexible and easy to bend.
Conduit Wiring Size:
The common conduit pipes are available in a variety of diameters, including 13, 16.2, 18.75, 20, 25, 37, 50, and 63 mm in diameter (or) 1/2, 5/8, 3/4, 1, 1.25, 1.5, and 2 inch.
Advantage of Conduit Wiring
- It is the most secure wiring system (Concealed conduit wring)
- The appearance is stunning in case of concealed conduit wiring.
- In the case of metallic pipes, there is no chance of mechanical wear and tear or fire.
- Customization according to future need is simple.
- Repairing and maintaining is simple.
- There is no danger of the cables’ insulation being damaged.
- It is free of corrosion (in the case of PVC conduit) and fire risk.
- It can be used in humid, chemically affected, and smokey environments.
- There is no danger of electric shock in case of proper earthing & grounding of metallic pipes.
- It is a dependable and widely used wiring system.
- Wiring system that is long-lasting and sustainable.
Disadvantages of Conduit Wiring
- It is an expensive wiring system (due to the use of PVC and metallic pipes, additional earthing for metallic pipes etc).
- It was quite difficult to locate the wiring problems.
- Installation is not simple or easy.
- Electric shock danger in case of metallic pipes without proper earthing & grounding system.
- It will be extremely difficult to manage new connections in the long term.
5). Lead-Sheathed Wiring
Conductors are insulated with VIR and covered with an outer sheath of lead aluminium alloy containing approximately 95% lead in this form of wire. The metal covering shielded the cables from mechanical damage, moisture, and air deterioration.

The entire lead covering is made electrically continuous and is connected to ground at the point of entrance to protect against electrolytic action caused by leaking current and to provide safety in the case the sheath becomes active. The cables are run on wooden battens and secured with link clips, precisely like TRS wiring.