Scope
This test procedure explains the steps involved in testing and commissioning the Vacuum Circuit Breaker.
- Scope
- Test Equipment
- Testing Procedure
- Step-1: Visual Inspection
- Step-2: IR Value Test
- Step-3: Contact Resistance Test (CRM Test)
- Step-4: Timing Test
- Step-5: Gas Leak Detection Test
- Step-6: High Voltage (HV) Test of Vacuum Bottle
- Step-7: Operational Check
- Step-8: Functional Check
- What is the CRM Test in VCB?
- Relevant Standards
All testing & commissioning activities must correspond to applicable international standards as well as the relevant codes of practice.
Test Equipment
The following test equipment and tools will be needed for performing out the tests outlined in this procedure:
- Megger (5KV)
- CRM Kit
- Timing Test Kit
- Gas Leakage Detector Test Kit
- Vacuum Bottle
Testing Procedure
Step-1: Visual Inspection
- Verify physical installation versus authorized drawings.
- Ensure breaker ratings align with authorized working drawings.
- Ensure general construction and finishing standards are adequate.
- Ensure leveling & alignment are right and acceptable.
- Ensure equipment is properly mounted as per manufacture instructions.
- Ensure warning labels & signage are installed.
- Verify equipment access for maintenance.
- Verify that the functioning handles and keys, along with the mounting cabinet, are given.
- Ensure rubber insulating mats are provided at the front and back of panels.
- Ensure ‘As Built’ record schematic schematics are installed in the room. The schematics will be framed and wall-mounted.
- Instructions for operating interlock facilities have been supplied.
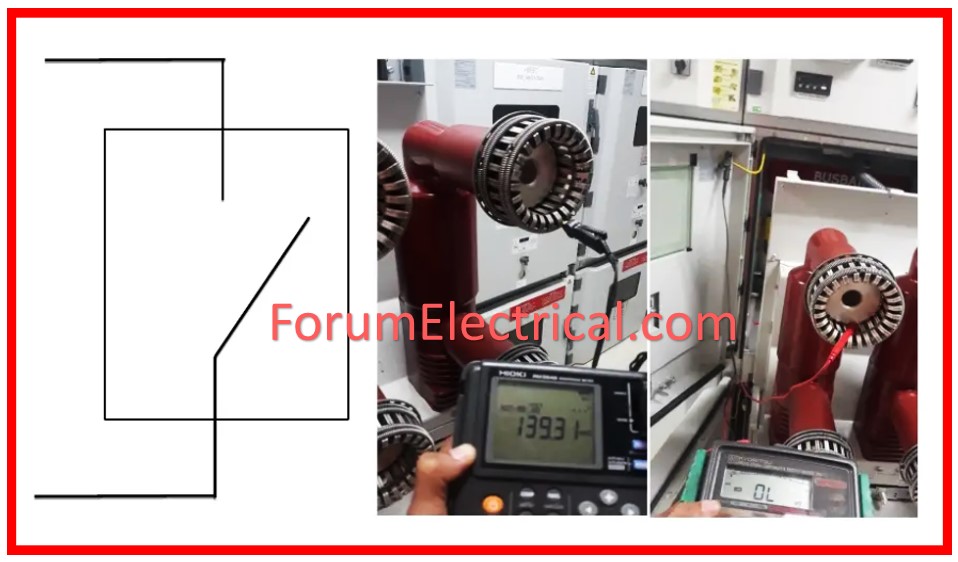
Step-2: IR Value Test
- The IR test of the breaker is performed using a 5KV Megger.
- Meggering is typically performed under certain conditions, notably when CB is closed & when CB is opened.
- During these settings, Megger values are recorded for all stages. The measured values are preferably in (GΩ) Gigaohms.
- The R, Y, and B poles are connected to Earth to close the breaker.
- The breaker open condition: R pole to Earth, Y pole to Earth, and B pole to Earth
- The breaker is open on the R-R, Y-Y, and B-B poles.
- The above values are recognized and documented in the site register/test report. The value must be in (MΩ) MegaOhms.
| Insulation Resistance (IR) Test | Values in (MΩ) | |||
| S. No | (With 5kV Megger) | “R” Phase | “Y” Phase | “B” Phase |
| 1 | Across Poles (or) Contacts (When Circuit Breaker Open) | |||
| 2 | Pole-to -Earth (When Circuit Breaker Closed) | |||
| 3 | Pole-to-Pole (When Circuit Breaker Open) | |||
Step-3: Contact Resistance Test (CRM Test)
The CRM Kit is used to measure the contact resistance of the breaker, which includes the R ph, Y ph, and B ph poles. This is accomplished by injecting 100A DC current & displays the resistance that is generated as a result.
The number displayed would be ideal to have less than 100 (µΩ) micro ohms.
Stationary and moving contacts are made of materials that are arc-resistant.
However, if contacts fail to be maintained on a consistent schedule, resistance from repeated arcing builds up, resulting in the contacts’ inability to transfer currents.
| Contact Resistance | Values in (µΩ) | |||
| S. No | Description | “R” Phase | “Y” Phase | “B” Phase |
| 1 | Contact Resistance Value | |||
Step-4: Timing Test
- It is important to time every breaker in order to obtain a functioning signature.
- Incorrect operation may result in devastating effects for the equipment and substation staff.
- In addition to mention the revenue loss and repair costs associated with being out of service.
- Timing tests are performed initially in the plant during normal tests, then after installation during commissioning tests.
- They must be performed on a regular basis to ensure the breaker’s proper operation and reliability.
- Timing tests are also an effective method for troubleshooting defective breakers.
- The main actions for completing a timed test consist of four steps:
- Installing and connecting cables
- Data Acquisition
- Data Interpretation and Analysis
| Breaker Closing and Opening Time Test | Timings (ms) | |||
| S. No | Description | “R” Phase | “Y” Phase | “B” Phase |
| 1 | Close | |||
| 2 | Open-1 | |||
| 3 | Open-2 | |||
Step-5: Gas Leak Detection Test
- The gas is placed in gas leakage detection test kit and left for 24 hours under observation.
- After 24 hours, the pipe joints are tested to see whether there is any gas leaking.
- If the pressure drop exceeds 1KV, the gas leakage detector recognizes it.
Step-6: High Voltage (HV) Test of Vacuum Bottle
- The device undergoes a high voltage test of up to 18 KV.
- If the apparatus trips, it is determined that the vacuum bottle is malfunctioning and needs to be replaced.
Step-7: Operational Check
| Manual Operation | Close / Open |
| Electrical Operation (L/R) | Close / Open |
| Protection Trip | Trip |
| Anti-Pumping | – |
Step-8: Functional Check
- On/Off Indication,
- Spring Charge Indication,
- CB Auxiliary Contact,
- Automatic Trip Indication,
- Trip Circuit Healthy,
- Vacuum Pressure Low (or) Lockout Alarm
The equipment installation is nearly complete and operational.
Equipment & system, testing documentation must be produced to verify that all subsequent tests & inspections have been completed.
Provide all testing documentation, particularly manufacturer advised procedures, to commissioning management team for confirmation.
Wear insulating gloves. Discharge and ground the circuit at the end of each test.
What is the CRM Test in VCB?
The CRM test is performed in the presence of a circuit breaker, hence the name “Static Contact Resistance Measurement (CRM) Test”.
In the CRM test of a circuit breaker, the breaker is closed and a 100 Amps DC current is delivered into its contacts. The CRM kit can measure the micro-ohm (µΩ) resistance of CB.
Relevant Standards
Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCBs) must be tested in accordance with relevant Indian standards such as IS 13118 (High Voltage Alternating Current Circuit Breakers), IS 8262 (Guide for Circuit Breaker Testing), and international standards such as IEC 62271-100.
These standards ensure the reliability, safety, and operating efficiency of VCBs by addressing mechanical & electrical endurance, insulation resistance, contact resistance, timing tests, and high-voltage withstand testing.
Compliance with these criteria ensures that the VCB meets all regulatory & functional requirements.









