Voltage Drop Calculation Excel Tool
What is Voltage Drop?
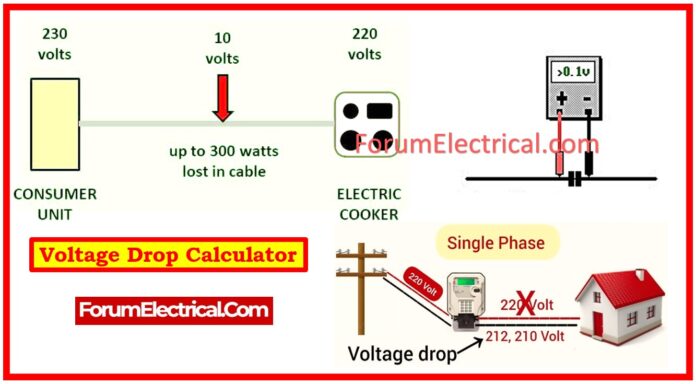
When electricity runs across wires, some energy is lost due to resistance in the conductors. This is referred to as voltage drop.
i.e., The voltage differential between the source & load. If the voltage drop is too high, the devices connected to the circuit may not function properly.
Formula of Voltage Drop
VD = (L×A×Vc)/1000
is employed in electrical circuit voltage drop (VD) calculations.
Here’s the terms represent:
VD – Voltage Drop (in volts)
L – Length of the conductor (in meters or feet) depending on the system used.
A – Current flows through the conductor (in A)
Vc – Voltage drop per unit length for the conductor
The voltage drop is a measurement of the voltage loss that occurs as current flows through a wire owing to resistance.
This formula estimates the amount of voltage lost between two points in a circuit.
Terms Purpose
VD (Voltage Drop): This is exactly what we are calculating. It’s measured in volts and indicates how much voltage is lost as current runs through the wire.
L (Wire Length): The distance traveled by the current through the conductor, measured in meters (or) feet. The longer the wire, it has higher resistance.
A (Current in Amps): The amount of electrical current passing through the cable is measured in amperes (amps).
Vc (Voltage Drop Coefficient): This is the voltage drop per unit length of the wire, expressed in millivolts per amp per unit length (mV/A/m for meters or mV/A/ft for feet). This value is determined by the wire’s size and material (such as copper or aluminum).
Solved Example
Assume you have a 50-meter-long copper wire carrying 20 amps of current and a voltage drop coefficient of 1.73 mV/A/m (typical for copper wire).
This is how the formula works.
VD = (L×A×Vc)/1000
VD = (50 x 20 x 1.73)/1000
VD = 1730/1000
VD = 1.73 V
So in this case, the voltage drop is 1.73 volts.
If you’re using a 120V system, this means that when the power reaches the end of the wire, it will be 120V – 1.73V = 118.27 V.
Why Is Voltage Drop Important?
If the voltage drop is too high, devices may not function properly because they do not receive enough power. Motors, for example, may operate at a slower speed or lights may dim.
This is the reason it is so important to consider voltage drop, particularly in lengthy cable runs.
Tips to Reduce Voltage Drop
- To minimize voltage drop, use shorter cables whenever practical.
- To reduce resistance, increase the wire diameter (lower gauge).
- Choose copper, which has lower resistance than aluminum.
- Limiting the current keeps the voltage drop under control.
Click here for more Electrical Calculators