- What is a Link Box (Electrical Link Box)?
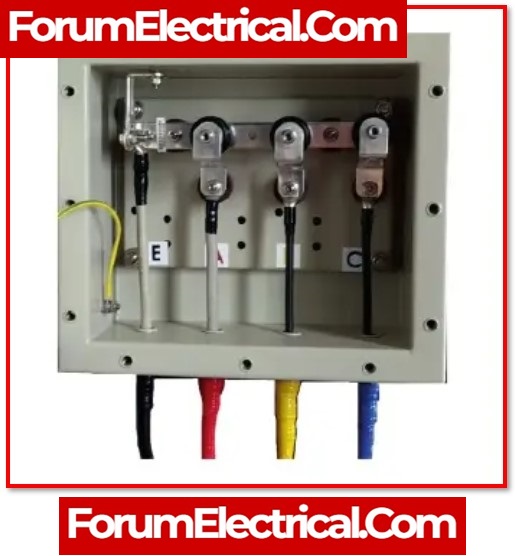
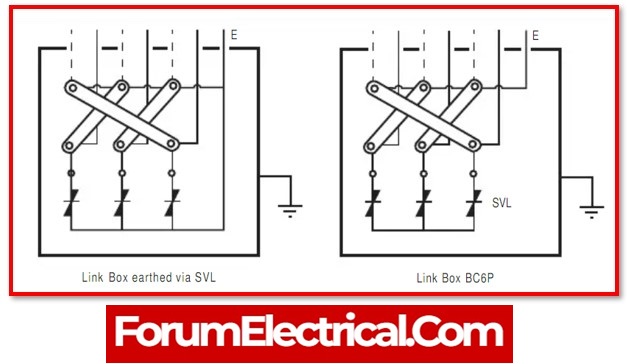
- Components of a Cable Link Box
- What effect does voltage have on the sheath?
- Solution for Reducing Sheath Induced Voltage
- Properties of Link Box
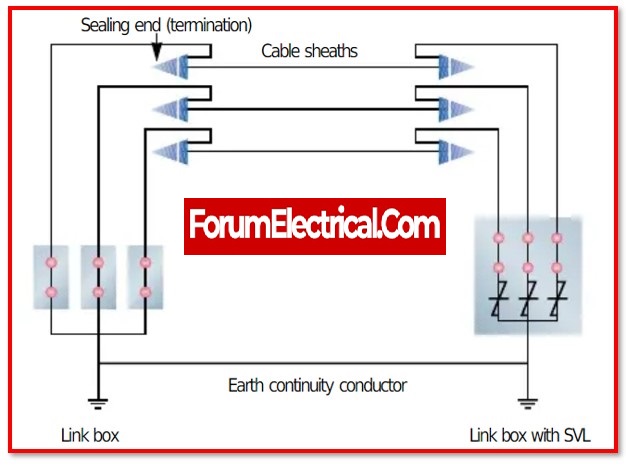
- Schematic of Connectivity in Link Box
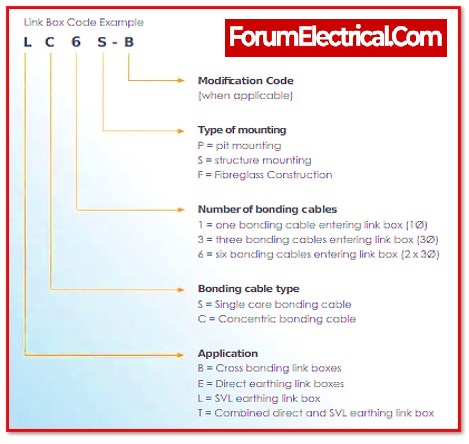
- Types of Link Box
- Applications of Link Box
- What is an underground Link Box?
- What is a LV link box?
- What is a HV link box?
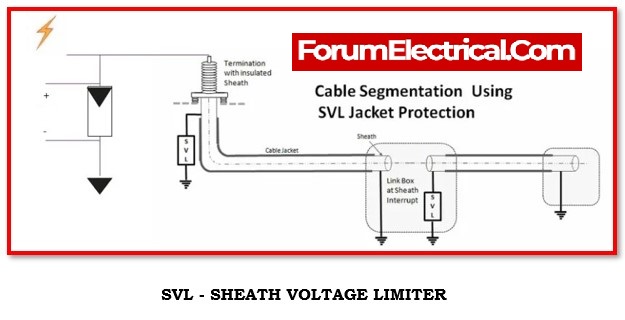
- What is SVL in a link box?
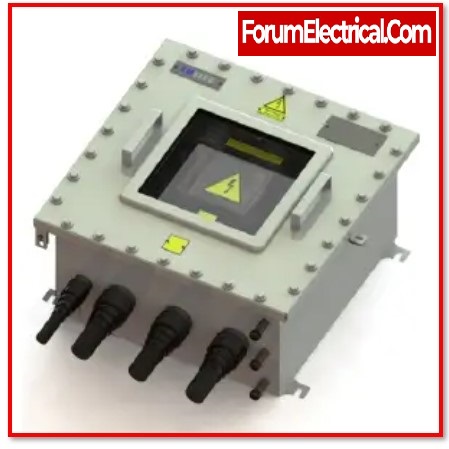
What is a Link Box (Electrical Link Box)?
A link box is a box that contains the components necessary to make a cable sheath braking system.
By adopting bonded systems with a maximum of 132 kilovolts, sheath breaking may stop circulating currents and restrict the voltage that is induced in the cable sheath.
Sheaths are used to provide cable sheath bonding for underground medium and high voltage cable bonding. This helps to limit the amount of circulating sheath current.
For reasons of safety, bonding the cable sheath lowers the voltages that are induced in the cable sheath.
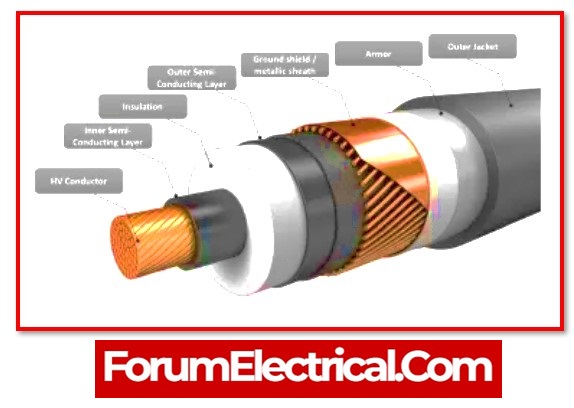
Components of a Cable Link Box
A cable is made up of three major components.
1). Conductor
2). Insulation and
3). Sheath
1). Conductor
The current is carried by the conductor because of its very low resistance.
In order to provide isolation between the conductor and the sheath, insulation is covered all the way around the conductor.
2). Insulation
The insulation is encased in a coating before being wrapped in the sheath.
The extra coating that improves the cable’s protection is provided by the insulation, which is placed over the sheath.
3). Sheath
Sheathing is not necessary for low voltage wires. On the other end, high-voltage and medium-voltage cables both include sheaths that protect them against overvoltage and transients.
Moreover, the sheath serves as a barrier against the transfer of moisture from the external environment into the primary insulation.
Because of this, the usable life of the cable insulation is increased as a result.
What effect does voltage have on the sheath?
Therefore, according to Faraday’s rule of electromagnetic induction, a revolving magnetic field will induce emf (induced emf) on a stationary conductor if it is linked to that conductor in some way.
Alternating current with a high magnitude is used for EHV cables; this creates a connection with the metallic sheath that surrounds the power wire.
This results in emf being produced in the metallic sheath, which in turn causes current to leak out of the cable, leading to losses in the power supply.
Electricity losses of this scale are unsustainable and unaffordable.
Solution for Reducing Sheath Induced Voltage
Install Link boxes in conjunction with cable joints to offer HV cable circuit bonding.
Properties of Link Box
- For the purpose of connecting cable and joints/terminations, link boxes feature a structure that is both sealed and waterproof.
- Make use of link boxes for the following to nullify out the voltage that is produced in the sheath
- In order to reduce cable losses brought on by the circulating current in the sheath
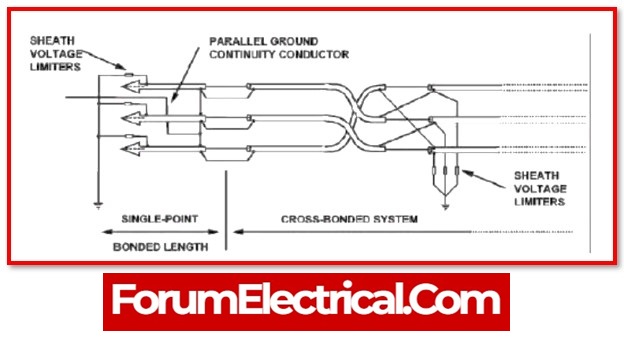
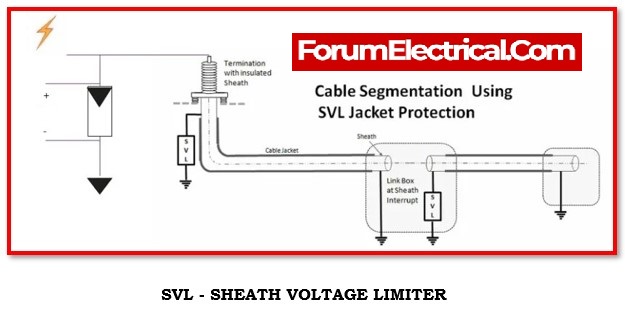
Schematic of Connectivity in Link Box
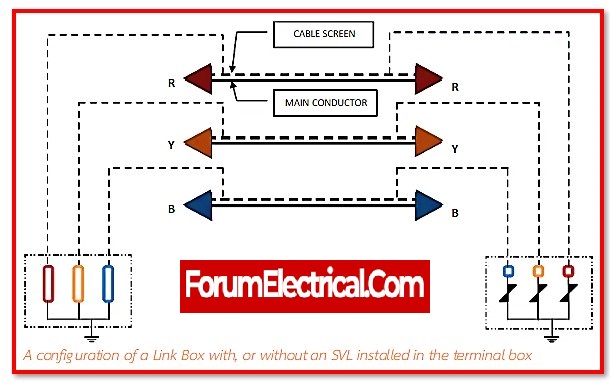
Conductor, insulation, and a sheath are all components of the power cable.
It may prevent the voltage from being induced in the sheaths by switching the positions of the sheaths for all three phases.
Remove a section of the sheath layer from each phase cable, and then connect the sections that are removed to the appropriate slots in the link box.
A connection may be made from one end of the sheath bonding cable to each of the three sheaths, and another section of the sheath cable can be connected to the grounding earth.
It is possible to reduce the induced voltage to nearly nothing if the sheaths are connected to the ground.
Moreover, there is a significant decrease in the amount of cable loss that may be attributed to sheath losses.
When a power connection is very long, the boxes should be spaced out at equal intervals along the distance from the source end to the load end.
The cable is not severed at any point throughout its whole length; rather, just a portion of the sheath is severed at predetermined intervals of distance.
This results in the cable’s sheath power losses being reduced to their absolute minimum.
Types of Link Box
Link Box are classified into 2 types,
1). Single Bonding Link Box and
2). Cross Bonding Link Box
1). Single Bonding Link Box
The most basic kind of special earth bonding involves making arrangements for the cable sheaths of the three high-voltage cables to be linked and bonded at a single point along the length of the circuit.
This method does not include any cable joints and often involves shorter cable circuits.
At every other point, there will be a voltage that appears from the sheath to the ground, and this voltage will reach its highest value at the place that is the furthest away from the earth bond.
As there is an open sheath circuit (except via the SVL), current does not generally flow longitudinally through the cable sheaths, hence there is no sheath circulation current loss that is incurred.
Therefore, the high voltage cable sheaths need to be suitably insulated from the ground.
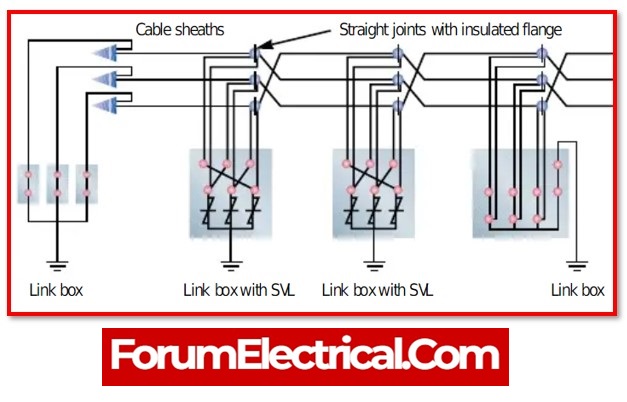
2). Cross Bonding Link Box
Cross bonding link box is used for
- Cross interconnection of high-voltage(HV) single-core cable metal sheath,
- Limiting overvoltage applied to cable sheath and both insulated part ends of insulated joint,
- Controlling induced voltage on metal sheath,
- Reducing (or) eliminating ring current on cable sheath,
- Increasing transmission capacity of power cable,
- Avoiding over-sheath breakdown, and
- Ensuring a safe operating for per cable.
With an enclosure made of stainless steel, the link box is possible to have resin poured inside of it.
In addition, the link box has a compact volume, low weight, is simple to install, and its limiter can be removed.
Applications of Link Box
- Reduces the amount of voltage that may build up on the sheath and helps limit as a voltage regulator, sheath circulating current is used
(Limits the lighting and switching surges).
- Provide convenient access to shield breaks for the sake of testing.
- They are often utilised in high-voltage (HV) applications ranging from 33 to 440 KV lines.
What is an underground Link Box?
Link boxes have a variety of applications in the high voltage cable industry. They provide a climate-controlled setting that is impervious to the elements for the connecting connections that are utilised in the earthing (or) cross-bonding of the metallic sheaths of (HV) high voltage cables.
What is a LV link box?
Link box also called as network box is an essential component of the underground (UG) low voltage network, and it plays an important role in ensuring to back feed electrical supplies and to find in cable fault (failure) situations.
What is a HV link box?
Earthing and bonding the cable sheaths of cables is accomplished with the assistance of a high voltage (HV) link box for single-core cables. This facilitates the reduction or elimination of induced voltages and currents that circulate through the cables.