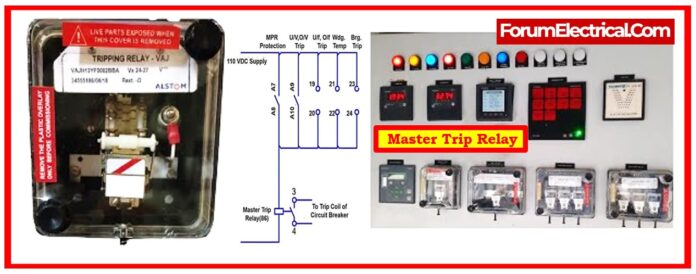
What is a Master Trip Relay?
The Master Trip Relay, which is also known as the Lockout Relay (Relay 86) (ANSI 86), is an essential component in electrical protection & control systems.
Its primary function is to make sure the coordinated tripping of the circuit breakers in reactions to fault conditions.
Though it does not directly detect the fault, it accepts tripping signals from a variety of protection devices, including
- Overcurrent relays,
- Differential relays,
- Earth fault relays, and so on,
and initiates the ultimate tripping operation.
Purpose & Functionality of Master Trip Relay
Master Trip is an auxiliary relay that functions as a link between several protection relays and circuit breaker trip coils.
It receives several tripping commands from the protection relays & sends one trip command to the breaker trip coil.

The master trip relay is not a type of monitoring relay. It is used to isolate the protection relay and the breaker trip coils.
It is utilized in an HT panel to ensure the safety of the protective relay.
The protection relay sends many commands, after which the breaker trip coil receives a single command from master trip coil.
When any one of protection relays detect a fault & send a trip signal, the Master Trip Relay locks in & activate its contacts, tripping the appropriate circuit breaker(s).
It assures that only the one strong, isolated output trips the breaker, irrespective of whichever protection relay detected the fault.
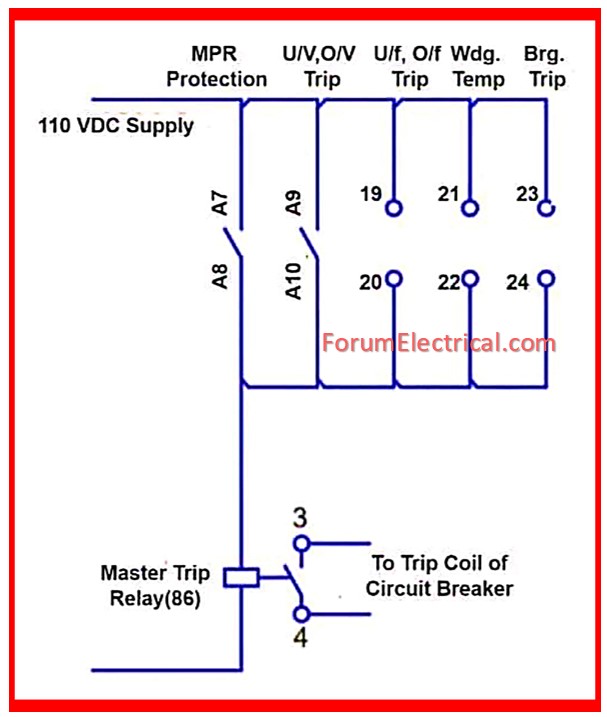
Working Principle of Master Trip Relay
The Master Trip Relay (MTR) is utilized to maintain safety conditions for all protection relays.It receives tripping commands from the
- Auxiliary alarm &
- Tripping relay,
as well as the over current and earth fault relays, and then sends a single tripping command to circuit breaker.
If a fault develops in the breaker trip circuit, a substantial fault current will move from the trip circuit to the master trip relay.
In this case, the master trip relay will be harmed, but protection relay will remain safe.
Because the master trip (lockout) does not monitor microprocessors, its cost is extremely low due to the reason that it only has one coil in the closing circuit.
In a 132 kV substation, protection relays such as
- Distance relays,
- Differential relays, and
- Overcurrent relays
all send trip signals to a single master trip relay (86).
This relay subsequently trips the breaker & locks it in the tripped position, ensuring a dependable & fail-safe disconnection of problematic portion.
Importance of Master Trip Relay
Protection of Protection Relays
It isolates sensitive protection relays from breaker trip circuits. In the circumstance of a short circuit or a problem with trip coil circuit, the Master Trip Relay (MTR) absorbs impact and protects important relays.
Centralized Tripping Logic
A single master relay handles all fault conditions. This allows for centralized tripping logic, eliminating the need to separately wire every protection relay to breaker trip coil.
Multiple Output Contacts
Relays often have many auxiliary contacts which can trip multiple breakers. It is set alerts or annunciations. Interlocks can be triggered. Also, send signals to the SCADA (or) DCS.
Fail Safe Operation
The relay structure assures that even under severe failure circumstances, the tripping function is performed reliably. It frequently includes mechanical latching, which holds the relay in tripped position till reset.
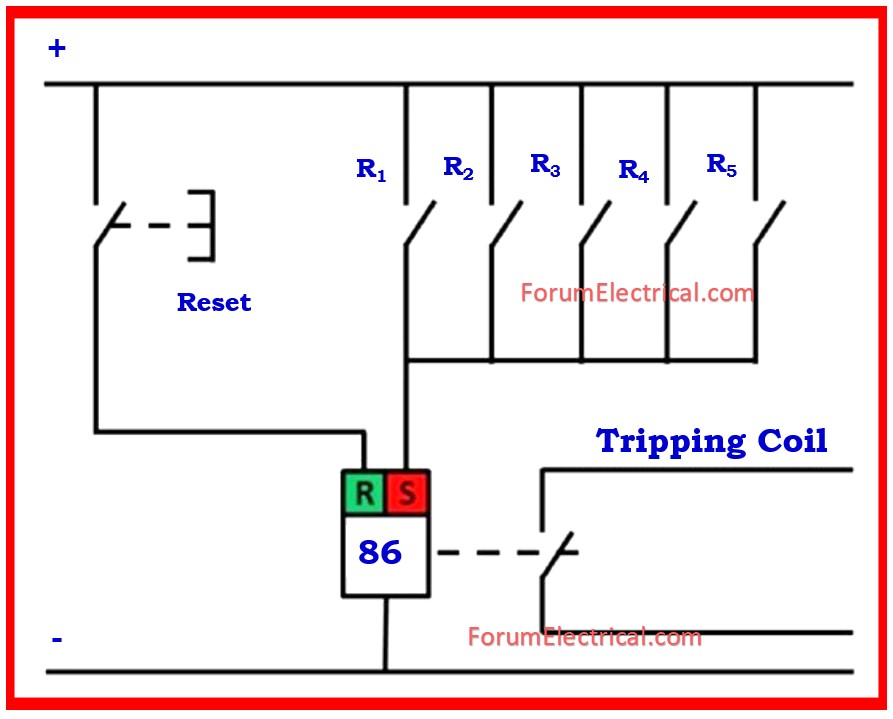
Reset Types
Hand Reset (Manual)
An operator must physically recognize the trip & reset the system. This guarantees that the cause of trip is identified before continuing.
Self-Reset (Auto)
Some modern relays can reset automatically once fault is resolved.
Application of Master Trip Relay
- The HT panel protection relays are isolated with a breaker trip coil via a master trip relay. If a fault arises in the tripping circuit, only master trip relay will be affected, while the protection relay will be safe.
- MTR is less expensive than protection relays. So we utilize MTR so that if a fault occurs in trip circuit, only the MTR contact burns, not the protective relay.
- If master trip relay is not utilized in HT panel, all protection relay outgoing wires will be linked to the trip coil; as a result, a large amount of wiring will be required to connect to the breaker trip coil.As a result, the DC supply may leak and the connection may be lost, increasing the wiring cost.
- However, if we utilize a master trip relay, only one wire will be linked to tripping circuit.
- The Master Trip Relay creates another parallel circuit that can be used for circuit breaker tripping, annunciator panels, interlocking, etc.
Types of Master Trip Relays
The different types of master trip relay based on brands are:
- Siemence 7PJ12 Mater Trip Relay
- L & T Master Trip Relays
- JVS Master Trip Relay
- Avana Master Trip Relay
- ABB PQ Series Relays
- Alstom Master Trip Relay
- Ashida Master Trip Relay
1). Siemens 7PJ12 Master Trip Relay
Siemens 7PJ12 auxiliary lockout relays are employed in control & protection circuits. High-speed operation, dependable tripping, and many interlocking contacts are available. This sturdy construction enables reliable operation in demanding substation conditions.
2). L&T Master Trip Relays
Master trip relays from Larsen & Toubro are compact and speedy. These electromechanical relays are frequently employed in Indian substations to isolate damaged sections and trip circuit breakers and isolators.
3). JVS Master Trip Relay
Indian-made JVS relays protect heavy equipment. Master trip relay versions are suited for transformer and feeder protection due to their powerful mechanical latch system & quick reset.
4). Avana Master Trip Relay
Avana trip relays are affordable and reliable for small to midsize substations. Electromechanical master trip relays provide many NO/NC contacts for trip & alarm circuits and are mechanically durable.
5). PQ Series ABB Relays
The PQ Series from ABB has multifunction auxiliary relays for master trip applications. They can perform many control and protection roles in modern substations because to their modular construction and fast speed.
6). Alstom Master Trip Relay
Alstom’s legacy master trip relays in older substations are reliable under GE. Many vintage setups employ these tough relays for backup and tripping.
7). Ashida Master Trip Relay
Ashida MT series master trip relays are popular in Indian substations & switchyards. They isolate faults and work with Ashida’s protection devices due to their fast response time & mechanical flag indicators.
Why are we Master Trip Relay?
In the case of the absence of a MTR-Master Trip Relay, all of the protection relays must be linked to the Breaker’s tripping coil, which increases wiring costs and causes DC leakage.
If a Master Trip Relay is employed, just one wire will connect the MTR contact to the tripping circuit.
Provides insulation across the protection relay & the breaker tripping coil.
If the 86 relay is not utilized in tripping circuit, the protection relay contacts may be burned if a fault occurs.
We cannot afford protection relays, therefore we employ master trip relay instead.
If there is a problem, MTR contacts will get burned rather than protection relays, & we know that master trip relay contacts may carry more current than a breaker tripping coil.
As a result, the odds of harming the 86 relay’s contacts are quite low.
So, as previously stated, the Master Trip Relay has a larger Contact Capacity, so if there is a fault in tripping circuit, contacts of 86 relay can sustain the fault current.
Tripping directly from protection relay may cause damage to the protection relay’s contacts, which we cannot afford because protection relays are expensive.
Conclusion
The Master Trip Relay ensures safe, dependable, & centralized tripping of electrical systems under fault conditions.
It protects the entire protective system, simplifies wiring, and aids in system integrity.
It serves an important role in
- Power plants,
- Substations, and
- Industrial switchgear panels,
where rapid and coordinated fault clearance is required.