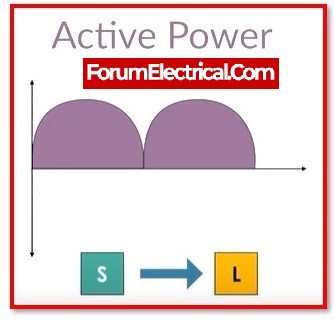
What exactly is the active power ?
Active power is defined as the power that moves in a continuous manner from the source to the load in an electric circuit.Other names for this type of power include Real power and true power. Kilowatts (kW) and megawatts (MW) are the units of measurement. The electric circuits, also known as the load, are kept operational by the actual result obtained by the electrical system.
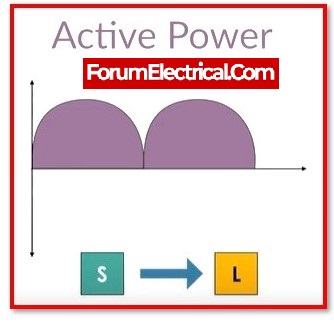
Where,
S = Source and
L = Load
How Active Power is determined ?
It is the amount of useful power that is consumed by loads in order to accomplish real work, which is to say to convert other types of energy into electric energy. The incandescent light bulb’s primary function is to transform the electrical energy it receives into visible light and thermal energy. When it comes to electric power, the component of the current that is in phase with the voltage is the part that actually does the job. Because the current and voltage
Watts are the units used to measure active power, which is the rate at which the load expends, dissipates, or consumes energy. Active power is measured in watts (W). Calculating P is as simple as taking the instantaneous product of the voltage and current and averaging the two values.
Formula for measuring Active Power

Where,
V = Voltage,
I = Current and
Cos ø = Power Factor
Active Components in Electrical
The current’s active component is as follows:
An active component, watt-full component, or in-phase component of the current is a current component that is in phase with the voltage of the circuit and adds to the active or actual power of the circuit. Other names for this type of current component include an in-phase component.