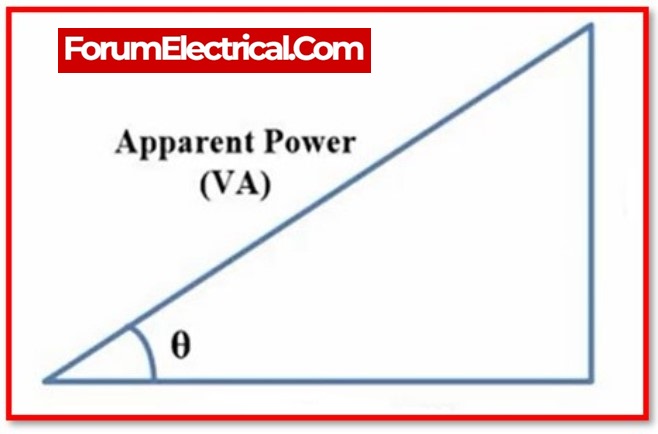
What is Apparent Power ?
The combination of a circuit’s reactive power and its active power is referred to as its apparent power, and it is calculated by multiplying the circuit’s voltage by its current without taking into account the phase angle.
The symbol for apparent power, which is denoted by the capital letter S, is the unit of measurement known as volt-amperes (VA).
Power from an alternating current (AC) source may be reflected back to the source rather than fully used by the load (e.g., a computer, motor, lights, or cooling system) (power company). The term “apparent power” is used to describe the entire amount of power that is being transmitted.
In an alternating current (AC) circuit, apparent power is defined as the product of the r.m.s voltage and the r.m.s current.
When the circuit is pure resistive, apparent power is the same as true or active power; however, when reactance is present in an inductive or capacitive circuit, apparent power is higher than real or active power.
Formula to determine Apparent Power
S = V X I
Where,
V = Voltage and
I = Current
Apparent Power Components
The overall impedance of a circuit has a direct impact on the apparent power of the circuit. Since working with scalar quantities in the power calculation, all complex beginning quantities like voltage, current, and impedance must be represented by their polar magnitudes and not by their real or imaginary rectangular components.
Application of Apparent Power
1). When it comes to the sizing and construction of electrical equipment like alternators and transformers, apparent power is a factor that must be considered.
2). The values of current and voltage are the primary factors that determine apparent power, the load power factor is essential.