- What is meant by Ballast Resistor?
- What is the function of a ballast resistor?
- Types of Ballast Resistor
- Ballast Resistor for the LED Circuit
- Ballast Resistor for an Ignition Coil
- Important Aspects of the Ballast Resistor
- How to conduct a Ballast Resistor Test?
- What is Ballast Resistance made of?
- Advantages of Ballast Resistor
- Disadvantages of Ballast Resistor
- Applications of Ballast Resistors
- Significant Applications for Ballast Resistor
- What elements affect to the failure of a ballast resistor?
- What are the symptoms of a bad ballast resistor?
Ballast resistors increase resistance when current flow increases and decrease resistance when the current flow drops. Despite applied voltage or circuit changes, this resistor maintains current flow. Resistance increases with temperature, providing ballast action. In some automobile ignition systems, these resistors correct for line voltage changes (or) negative voltage-ampere characteristics of devices like vapour lamps and fluorescent bulbs. This article discusses ballast resistors and their uses.
What is meant by Ballast Resistor?
A ballast resistor is a resistor that is used in a circuit to reduce current. Ballast resistors also helps in the prevention of overcurrent faults in the circuit.

An “electric ballast” is a more general term for an electrical device that used to maintain the stability of a circuit by limiting the value of current & voltage.
- Resistors,
- Capacitors,
- Inductors,
or a combination of these can be used as electric ballasts.
Ballast resistors can change resistance in response to current. The resistance increases as that the current flows through the resistor exceeds the threshold value. As the current decreases, the resistance will decrease as well.
The ballast resistor attempts to maintain constant current flowing through a circuit in this way.
The ballast resistor is not the same as the load resistor. Because it functions as a variable load connected to the system. In the case of a load resistor, however, resistance remains constant with varying current and voltage values.
What is the function of a ballast resistor?
The word “ballast” refers to something that provides stability. Hence, these resistors are helping to sustain the electrical circuit stable.
In order to adapt to new conditions and maintain the integrity of the other parts of a network, certain devices make utilize a component called a ballast resistor.
Temperature increases in proportion to the increase in the amount of current that is flowing through the resistor. And as a result of the rise in temperature, there is also an increase in the resistance.
As a result, an increase in the resistance restricts the amount of current that can flow through the network.
Types of Ballast Resistor
There are two different types of ballast resistors.
- Fixed resistors &
- Self- variable resistors.
1). Fixed resistors
This type of resistor has a fixed resistance. In most circumstances, this type of ballast resistor is only used in simple circuits.
Fixed ballast resistors are used in a variety of applications that require a high resistance value.
It is used in circuits with neon lamps or LEDs,. It’s also found in variable-speed fans.
A fixed ballast resistor with two centre taps is used in a variable-speed fan. The resistance value is set by the fan selector switch using the centre tap. The speed of a fan varies with the value of resistance.
2). Self- variable resistors
This resistor’s resistance shifts in response to alterations in the current flowing through it. The temperature of ballast resistor increases as the current through it increases. This causes an increase in resistance.
For an incandescent light bulb, this type of the ballast resistor is required. Since the ballast resistor’s resistance increase as the lamp’s current increases, this indicates that the lamp’s light output can be increased. The voltage drop across the resistor is also increased.
When the current is reduced, temperature and resistance both drop. Moreover, this resistance is employed as a safeguard for sensitive electronic components in a circuit.
Ballast Resistor for the LED Circuit
A light emitting diode is a highly sensitive device. As a result, if the voltage supply applied to this is greater than the rated voltage, the diode may be damaged. To fix that, a ballast resistor is used within the LED circuit.
A LED, ballast resistor, & battery are required components for this simple circuit. The ballast resistor is linked (connected) in series with a light emitting diode in this LED circuit. As a result, the voltage across the (LED) light emitting diode will be lower than its rated voltage.
The LED is linked in series with a voltage supply source, such as a battery. If the voltage supply value is greater than the rated voltage, the circuit cannot be connected without a resistor. As a result, the resistance value of such resistor should be calculated using the formula:
R = (E-VF/IF)
Where,
‘VF’ – Forward voltage of the LED
‘IF’ -Forward current of LED
‘R’ – Resistance of the resistor
‘E’ – Voltage supply
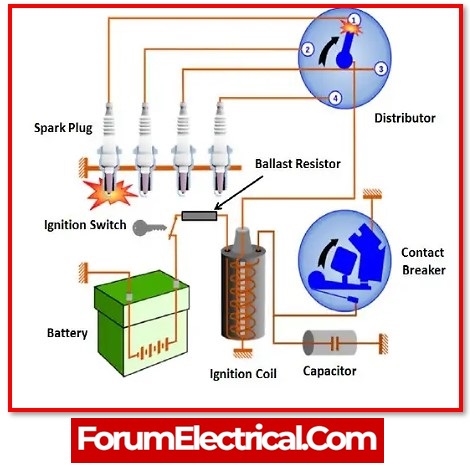
Ballast Resistor for an Ignition Coil
An ignition ballast resistor is a ballast resistor that can be used in an automobile engine’s ignition system. This resistor is typically connected between the ignition coil’s main source and the coil stud. As a result, the coil’s malfunction risk is reduced. The ignition ballast resistor helps to reduce the voltage and current of the coil after the starter motor starts car engine.

As a result, low current can cause a low temperature rise, resulting in the ignition coil’s longevity. The ignition system, on the other hand, requires maximum voltage, which is equivalent to power source voltage. As a result, the jumper wire can be connected (linked) through an ignition ballast resistor. This wire supplies the necessary voltage to the ignition coil when the car engine is started.
Important Aspects of the Ballast Resistor
- Parallel connections with the ballast resistors have the potential to allow output currents to be distributed in a way that corresponds to a value computed using an equation.
- Output currents go through the ballast resistors, which results in a drop in voltage at the load point as well as power losses in the resistors itself.
- There is a tradeoff involved in the difference between the output voltages of the LDO, the distribution of the output current, and the drop in output voltage. Calculating the value of the ballast resistors while ensuring that all other aspects are in balance is required.
How to conduct a Ballast Resistor Test?
Ballast resistors are commonly found in automotive applications. It is used to lower the ignition coil’s voltage level. It is necessary need of an ohmmeter and a multimeter to test the ballast resistor.
If the ballast resistor is not connected to the ignition coil, the ignition coil receives the full supply voltage.
The battery is typically used to power the ignition system. In most cases, the voltage of the battery will be 12V (or) 24V.
Users need to lower the voltage to extend the life of ignition coil. To accomplish this, connect a ballast resistor to the ignition coil.
So, can measure the voltage across ignition coil to test the ballast resistor.
If the ballast resistor is in good condition, it will reduce the voltage level to 7-8V. If the ballast is damaged, the ignition coil’s voltage level will be high.
An ohmmeter can be used to measure the resistance of a ballast resistor. If it is close to the rated resistance, it indicates that ballast resistor is in good condition for operation.
What is Ballast Resistance made of?
Copper windings & iron core transformers are the two primary parts that comprise ballast resistance in most applications. The iron core contributes to a reduction in the effects that are caused by stray magnetic fields, and the copper windings contribute to a barrier to the flow of current.
It is also made by winding enamelled wirearound a silicon steel iron core.
Advantages of Ballast Resistor
- These resistors help in the regulation of voltage and current in an electrical system.
- This resistor helps to protect the equipment against overvoltage and overcurrent.
- These resistors reduce current and voltage differences in the major part of an electric circuit.
Disadvantages of Ballast Resistor
- Using this kind of ballast resistor in lighting system includes with several disadvantages that should be considered.
- It generates a lot of heat when it is connected directly to a power supply.
- This is because of the unpredictable amount of current that is drawn by the lamp when it is turned on.
Applications of Ballast Resistors
- These resistors are primarily used in lighting and automotive applications.
- LED circuits, fluorescent lamps, and automotive applications all make use of these resistors.
- The ballast in the HeNe laser is used to stabilise the laser and limit the tube current. As a result, the typical ballast resistance for most HeNe lasers is around 75 K.
- These are used in low-power devices such as LEDs and neon lamps.
- Because of the low-powered loads, this resistor is mostly used in simple circuits.
- These resistors aid in the regulation of voltage flow in an electrical system, preventing battery drain and overloads.
- This resistor is used in a battery ignition system to change the main current by connecting in series through the primary winding.
- These are used in vapour lamp and laser circuits to compensate for fluctuations in line voltage.
Significant Applications for Ballast Resistor
A ballast resistor controls current and voltage in an electrical system. It helps to protect equipment against overcurrent & overvoltage problems.
The majority of ballast resistors are used in lighting & automotive applications.
What elements affect to the failure of a ballast resistor?
The amount of current flowing through the ballast resistor causes it to change, which in turn causes the resistance of the resistor to change.
As a result of heat, the resistor will undergo a natural process of expansion and compression. Because of this, they will eventually be failed.
What are the symptoms of a bad ballast resistor?
- Engine misfiring,
- Engine stalling,
- Reduction in fuel efficiency, and
- Rough idling
are some of the symptoms associated with a bad ballast resistor.
There is also a possibility that the check engine light may turned ON.