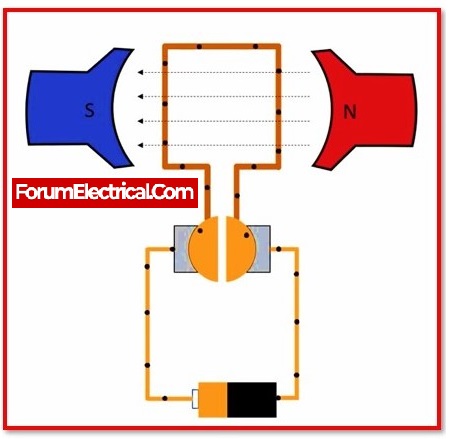
What is DC Motor?
Direct Current Motor or DC Motor transforms electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical loads are driven by the electric motor. It is based on the force acting on a wire carrying a current within a magnetic field. When an electric current is passed through the coil, equal and opposing forces apply on the coil’s opposite arms, causing the coil to rotate. Brush contact maintains coil rotating in the same direction by reversing the direction of the current after each cycle. Electric motor has several applications, including washing machines and electric fans.
The DC motor and DC generator are structurally identical, but electrically opposite. Mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy by the DC generator.
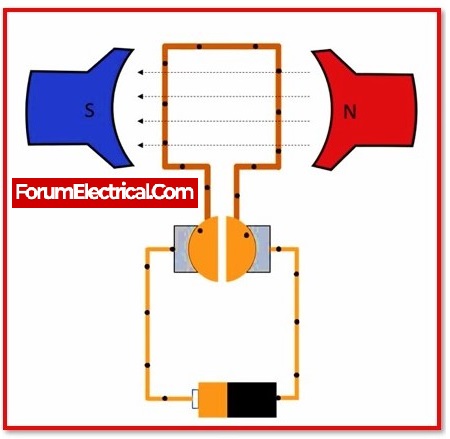
Principle of Operation of a DC Motor:
A motor is an electrical machine that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. When a current-carrying conductor is put in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force, according to the fundamental operating principle of a DC motor. The direction and amplitude of this force are determined by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
F = BIL
Where,
B = magnetic flux density,
I = current and
L = the conductor’s length inside the magnetic field.
“Fleming’s left hand rule: If we stretch the first finger, second finger, and thumb of our left hand so that they are perpendicular to each other, then the first finger represents the direction of the magnetic field, the second finger represents the direction of the current, and the thumb represents the direction of the force experienced by the current-carrying conductor”.
When armature windings are coupled to a DC source, a current develops in the winding. Permanent magnets or field winding (electromagnetism) may be used to generate a magnetic field. According to the above principle, current-carrying armature conductors experience a force due to the magnetic field.
The segmentation of the commutator generates unidirectional torque. Alternatively, the direction of force would reverse whenever the direction of movement of a conductor in a magnetic field is reversed. This is the operation of a DC motor.
Components of a DC Motor:
A DC motor consists of the following components:
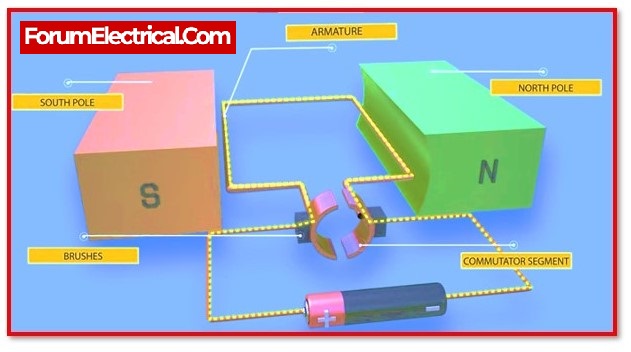
Armature or Rotor:
The armature of a DC motor is an insulated cylinder of magnetic laminations. The armature is perpendicular to the cylinder’s axis. The armature is a rotating component that revolves on its axis and is separated by an air gap from the field coil.
Field Coil or Stator:
A DC motor’s field coil is a stationary component on which a magnetic field is produced by windings. Between its poles, this electromagnet contains a cylindrical hollow.
Brushes and the Commutator:
Commutator:
The commutator of a DC motor is a cylindrical device composed of copper segments that are stacked and insulated with mica. A commutator’s primary duty is to supply electrical current to the armature winding.
Brushes:
The structure of a DC motor’s brushes is composed of graphite and carbon. These brushes conduct current from the external circuit to the commutator when it is revolving. Therefore, the commutator and brush components are capable of transmitting power from the static electrical circuit to the mechanically revolving rotor.
Types of DC Motor:
The various types of DC motors are as follows:
- Series DC Motor,
- Shunt DC Motor,
- Compound Motor,
- Separately Excited DC Motor,
- Permanent Magnet DC Motor and
- Brushless DC Motor.
Advantages of DC Motor:
- When it comes to starting and speed regulation, brushed DC motors work admirably.
- DC motors have a rather high torque density.
- A Direct Current motor operates smoothly and has a broad range of speed regulation.
- Overload capacity is high and electromagnetic interference is minimal.
Disadvantages of DC Motor:
- The construction of the DC motor is a drawback.
- The contact between the commutator and the brush is sliding. This generates mechanical wear and sparks.
- Direct Current motors have a very limited life span and high maintenance costs.
- It also raises problems about dependability.
Applications of DC Motor:
Applications for DC motors include:
- Elevators,
- Steel mills,
- Rolling mills,
- Locomotives, and
- Excavators.
Some Useful Questions related to DC motor:
1.When should a DC motor be used instead of an AC motor?
- When precise control is required, DC motors provide a wide range of speed control options. As a result, DC motors are used in industrial machinery that requires high precision.
- When starting, stopping, and reversing their spin direction, DC motors have exceptional reaction characteristics.
- The energy stored in electric vehicle batteries is in the form of direct current (DC). As a result, DC motors can be used in electric cars.
2. Why is a direct current motor used?
A strong starting torque is required for many applications. The D.C. motor has a high torque vs. speed characteristic by construction, allowing it to manage with large resistive torques and absorb rapid increases in load with ease; the motor speed adapts to the load.
3. Why is DC not employed in homes?
Transformers make it easier to convert alternating current from low voltage to high voltage or vice versa than direct current, which cannot be simply stepped up or down. In DC rather than AC, there is a higher risk of electrolytic corrosion.