What is meant by the term ’Frequency’?
The frequency is the number of times that the alternating current (AC) flips between positive and negative in one second. This switching is non-existent in direct currents (DC).The number of complete cycles that occur in one second is the frequency of an alternating current sine wave. The pace at which an electric current reverses its flow is referred to as its frequency. Hertz (Hz), an international unit of measurement in which 1 hertz is equivalent to 1 cycle per second, is the unit that is used to measure it.
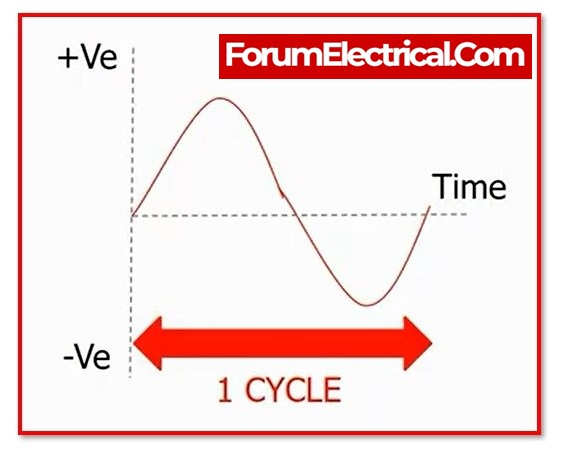
- One cycle in one second is equivalent to one hertz, which is denoted by the symbol “Hz.”
- One complete wave of an alternating current or voltage is referred to as a cycle.
- One half of a cycle is represented by an alternation.
Many types of circuits and machinery are designed to function at a predetermined frequency. When used beyond its specified operating frequency range, equipment with a frequency dependence exhibits abnormality.
How can frequency be measured?
A digital multimeter with a frequency counter mode may measure the frequency of ac signals and may furthermore provide the following:
- MAX/MIN recording, which enables frequency measurements to be recorded over a set time period or in the same manner as voltage, current, or resistance measurements.
- Auto-range, which automatically picks the frequency range, unless the recorded voltage falls outside of the frequency measuring range.
Typically, frequency is used to describe the operation of electrical equipment. The following are popular frequency ranges:
- Power transmission frequency (normally 50 Hz or 60 Hz).
- Typically, variable-frequency drives employ a 1-20 kilohertz (kHz) carrier frequency.
- Auditory frequency range: 15 Hz to 20 kHz (the range of human hearing).
- Radio frequency: 30-300 kHz.
- Low frequency: between 300 kHz and 3 MHz (MHz).
- Medium frequency: 3-30 MHz.
- Extremely high frequency: 30-300 MHz.
Variation in frequency per country:
Regional variations in frequency include
- 60 Hz in the United States,
- 50 Hz in the United Kingdom and Germany, and
- 60 Hz in South Korea.
Typically, each country employs a single frequency.
What makes frequency such a significant factor?
In the fields of science and engineering, frequency is an essential characteristic that is used to characterise the temporal rate of change observed in oscillatory and periodic phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, acoustic signals (sound), radio waves, and electromagnetic radiation.
What is the nature of frequency in AC and DC?
- The frequency of alternating current (AC) varies by country. However, the frequency is usually 50 or 60 hertz.
- DC has zero or no frequency.









