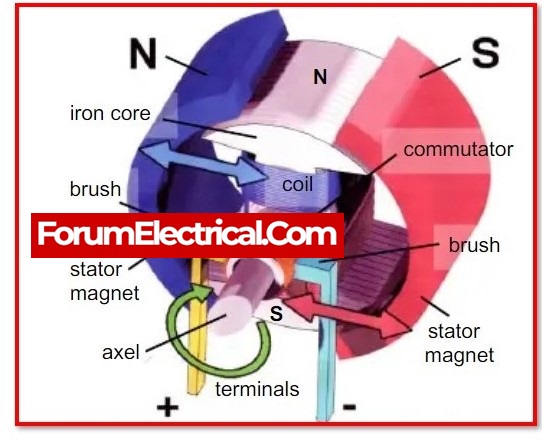
What is Electric Motor?
An electric motoris a mechanism that uses electricity to generate mechanical motion. Typically, a motor’s magnetic field and the electric current in a wire winding work together to create motion. According to Faraday’s Law, this interaction exerts a force on the motor’s shaft in the form of torque.
Electric motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy through the mutual attraction of the magnetic fields generated by the stator and rotor windings.
Electric motors are used for a wide variety of applications, the most common of which include blowers, fans, machine tools, turbines, pumps, power tools, compressors etc.
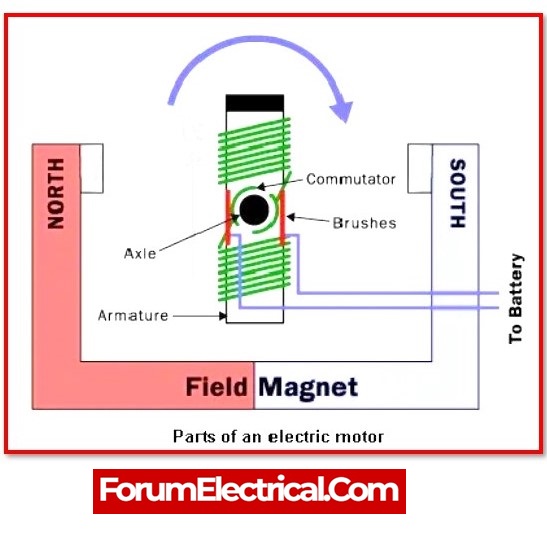
- Stator (which contains the stationary windings),
- Rotor (which contains the spinning windings),
- Bearings, and
- Frame or enclosure
are the four main working parts of any electric motor.
Types of Electric Motor:
In general, industrial electric motors can be divided into three distinct types:
- AC Motors (AC sources like inverters, generators, or a power grid),
- DC motors (Batteries or rectifiers can power DC electric motors), and
- Special type motors.

Operation of an electric motor:
The operation of an electric motor is based on the principle that an electric current will cause a coil to rotate if the coil is placed in a magnetic field and the current is allowed to pass through it.
Electric motors are designed to convert the electrical power (either AC or DC) they receive into mechanical power, in order to generate motion. The interplay of a winding current, either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC), and a magnetic field results in the production of force within a motor. The intensity of the magnetic field increases in parallel with the rising strength of the current flow.
By Ohm’s rule, which states that
V = I x R
the voltage should increase in order to keep the current from changing when the resistance increases.

What are the primary advantages of electric motors?
Electric motors are able to convert nearly all of the energy from their source into useable power. Less than 20% of fuel is utilised effectively by the internal combustion engine (ICE). With an electric car, the costs of maintenance, including the cost of fuel, are significantly reduced. There is no requirement for tune-ups or oil changes to be performed.
Aspects to Consider When Selecting Electric Motors:
Consider the following factors while selecting electric motors:
- Voltage,
- Frequency,
- Torque,
- Power,
- Duty Cycle and
- Life Cycle.
Voltage:
For industrial application, the voltage standard may be 230VAC or higher if a power connection is available or battery capacity for DC source.
Frequency:
Motors operate at 60Hz for components used in the United States, however if a product will be used outside of the United States, a 50Hz option should be considered. If changeable or accurate speeds are required, motor control may need to be improved.
Torque:
The absolute maximum amount of torque that a load demand must be taken into consideration.
Power:
It is necessary to determine whether the motor will be operating at its maximum power before providing specifications.
Duty Cycle:
It’s important to know a motor’s duty cycle. If the application will run constantly so the motor reaches full operating temperature or in short spans to cool down entirely between cycles. Small motors with the same torque and speed can be used in discontinuous motors.
Life Cycle:
Universal and DC motors are occasionally used in applications where the work is done in short intervals. However, they have a short life cycle and need a lot of maintenance.
Applications that run all the time and are not required to be maintained for a long time may need a brushless DC motor or an AC motor with a very long life.
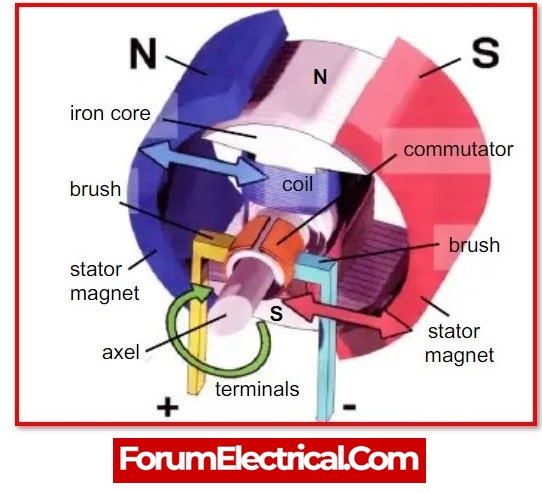
Advantages of Electric Motor:
- Electric motors, in comparison to fossil fuel engines, have lower initial costs; although, their horsepower ratings are comparable to one another.
- Because they have moving parts, electric motors have a longer lifespan than other types of motors.
- When electric motors are maintained correctly, their capability can last for up to 30,000 hours.
- Electric motors are incredibly efficient, and their automatic controls allow for functions such as automatic stopping and starting.
- They are safe for the environment since the contaminants they produce are eliminated.
Disadvantages of Electric Motor:
- The movement of large electric motors can be challenging, and careful attention must be paid to the precise current and voltage supply.
- In other circumstances, costly line expansions are required to be carried out in remote areas where there is no access to electrical power.
- It is possible that the cost of labour will be higher per hour when a motor with a high horsepower rating and a low load factor is used.
Applications of Electric Motor:
- Electric motors are used for a wide variety of applications, the most common of which include blowers, fans, machine tools, turbines, pumps, power tools, compressors, alternators, rolling mills, movers, ships, and paper mills.
- Other applications include fans, blowers, machine tools, and turbines.
- The electric motor is a device that is essential in many different applications, including high voltage AC heating, cooling, and ventilation equipment, motor vehicles, and home appliances.
Guidelines for the Safe Operation of Electric Motors:
- The working environment needs to be maintained spotless and well-lit at all times.
- Because there are so many tiny parts in every motor, it is imperative that young children be kept away from the workspace.
- Because of the high rotational speed of the motors, personal protective equipment is required at all times.
- Motor should not be left unattended.
- It is imperative that the operating voltage not be exceeded. Overheating and fires are two potential consequences of high voltages.
- Motors can only be operated by trained and authorised people.
Mechanical energy is created from electrical energy in electric motors. Most of them generate torque on the motor shaft by combining the magnetic field of the motor with the current through a wrapped wire. The rotor and stator are the heart and soul of any motor. Electricity can be supplied either in the form of direct current or alternating current. Induction motors, servo motors, three-phase motors, and industrial motors are only a few of the varieties available in the field of electric propulsion.