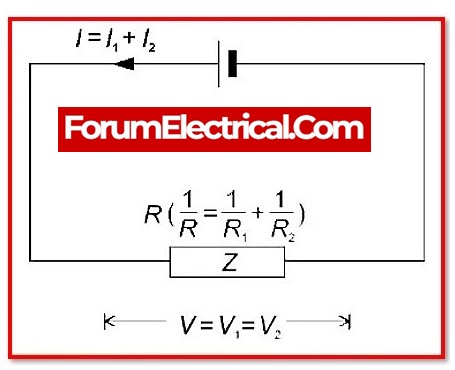
Parallel Circuit:
A parallel circuit is one that has multiple paths for the electric current to travel through. A steady voltage will exist along the entire length of the parallel circuit components.
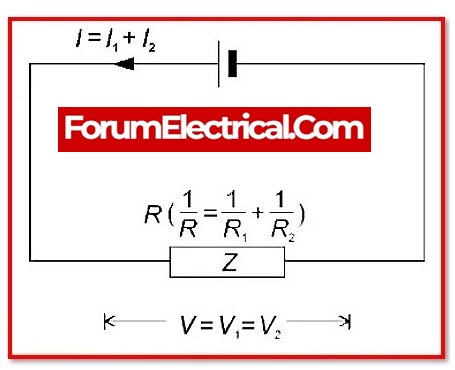
In parallel circuits, branching is used to divide the current and restrict the amount of current flowing through each branch. The currents in a parallel circuit may vary, but the voltage, or potential difference, across each branch remains constant.
Parallel circuits have the following three crucial properties:
- Voltage,
- Current, and
- Resistance.
1. Voltage: Every component in a parallel circuit has the same voltage.
2. Current: The sum of the various branch currents equals the total circuit current.
3. Resistance: In a parallel circuit, the overall resistance is lower than the resistances of the several branches.
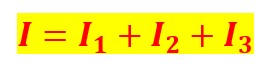
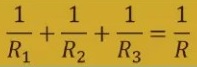
Characteristics of a parallel circuit:
1. Parallel circuits use branches to enable numerous directions of current flow via the circuit.
2. A battery or voltage source’s positive and negative ends both experience current flow.
3. The voltage is constant throughout the circuit, but the current varies according to the resistance of each branch.
4. In series-parallel circuits, the circuit can be handled as both a series and a parallel circuit.