According to the International System of Units, power is measured in kVA and kW.
The unit of measurement for apparent power is kilovolt-amps, or kVA, whereas the unit of measurement for real power is kilowatts, or kW.
KW and kVA have a proportional relationship.
The ‘real power’ of an electrical system is measured in kW. This shows you the amount of power being converted into a working, effective output.
On the other end, kVA represents the percentage of “apparent” power.
If kW is the maximum force you can use, then kVA shows you how much is typically used.
In the rare occurrence that an electrical system had exceptional output, kW would be equal to kVA.
Kilowatt (kW)
The term “kilowatt” describes the actual power that is transformed into an output that is utilized.
As a result, working power or actual power are other names for kW. Voltage and current are multiplied to determine kW. Kilowatts (kW) can be expressed in a number of ways.
- 1kW = 1000W
The energy consumption of 1000 joules for one second is equivalent to one kilowatt:
- 1000J /1s = 1kW
1000000 milliwatts is equal to one kilowatt:
- 1kW = 1000000mW
The power consumption of an electric appliance is measured in kilowatts (kW). It is discovered to be equal to 1,000 watts (1000 W) of electrical power.
Kilovolt-Ampere (KVA)
The unit of measurement for a machine’s apparent power consumption is Kilovolt-Ampere.
A kVA is just 1000 VA. An amp represents the electrical current in this case, while a volt is the electrical pressure.
Thus, the product of a volt & an ampere is what is referred to as perceived power.
Although kVA is frequently regarded as unnecessary information because it relates to visible power, it is also essential in determining whether the system has the wire capacity to support the additional current even if the machine is not in use. In order to determine whether a generator can manage the additional current required for reactive loads, it is common for them to display their kVA rating.
Power Factor (PF)
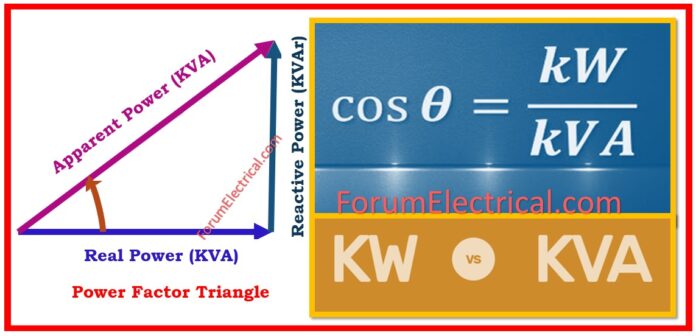
The power factor (PF) that measures how effectively the current is being transformed into productive work, establishes the connection between kW and kVA.
The definition of Power Factor (PF), which ranges from 0 to 1, is as follows:
Power Factor (PF) = kW / kVA
KW = KVA × PF
Where
The unit used to measure actual power is kW.
The unit used to measure apparent power is kVA.
The Power Factor is PF.
A power factor of 1 (100%) indicates that all of the power – in this case, kW = kVA is being used efficiently as real power. kW will be less than kVA if power factor is less than 1, as some of the power is discarded as reactive power.
If you know how efficient your electrical system is, you can convert from kVA to kW.
Electrical efficiency is measured as a power factor ranging from 0 to 1: depending on how close the power factor is to 1, greater efficiently the kVA is transformed into useable kW. A generator has a power factor of 0.8.
KW and KVA in relation to AC & DC circuits
From alternating current (AC) circuits to direct current (DC) circuits, the relationship between kVA and kW changes, as does the power of AC and DC. It can be expressed numerically as follows:
| Condition | Power Factor | Formula |
| AC Circuit | Power Factor (PF) >1 | KW = KVA × PF |
| DC Circuit | Power Factor (PF) <1 | KW = KVA |
KVA to KW Calculation
In electrical, both kVA and kW power units are essential for resolving a number of problems The formula for converting kVA to kW is as follows:
KVA = KW/PF
Calculator: Click here for KVA TO KW Calculator
KW to KVA Calculation
The following formula can be used to convert kW to kVA:
KW = KVA × PF
Calculator: Click here for KW to KVA Calculator
I hope you now understand how kW and kVA of electric current relate to direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) circuits.
Difference between KW and KVA
KW vs KVA
| KW | KVA |
| Kilowatts is the full term of KW. | KVA stands for kilovolt amperes |
| Actual power is represented in KW. | The representation for apparent power is KVA. |
| In AC circuits, the two powers are different. | In DC circuits, both powers are equivalent. |
| The real power that performs actual work is shown by KW. | While the remaining power is considered to be excess current, a kVA fraction can be utilized to perform work. |
| KW = KVA X PF | KVA = KW/PF |
| Utilized to mention power rating of devices. | Utilized for transformers, generators, & UPS systems |
Points to Remember
- Power measuring units include both kVA and kW.
- The term kVA, or kilovolt ampere, simply means 1000 VA. It relates to the apparent power of the system.
- The term kW (kilowatt) refers to the amount of electricity that has been turned into useful power.
- The power factor is ratio of real power absorbed to apparent power flowing through the circuit. It demonstrates how efficient the system works.
- The power factor varies from 0 to 1, with 1 representing the most efficiency system.
- The formula for converting kW to kVA is kW = kVA x PF.
- In the condition of DC current, there is no distinction between kW & kVA, however in the case of AC current, kVA and kW differ depending on the power factor.
- Kilovolt ampere (KVA) is always greater than kilowatt (KW).