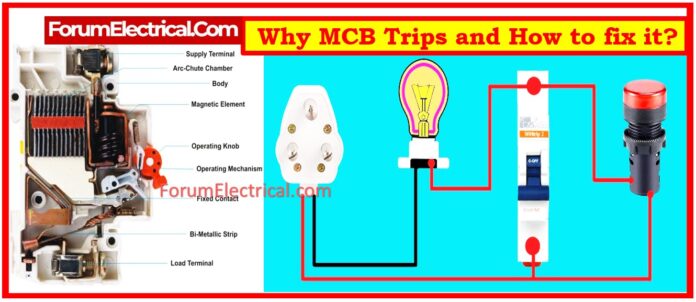
- What is MCB?
- Common Causes of MCB Tripping
- 1). Overloading
- 2). Short Circuit
- 3). Ground Fault
- 4). Fault (or) Aging MCB
- How to avoid MCB Tripping?
- 1). Distribute Electrical Load
- 2). Regular Maintenance
- 3). Upgrade Wiring & Components
- 4). Install Surge Protection
- 5). Educate Users
- Advantages of Selecting a High-Quality MCB
- How to avoid MCB Tripping?
- Conclusion
MCBs are important parts of electrical systems that protect against overload and short circuits.
The apparently regular interruption in form of MCB tripping is extremely inconvenient and might lead to further troubles with the electrical system.
This post discusses at the most prevalent causes of MCB tripping, as well as diagnostic techniques and preventative actions.
What is MCB?
An automatic switch known as a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) opens when the circuit experiences an excessive amount of current.
It doesn’t require a manual replacement to be reclosed.
The type of MCB will determine whether a fuse needs to be changed or rewired after it has been operated. Fuse is hence referred to be one of disposable devices.
This is the primary reason for using MCBs in most circuits instead of fuses. Additionally, the MCB’s switches immediately cut off when there is a circuit failure, making it simple to identify the device’s fault.
Common Causes of MCB Tripping
Some MCB tripping causes are listed below:
1). Overloading
2). Short Circuit
3). Ground Fault
4). Fault (or) Aging MCB
1). Overloading
The most fundamental reason for MCB trips is circuit overload. This happens if the flow of electric current exceeds the MCB’s capability.
Ex: Putting a lot of high-power appliances on the same circuit, such as air conditioners, pumps, and televisions, can cause the MCB to trip. Make sure the MCB is as enormous as the load size to prevent overloading.
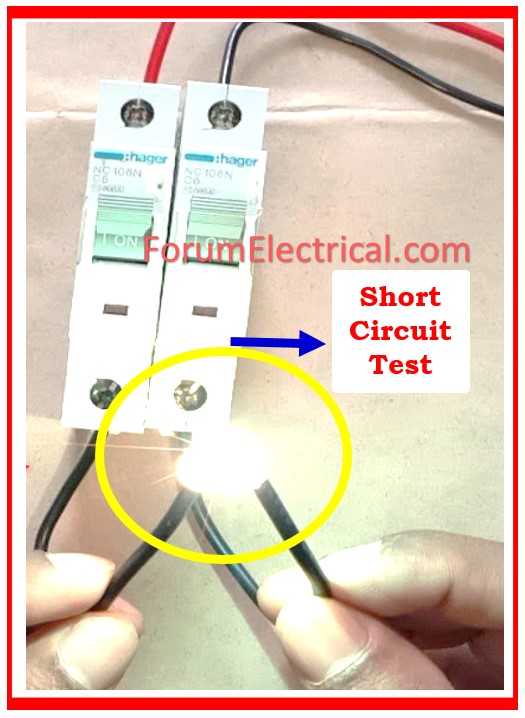
2). Short Circuit
Short circuits are major common cause of tripped MCBs. When current flows directly via the earth (or) a live wire, it generates a surge in current. This excessively large surge can exceed the MCB’s trait limit, necessitating an immediate disconnection to avoid additional failure.
Solution
Inspect Wiring: Examine the cables on a regular basis to ensure that they are not damaged.
Replacement: Replace faulty devices. Replace any faulty units that might trigger a short circuit.
3). Ground Fault
A ground fault, like a short circuit, occurs when a live wire contacts the grounded section of an appliance or building structure, allowing current to flow to ground. In this case, the abrupt rise in current speed causes the MCB to trip.
Isolate Fault Devices: Unplug any device that is suspected of causing ground faults.
Solution
Install ELCB or RCCB: The introduction of Earth Leakage (or) Residual Current Circuit (RCB) Breakers has made it simple to identify any ground fault and shut off the circuit.
4). Fault (or) Aging MCB
The fault could be with the MCB itself. Long-term use or tension can damage elements such as batteries and tiny electronics, resulting in sensitivity concerns. Even under typical load circumstances, an outdated or faulty MCB might trip.
Solution
Recurring MCB trips need to be addressed. You can avoid the possibility in the shortest possible time by having a skilled electrician repair and inspect it on a regular basis.
This will ensure the safety and efficiency of the electrical system.
How to avoid MCB Tripping?
Preventive activities can reduce the likelihood of MCB failure, resulting in more reliable electrical system performance and reduced downtime or machine damage.
Here are a few options that you can try.
1). Distribute Electrical Load
Provide electrical appliances equally across multiple circuits to guarantee that no circuit is gets overloaded. Heavy watts appliances need to be connected to single circuits,
- Extension cords, and
- Power strips.
Single circuits is used to make sure relatively uncongested circuits, preventing undesired short-circuiting or overloading.
2). Regular Maintenance
Periodical inspections & monitoring of electrical system, which includes wiring, connections, and appliances, should help to prevent electrical fires.
- Short circuits,
- Accidents, &
- Ground faults
can all be avoided if damaged components or parts are repaired promptly.
3). Upgrade Wiring & Components
A great alternative would be to switch internal wiring, whether outdated (or)
- Inadequate switches,
- Sockets, &
- MCBs,
to meet modern safety standards while also catering to the electrical demands of current appliances.
4). Install Surge Protection
Installing a surge protection device (SPD) at the main distribution panel (MDP) (or) specific circuitry protects against lightning strikes and voltage surges in the circuit.
Install ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs). Installing GFCIs in moisture-prone areas, which include the kitchen, bathroom, & outdoor outlets, will protect against the risk of electrical shock.
Devices put within GFCIS also increase equipment life and reduce the danger of receiving a shock.
5). Educate Users
Inform the other members of the house on electrical safety, such as how to utilize the appliances correctly, the dangers of overloading the circuits, and the importance of being aware of unusual electrical difficulties.
Advantages of Selecting a High-Quality MCB
Typically, when the MCB trips frequently, the fault should be repaired promptly. On identical observation, arc faults cause MCB trips. Purchasing a low-cost MCB will not sufficient.
Make sure you buy an adequate MCB to successfully secure your linked devices.
Here are a few reasons why purchasing a high quality MCB is necessary:
- The best type of MCB is built of rivet body material and can withstand the arc energy created when an electrical current is disrupted. It is a powerful devices to employ in the case of an accident, fire, (or) any other form of hazard. This mitigates the risk and safeguards the MCB.
- High-quality MCBs are constructed with larger coil diameters to prevent temperature increases, which, in the long term, allow for lengthy circuit closure.
- MCBs can detect better contact substances that react fast in the event of a power failure. This improves process efficiency and prevents component failure.
- A perfect identified MCB is designed to trip instantly in the event of an overload, ensuring the circuit and its attached equipment remain safe.
- Good quality MCBs include high-grade bi-metal strips that touch the breaker immediately during short circuits, interrupting the stock right away.
How to avoid MCB Tripping?
- Avoid utilizing several plugs or extension cords.
- Replace all broken or damaged wires on electrical equipment and appliances.
- Ensure that all electrical appliances and equipment are unplugged whenever they are not being used.
- Must keep track of the total number of devices in use in both hot & cold weather.
Conclusion
Maintaining a secure and effective electrical system requires knowing why and how to fix your MCB.
This post helps you diagnose and fix typical MCB trip issues. Maintenance, load distribution, and trusted brands like Siemens & Schneider MCBs can prevent potential challenges.
After following these methods, a professional electrician may be needed if problems occur.
Electrical systems that are dependable are essential to the security and efficiency of your home or place of work.
Regular maintenance will keep the electrical systems functioning properly, reducing MCB trips.