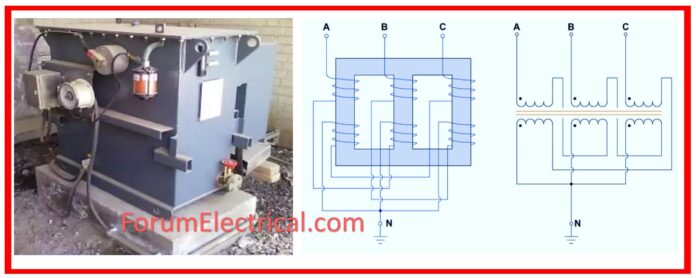
What is ZigZag Transformer?
A zig-zag transformer is utilized to provide grounding for the transformer. It provides insulation across the ground & the component, ensuring that the system component is not impacted by fault currents.
The zigzag transformer terminates the electricity system’s harmonics. It also protects the electricity system by minimizing voltage stress during a fault.
A Y-Y (Star-Star Connection) transformer connection is the most cost-effective and easy.
However, this connection has the disadvantage of reflecting an earth fault from the secondary to the primary.
Similarly, in
- Delta Delta connection
- Star Delta connection
delta winding isolates the earth fault but has several disadvantages.
A zig-zag winding connection can provide a great alternative by combining the advantages of both star & delta connections.
Construction of Zig-Zag Transformer
A secondary winding is not present in the zig-zag transformer structure. It is a transformer that has three limbs, often known as branches. Every single limbed has two windings that are exactly the same.

The neutral point is provided by a single set of windings that are connected in the star connection.
The other ends of this winding set are connected to the second winding set. Both of the windings on each limb are set up in such a way that the direction of current flows in the opposite direction.
Zig-Zag Transformer Winding Connections
The Zig Zag transformer has a unique arrangement of six coils:
- Three Outer Coils (ZIG windings) &
- Three Inside Coils (ZAG windings).
The interconnected star winding design connects the outer coil of one phase to the inner coil of the neighboring phase, creating a series connection between them.
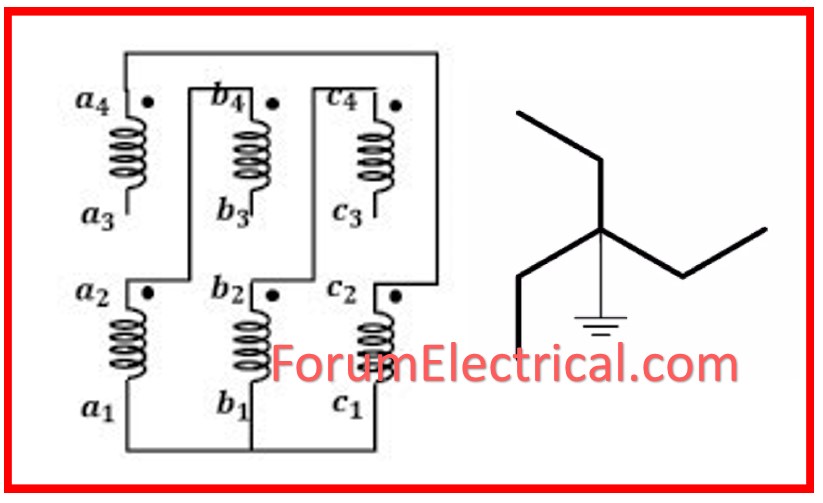
This interconnected star winding assists to cancel out mismatch voltages since the windings in each phase have the same number of turns but are wound in different directions.
The inner coil terminals are connected to the neutral terminal, which allows zero sequence current components to pass over.
Specifically, the outer coil of phase ‘a’ is connected to the inner coil of phase ‘b’, the outer coil of phase ‘b’ is connected to the inner coil of phase ‘c’, & the outer coil of phase ‘c’ connects to the inner coil of phase ‘a’..
This hookup causes a 30-degree phase shift across the zag winding and the line-to-neutral voltage.
Notably, the Zig Zag transformer requires around 15.47% more turns than conventional transformers to attain the same voltage magnitudes.
While this design works well for some applications, it is more expensive because of the greater number of turns.
Working of Zig-Zag Transformer
Under typical operating conditions, the total flux in every limb is negligibly low. As a result, the transformer draws a small amount of magnetizing current. Under fault conditions, the grounding transformer’s impedance is extremely low.
To reduce the fault current, put a resistor in series with the neutral grounding. It is intended for a short-term kVA rating and can carry the rated current for only 10 seconds.
A zig zag secondary with the neutral solidly earthed provides an appropriate option, especially when the impedance requirement is high, because the zig zag transformer has a higher impedance due to its construction.
Advantages of Zig-Zag Transformer
- In ungrounded systems, Zig-Zag transformers create a neutral point for steady grounding and safer operation.
- In systems with nonlinear loads, they reduce triplen (3rd, 9th, etc.) harmonic currents, enhancing power quality.
- Zig-Zag transformers are cheaper than other grounding transformers due to their simpler design & smaller size.
- The Zig-Zag transformer can balance imbalanced loads across phases, decreasing equipment strain and improving system performance.
- Controlled zero-sequence current paths limit fault current in line-to-ground faults, enhancing safety.
- Their compact and efficient design makes them perfect for space-constrained installations.
- Zig-Zag transformers are more reliable and require less maintenance due to their simpler design and fewer windings.
- They can be used for industrial power distribution, grounding, & neutral formation in low- and medium-voltage systems.
- Zig-Zag transformers may offer neutral grounding without a load, increasing its versatility.
- They lower zero-sequence impedance, minimizing voltage drops during unbalanced load conditions.
Disadvantages of Zig-Zag Transformer
- Zig-Zag transformers are employed for neutral grounding (or) phase shifting and cannot handle large power loads, hence they are limited to low- to medium-voltage applications.
- Its zig-zag winding pattern makes it more expensive to manufacture & maintain than simpler transformer designs.
- Zig-Zag transformers may have voltage control issues, especially under unbalanced loads, impacting system stability.
- Due to their specialization in grounding or harmonic mitigation, these transformers are not suitable for ordinary transformer functions.
- Zig-zag transformers are more expensive to buy and maintain due to their unique design.
- Zig-Zag transformers are not suitable for heavy-duty or industrial applications with high fault current levels.
- Zig-zag transformers reduce third harmonics but can cause higher-order harmonic distortions.
- Zig-Zag transformers are harder to find and more expensive to repair or replace.
- Due to its configuration, zig-zag transformers have higher core losses, reducing energy efficiency.
- These transformers cannot sustain prolonged overloads, making them less robust in high-demand applications.
Application OF Zig Zag Transformer
Grounding Transformer
Power systems use zig zag transformers as grounding transformers to carry zero-sequence currents during imbalanced or fault cases.
Zig Zag transformers keep system stability and equipment safe by deflecting these electrical currents away from the primary windings.
In distribution systems that need a reliable grounding solution, their ground fault tolerance makes them essential.
Power Electronic Converters
Zig Zag transformers improve performance and eliminate harmonic distortions.
Their unique configuration reduces harmonics, improving power quality.
Zig Zag transformers improve power electronic converter efficiency and dependability in variable speed drives, renewable energy systems, & other electronic power control systems by giving a more steady and balanced output.
Earthing Reference (or) Earthing Transformer
Zig Zag transformers are used as earthing references or transformers in power systems that need a clear earth reference.
Zig Zag transformers stabilize system earthing by connecting the inner coil terminals to the neutral & grounding the outer coil.
This is necessary to prevent floating grounds and ensure power system stability.
Zig Zag transformers help maintain a steady potential and reduce equipment damage from electrical failures.