What is UPS?
UPS – Uninterrupted Power Supply
A UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, is a device designed to provide continuous power to critical loads that must operate without interruption. Even during a power outage, the UPS system continues to operate, suppressing line transients and harmonic distortions in the power supply.
It protects the instrument and equipment and prevents the plant from shutting down.
Many instruments require a safe shutdown to function properly; otherwise, a sudden power outage can destroy the equipment.
Other names for UPS include uninterruptible power source, battery backup, and flywheel backup. The size of UPS units available varies from 200 VA for a single computer to progressively significant units up to 46 MVA.
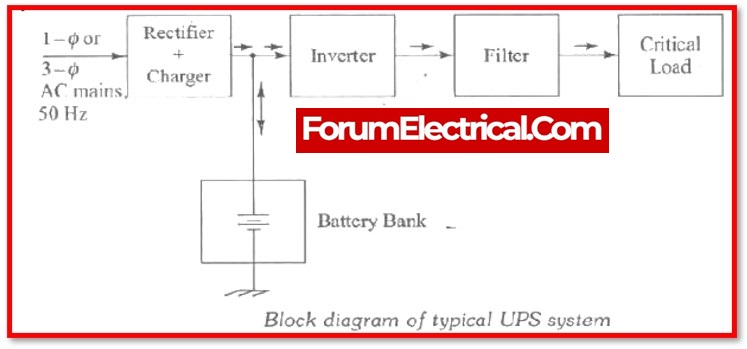
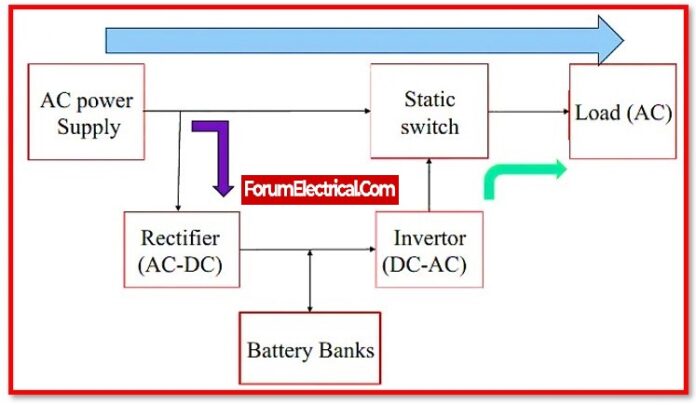
Components of UPS
UPS’s basic components are as follows:
- Rectifier – conversion of AC to DC for feeding batteries,
- Inverter – conversion of DC to AC for feeding load,
- Battery – to supply DC power to the inverter, and
- Semiconductor switch is used to switch load transfer between the mains AC supply and the inverter supply.
1). Rectifier
The Rectifier’s function is to convert alternating power to direct current using a 6- or 12-pulse thyristor to supply both the battery and the inverter. The main current distortion is roughly half that of a 6-pulse thyristor rectifier when employing a 12-pulse thyristor rectifier.
2). Inverter
By implementing an IGBT – pulse width modulated (PWM) inverter module, the inverter is able to perform the task of converting DC current to AC current.
3). Battery
In the condition that there is a disruption to the power supplied by the mains, the battery pack that is included within this module will be used to power the UPS module. There are many distinct categories of batteries, including SMFB, LATB, NI-CD, and others.
4). Semiconductor Switch
When a semiconductor switch is in the UPS state, it is powered by either mains or battery power and connects the inverter output to the load. In the event of a heavy inrush or an inverter fault, the semiconductor switch quickly switches the load back to bypass. This is a significant consideration, particularly for critical loads where even a 5-10 ms switchover time from bypass to inverter can be critical.
The semiconductor switch has the advantage of transferring data in less than four milliseconds.
Features of UPS
- The output of a regulated sinusoidal with total harmonic distortion (TDH) is independent of changes in load or input voltage, whether linear or nonlinear, balanced or unbalanced.
- It should be highly reliable and require little maintenance.
- Low TDH sinusoidal input current and power factor of unity (PF).
- Low cost, high efficiency.
- Weight and size are reduced.
- Low noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Mains supply frequency instabilities can be minimized.
The working principle of UPS differs depending on the type.
UPS System output waveforms
UPS systems output have either
- Sine wave or
- Simulated sine wave output
depending on the model.
1). Sine Wave Output
The sine wave, which is a smooth, repeated oscillation of alternating current power, produces the finest quality waveform output. Industry UPS systems generate sine wave power, which is used to power sensitive electronic equipment. When switching from grid power to battery power, sine wave output assures that equipment using Active PFC power supplies does not shut down.
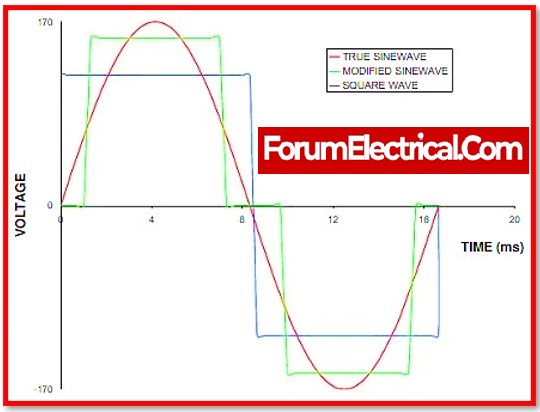
2).Simulated Sine Wave Output
A sine wave output waveform that is approximated. It generates a stepped, approximated sine wave using pulse wave modulation to provide more cost-effective battery backup power for equipment that does not require sine wave output. This sort of simulated sine wave output (power output) technology is less expensive to build and is commonly seen in standby and line interactive UPS systems.
Types of UPS
There are 3 different types of UPS as follows
- Online UPS
- Offline UPS and
- Line-Interactive UPS
1). Online UPS
Online UPSs are used to ensure continuous power supply. Online UPSs, unlike offline UPSs, do not connect utility power to the outlet. The rectifier-inverter system provides alternating current to the load while simultaneously charging the battery. When there is a break in the operation because its battery is always linked to the inverter through which the load is supplied, online UPSs may deliver uninterruptible power without any transfer delay.
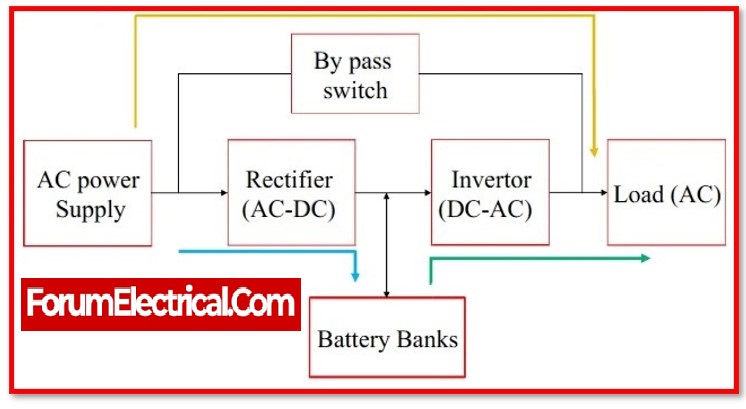
Working Principle of Online UPS
Normally, the semiconductor switch in an online UPS is turned off. It is only used when an overload condition exists or when the associated motor pulls a large inrush current. In this case, the power electronic circuit connected to the semiconductor switch senses the high current and transfers power from the inverter to the main power. This protects the UPS internal hardware from damage.

There would be no transfer time on online UPSs in an online UPS system. Because the rectifier converts the AC input to DC and then back to AC, these are also known as double conversion UPS. In online UPSs, the rectifier must deliver power to both the load and the load’s battery bank. As a result, the rectifier must withstand a higher load, and online UPSs often have substantial heat sinks.
Advantages of the Online UPS
- Because the battery is always linked to the load, an online UPS requires no transfer time.
- Although employed for applications requiring more than 10 kW, online UPSs are now accessible for devices requiring less than 500 W due to remarkable advancements in technology and cost reduction.
- Because the rectifier is intended to handle high power for simultaneous load and load supply, the cost of an online UPS is higher.
Disadvantages of the Online UPS
- The above-described UPS topology has a poor transient responsiveness to load variations.
- The transformer could generate a lot of acoustic noise.
2). Offline UPS
The Offline UPS is so termed because the inverter is positioned outside the main current line, whereas the Stand-By UPS is so called because the inverter is switched off and “waiting” to be activated.
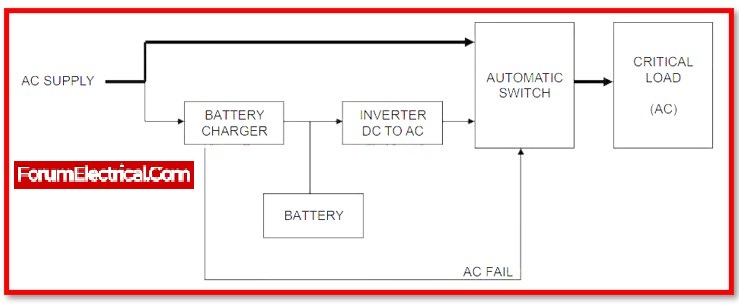
Working Principle of Offline UPS
When main power is connected, the battery bank is not connected (offline to the load). In this condition, the main power is probably connected to the load output via a normally on semiconductor switch. When mains power is available, the backup bank is charged by DC using a charger device that includes a rectifier circuit.
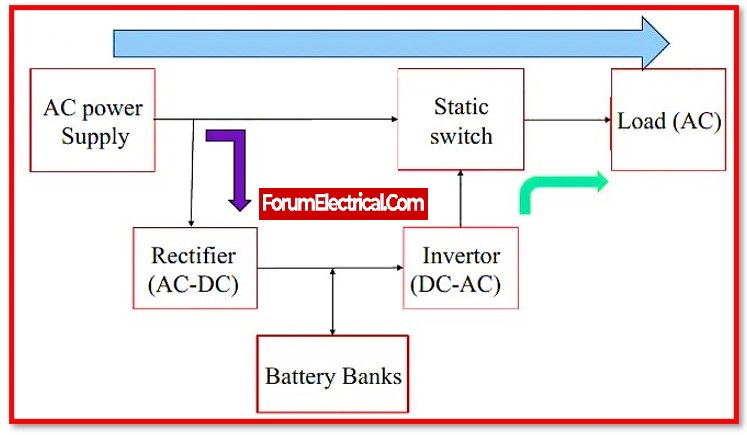
In the event of a power outage or surge, the semiconductor switch quickly disconnects the main power to the load and reconnects the battery to the load. This transfer time from mains to battery is typically 10 to 25 ms and is determined by the semiconductor (or) power electronic circuit that detects the loss of mains power and implements the switching.
Because the utility power is directly connected to the load in normal operation, any distortion including such spikes, sags, and noise on the utility appear at the UPS output. However, some UPS systems do power conditioning on the output.
Advantages of the Offline UPS
- Offline UPSs are the most affordable of all UPS systems due to their simple construction.

Disadvantages of the Offline UPS
- Because switching time is unavoidable with offline UPSs, there is a visible power outage in linked loads. As a result, this form of UPS is employed with loads that can withstand such a brief blackout, such as desktop PCs, printers, emergency lighting circuits, and so on.
3). Line-Interactive UPS
Working Principle of Line-Interactive UPS
Line-interactive UPS’s are a sort of offline UPS that deals with minor overvoltages and undervoltages on the network. They use a multi-tapped autotransformer (or) a boost transformer to convert the input mains voltage to the correct (exact) output voltagewithout requiring a battery switch.

Advantages of the Line-Interactive UPS
- They supply power during a blackout, voltage sag, voltage spike, or over-voltage.
- It does not require any switching time.
Disadvantages of the Line-Interactive UPS
- Usually larger than both offline and online UPS.
- When AC power is inconsistent, battery power is frequently employed.
Applications of UPS
The following are some uses for a UPS:
- Data centers
- Process Industries
- Telecommunications
- Hospitals
- Banking and insurance companies
Difference between Online UPS and Offline UPS
Online UPS Vs Offline UPS
| SL NO | Online UPS | Offline UPS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The UPS provides power from the alternating current mains to the load via the rectifier & inverter combination. | The UPS provides direct AC mains power to the load. |
| 2 | It constantly draws power from the battery. | It only draws power from the battery when the primary source fails or there is a power outage. |
| 3 | Because Online UPS carries the entire load current, it requires the large battery charger circuit. | Since it only charges the battery, it generally requires a small charger circuit. |
| 4 | The input supply & the load is totally isolated. | There is no separation between the power supply and the load. |
| 5 | It provides high-performance output by shielding the output load from the input voltage spikes and distortion. | The input voltage distortion, which is connected directly to the load, reduces its performance. |
| 6 | There is no switching between sources, so there is no time delay. | It switches between its sources with a 5ms time delay using a static transfer switch. |
| 7 | It is almost always turned ON. | It only turns on when the power is cut out. |
| 8 | It is inefficient & unreliable due to its constant ON state. | The system is more efficient & dependable because it is mostly turned off. |
| 9 | It is inefficient & unreliable due to its constant ON state. | The system is more efficient & dependable because it is mostly turned off. |
| 10 | The components used must be able to withstand high temperatures. | There is no requirement for the components to be temperature-tolerant. |
| 11 | It costs more than Offline UPS. | It is less expensive than Online UPS. |
| 12 | It is used for extremely sensitive electronic devices that cannot handle any supply gaps, such as in-hospital ICUs. | It is used for the electronic devices that can withstand a 5ms delay, such as computers. |