The power grid is an important part of the systems for generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity. For all functions of the power grid, electrical substations are necessary. These are essential instruments used in the substations to generate electricity. The quantity of electricity needed in substations to supply electricity to customers can be altered by adjusting the levels of frequency and voltage.
Components of Electrical Substations
Various electrical substation components, such as power transformers, isolators, bus bars, etc., are coupled together at the substation and can be used to carry electrical power from the generation units to distribution. For the substation to be installed, the electrical substation components are necessary.
The following is a summary of the primary functions served by each component of equipment found in substations.
Power Transformer
Current Transformer
Potential Transformer
Conductors
Insulators
Isolators
Bus Bars
Lightening Arresters
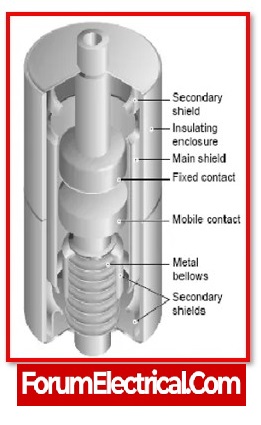
Circuit Breakers
Relays
Capacitor Banks
The design of an electrical substation is a difficult process that requires extensive engineer planning. Switching systems, equipment placement and planning, component selection and ordering, engineer assistance, structural design, electrical layout design, relay protection, & major apparatus ratings are some of the key steps in substation design.
Power Transformer for Electrical Systems
The term “power transformer” refers to a non-moving electrical machine that may move power from one electrical circuit to another electrical circuit while maintaining the primary frequency. The voltage levels of a system can typically be stepped down or up with the use of transformers, which are employed for transmission & generation purposes respectively. These transformers are separated into their respective types according to their construction, the functions they are intended to full-fill, the installation procedures they require, and so on.
Current Transformer
The current transformer is used to measure alternating current through gathering measurements of the system’s higher currents. This allows the current to be accurately measured. These reduced measurements are accurate representations of the system’s actual high currents and are proportioned accordingly. These are utilized in the process of installing and maintaining the current relays that are utilized for protection purposes in substations. These relays typically have low-current ratings for their capacity to work.
Potential Transformer
The potential transformer appears to be identical to the current transformer, but its primary function is to take measurements of high voltages from a system in order to supply low voltage to the relays that are part of the protection system as well as to low-rating meters that are used to monitor voltage. In order to avoid spending money on the measurement equipment, it is possible to compute the actual high voltage of the system based on the measurement of the low voltage. This can be done without actually measuring the high voltages.
Conductors
The term “conductor” refers to any material or object (often composed of metals like aluminium and copper) that satisfies the requirements of the electrical property known as conductance and enables the flow of electric charge.
Conductors are materials that do not restrict the passage of electrons as they go through them. Substations are used to transmit power (or) electrical energy from one location (the generating station) to another location (the consumer point where the power is consumed by the loads), and these are utilized for the transmission.
There are many distinct varieties of conductors, but aluminium conductors are the ones most commonly used in operational power systems.
Insulators
An insulator is a type of metal that does not permit the free movement of electrons (or) electric charge and so has this feature.
Because of its high resistive property, insulators are able to block the flow of electricity.
Insulators can be found in a number of different forms, including
- The suspension type,
- The strain type,
- The stray type,
- The shackle type, and
- The pin type, amongst others.
Isolators
An isolator is a manually controlled mechanical switch that disconnects a damaged section, a segment of a conductor, or a portion of a circuit in a substation that is intended for repair from a component of the system that is operating normally in order to prevent the occurrence of faults that are more severe.
As a result of this, it is also known as a disconnected switch or a switch that disconnects. Isolators come in a wide variety of forms and can serve a variety of purposes.
Some examples include
- The single-break isolator,
- The double-break isolator,
- The bus isolator, and
- The line isolator.
Bus Bars
A bus bar is a type of conductor that is typically found in substations. It is distinguished from other types of conductors by the reason that it carries electricity and has several connections for lines coming in and going out.
These are broken down into a few distinct categories, including
- Single bus,
- Double bus, and
- Ring bus types.
Lightening Arresters
All of the substation equipment, including cables, transformers, and the like, is permanently installed outside.
When a light surge occurs, a high voltage will flow through these electrical components, inflicting damage to them [whether the damage is temporary (or) permanent will depend on how much it is damaged as a result of the voltage surge].
Therefore, in order to get beyond this problem, lightning arresters are positioned so that they direct all of the lightning surges to the ground below. There is another type of arrester known as a surge arrester, and its purpose is to ground switching surges.
Circuit Breakers
The faulty segment is cut off from the healthy section, either manually or automatically, with the purpose of protecting the substation and the components within it from excessive currents or loads that could be caused by a short circuit or another type of malfunction.
If the problem is fixed, the initial circuit can be reconstructed either manually or automatically, depending on the preference. Circuit breakers come in a wide variety of styles, each of which corresponds to a certain set of requirements and applications.
However, the types of circuit breakers that are used the most frequently include
- Oil circuit breakers,
- Air circuit breakers,
- SF6 circuit breakers,
- Vacuum circuit breakers, and so on.
Relays
In order to break the connection between two circuits, either manually or automatically, relays are utilized. The relay consists of a coil that is either stimulated or energized, and it is designed in such a way that when the contacts of the relay are closed, it activates the relay to either break (or) make the circuit connection.
There are many different types of relays, some of which include
- Over current relays,
- Definite time over current relays,
- Voltage relays,
- Auxiliary relays,
- Reclosing relays,
- Solid state relays,
- Directional relays,
- Microcontroller relays, and
- Inverse time over current relays, among others.
Capacitor Banks
A capacitor bank is a collection of numerous capacitors of the same type that are connected in series or parallel inside of an enclosure.
Capacitor banks are utilized for the power factor correction & fundamental protection of substations. These capacitor banks are a source of reactive power, & as a result, they are able to lessen the phase difference that exists between the voltage and the current.
They will boost the capacity of the supply for ripple current. It prevents the power system from exhibiting undesired features. The power factor can be maintained and problems with power lag may be corrected using this methodology, which is also the method that will save the largest amount of money.