Table of Contents
What is the uninterrupted power supply?
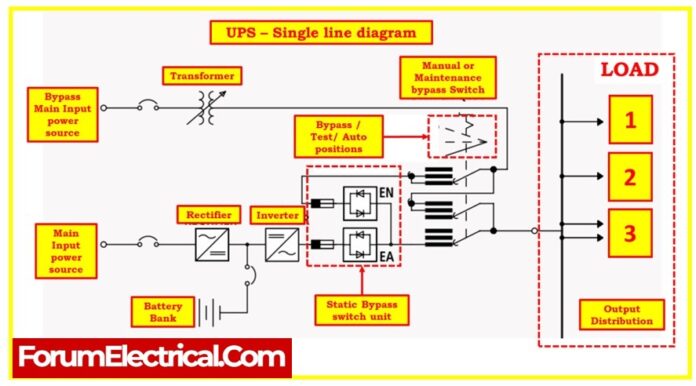
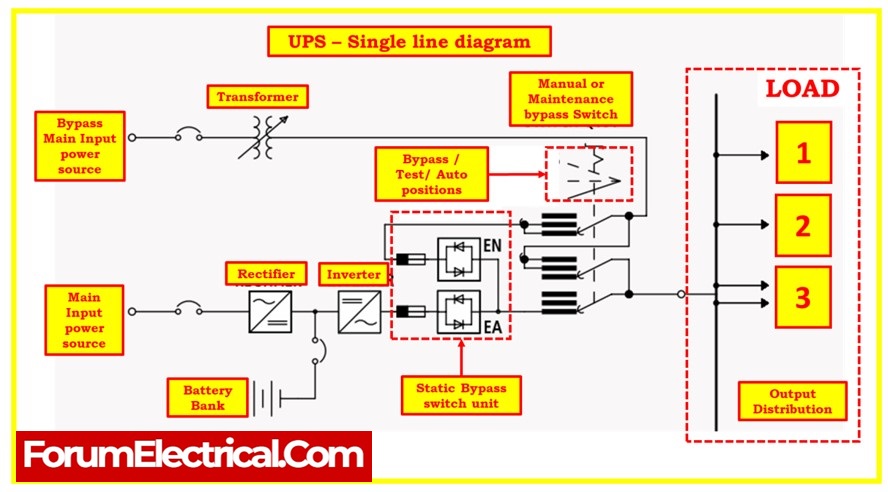
Single line diagram of UPS system
- A device that continues to provide power in the case of a disruption is known as an uninterruptible power supply, or UPS for short.
- A battery is often found in UPSs and is kept charged and ready. The battery provides power during power outages for however long it lasts.
- A UPS may have circuitry that will initiate a controlled shutdown in the event that the battery fails.
- An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) might also be able to provide line regulation, which would guard against voltage fluctuations.
- The most effective remedy for electrical power issues is typically recognized as a UPS, or uninterruptible power supply. It guards against disruptions in the AC Utility supply for the essential AC load, which demands dependable, uninterrupted power.
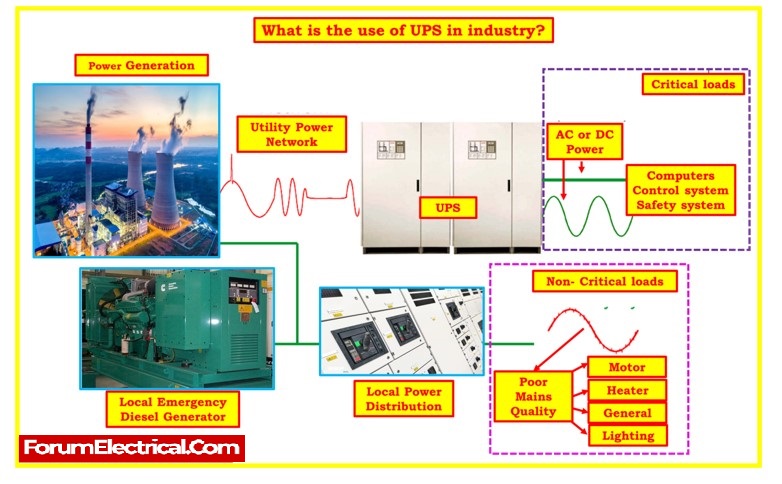
What is the use of UPS in industry?
- Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) in continuous process industries plays a critical role in ensuring the reliable and uninterrupted operation of essential equipment and processes.
- It is a vital component of industrial infrastructure designed to safeguard against power interruptions, voltage fluctuations, and electrical disturbances.
- A UPS system consists of various components, including batteries, inverters, and rectifiers, all working in tandem to provide seamless power backup.
- A UPS is often used to protect electrical equipment including computers, process control system, data centers, telecommunications devices, and other hardware where an unanticipated power outage could result in major business interruption, injury or fatalities, or data loss.
- The subsequent set of utility (Mains) supply-related problems have been resolved by UPS.
- Interruptions can take many different forms, such as temporary interruption, long-term interruption, unexpected interruption, sag or undervoltage, swell or overvoltage, transient, impulse, or spike, notch, noise, and harmonic distortion.
What is the importance of UPS?
1). Reliability:
- Continuous process industries, such as manufacturing plants, chemical refineries, and data centers, rely on uninterrupted power supply to maintain operational integrity.
- Any power disruption, even for a fraction of a second, can lead to significant production losses, safety risks, or data corruption.
2). Voltage Regulation:
- UPS systems are equipped with voltage regulation capabilities, ensuring that connected equipment receives a stable and consistent power supply.
- Fluctuations or surges in voltage can damage sensitive machinery and disrupt processes.
3). Transitional Power:
- In the event of a power outage, UPS systems seamlessly switch to battery power within milliseconds.
- This transitional power allows critical equipment to keep running while backup generators or alternative power sources come online, preventing costly downtime.
4). Data Protection:
- In industries that rely heavily on data processing and storage, like pharmaceuticals or financial services, UPS systems protect against data loss and corruption.
- They provide a buffer period for data center operations to save and back up critical information.
5). Safety:
- In some industries, a sudden loss of power can pose significant safety risks.
- UPS systems ensure that safety systems, such as emergency lighting and ventilation, remain operational during power interruptions.
6). Process Continuity:
- Continuous process industries often involve complex production lines where even a momentary interruption can lead to product defects or production bottlenecks.
- UPS systems maintain process continuity, minimizing waste and ensuring product quality.
7). Cost Savings:
- While UPS systems require an initial investment, they can save substantial money in the long run by preventing losses due to downtime, equipment damage, and process disruptions.
What are the applications of UPS?
The following are some examples of typical applications for a UPS system: –
- Process control and Monitoring systems
- Security systems
- Telecommunication systems
- Health care systems
- Data Centers
- Server farms and personal computers
- pharmaceuticals and laboratory instruments/analyzers etc.