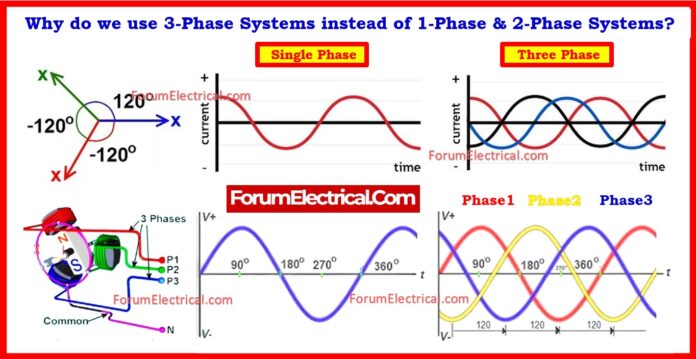
What is a “Phase” in Electrical Systems?
In alternating current (AC) power systems, a phase is a sinusoidal voltage or current wave. The phase concept is essential to understanding how electricity is generated & distributed.
- What is a “Phase” in Electrical Systems?
- Why 3-Phase Systems pre-dominate in Electrical Power Distribution?
- 1). Continuous & Balanced Power Flow
- 2). Superior Motor Performance
- 3). Improved Efficiency in Power Transmission
- Why 2-Phase Systems were Abandoned?
- Understanding 3-Phase Phase Angles
- Advantages of 3-Phase Systems
- Difference Between Single Phase, Two Phase & Three Phase Systems
- Single Phase vs Two Phase vs Three Phase
- How do Three-Phase Systems improve Power Quality?
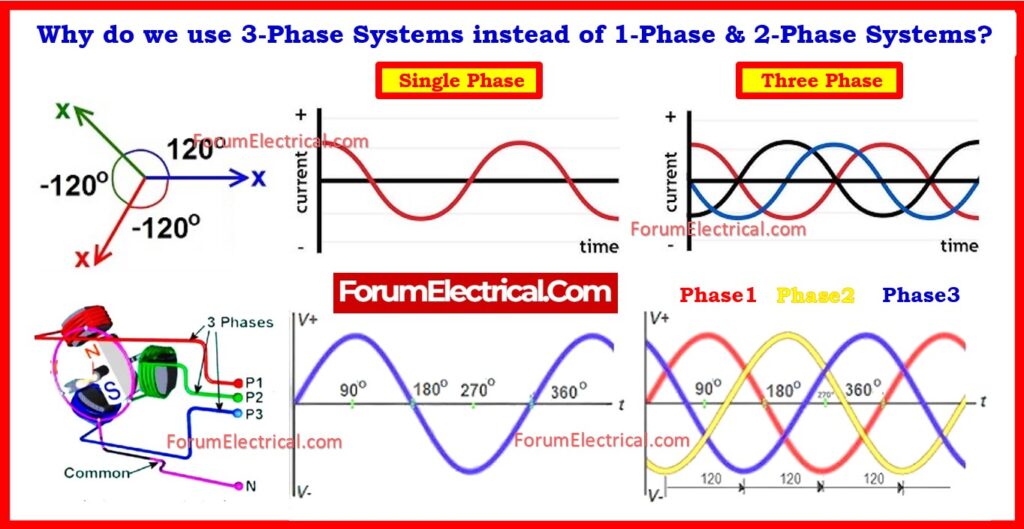
Single Phase:
- A single phase supply system is characterized as a sinusoidal alternating voltage with a certain time period & frequency generated by the single winding alternator serving as the source voltage.
- A circuit powered by these voltages is referred to as a 1-phase AC circuit.
- In other terms, a circuit containing a single alternating current (1-phase AC) & voltage is denoted as 1-Φ.
Two Phase:
- Two-phase means 2 sine waves, each altered by 90 degrees.
Three Phase:
- A system with more than one phase is referred to as a polyphase (or) multiphase system.
- A 3-Φ system has three phases with a constant frequency and a fixed angle of 120° across the source voltages delivered by the alternator’s three windings.
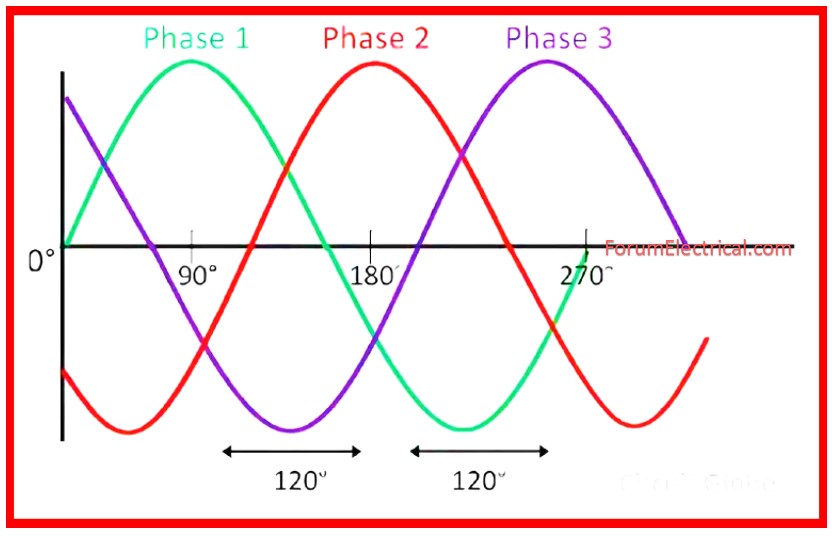
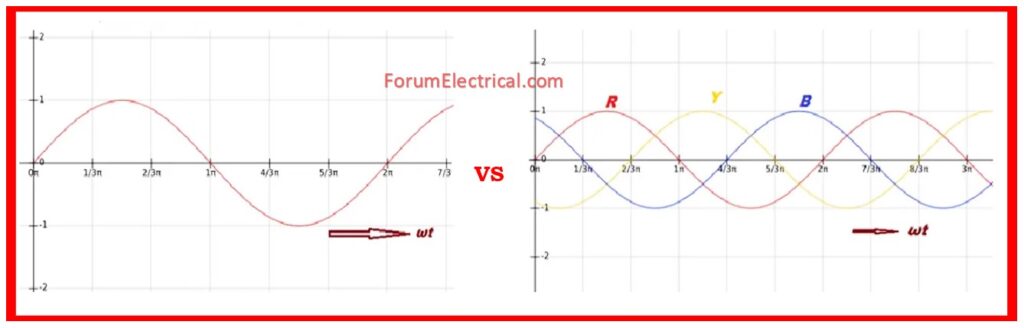
- Three-phase means three sine waves spaced by 120°, resulting in balanced & continuous power.
Why 3-Phase Systems pre-dominate in Electrical Power Distribution?
1). Continuous & Balanced Power Flow
In single-phase systems, the power output fluctuates cyclically. It approaches zero twice per cycle, at the negative and positive peaks.
This fluctuation generates pulsating electricity, which is unsuitable for stable operations.
In two-phase systems (with a 90° separation), fluctuations are reduced but remain present.
Three-phase systems, on the other hand, give a more consistent and smoother power output due to their 120° phase separation.
When one phase’s voltage lowers, the other two maintain the supply.
This ensures that:
- Less vibration in motors.
- Industrial equipment operates with stability.
- Reduced strain on electrical components.
2). Superior Motor Performance
Three-phase motors are self-starting, which eliminates the requirement for external starting devices such as capacitors seen in single-phase motors.
Advantages of Three-phase motors include:
- Balanced spinning magnetic field (owing to a 120° phase shift).
- Increased efficiency and lower maintenance.
- Improved torque characteristics.
This makes them suitable for industrial machinery and large HVAC systems.
3). Improved Efficiency in Power Transmission
3-phase systems can transmit more power with fewer conductors than single- or two-phase systems.
In a balanced three-phase load, the return current is distributed across all three lines, reducing energy loss.
A 3-phase system generates approximately 1.732 times more power than a single-phase system with the same voltage and current rating.
This results in:
- Lower transmission losses.
- Smaller conductor size requirements.
- Infrastructure that is cost-effective.
Why 2-Phase Systems were Abandoned?
Two-phase systems were previously employed, but they had disadvantages.
And also not as efficient (or) balanced as three-phase.
It is difficult to scale for the high power demands.
Because of these difficulties, three-phase systems have become the global standard for the industrial & utility power distribution.
Understanding 3-Phase Phase Angles
In a balanced three-phase system:
- R phase equals 0°.
- Y phase equals 120°.
- B phase equals 240° (or -120°).
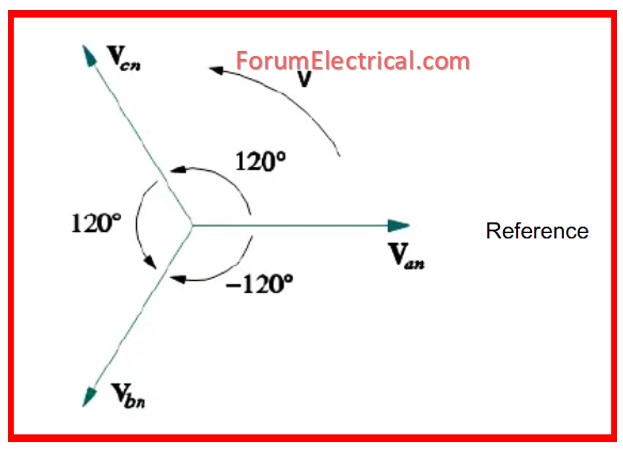
This 120° spacing assures symmetry, and under ideal conditions:
- The total of instantaneous voltages and currents is always 0.
This is why no current travels via the neutral wire in a perfectly balanced load, resulting in less heat and energy loss.
Advantages of 3-Phase Systems
- Continuous power supply (suitable for rotating machinery).
- Effective transmission across large distances.
- Cost-effective – less wiring means less loss.
- Simplified the electrical infrastructure.
- Motors perform poorly with single-phase power due to power pulsation.
- Two-phase power is obsolete, inefficient, and requires additional wiring.
Thus, 3-phase is the international standard for industrial, commercial, & utility-scale power systems.
Difference Between Single Phase, Two Phase & Three Phase Systems
Single Phase vs Two Phase vs Three Phase
| Parameters | Single Phase (1Ø) | Two Phase (2Ø) | Three Phase (3Ø) |
| Number of Conductors | 2 (Phase and Neutral) | 2 phases (typically 90° apart) | 3 phases (120° apart) + neutral (optional) |
| Phase Angle | N/A | 90° apart | 120° apart |
| Power Consistency | Varies sinusoidally (pulsating power) | Better than single-phase yet still not ideal | Constant power transfer |
| Voltage Levels | Commonly 120V (or) 240V | Rare; utilized in early systems | Typically 240V, 400V, 415V, etc. |
| Applications | Residential, commercial lighting | Mostly obsolete | Industrial, commercial & heavy-load applications |
| Power Capacity | Lower | Moderate (presently not applicable) | High |
| Efficiency | Less Efficient | More Efficient than single phase | Most Efficient for power distribution |
| Nature of Availability | Very common | Rarely used today | Common in industrial & commercial settings |
| Motor Performance | Less Torque & Efficiency | Better than single-phase | High Torque & Smoother Operation |
How do Three-Phase Systems improve Power Quality?
Three-phase systems enhance power quality in numerous ways:
- They stabilize electricity, reducing voltage dips that may harm sensitive equipment.
- Power distribution is smoother & more balanced than single-phase systems, avoiding surges and interruptions.
- Three-phase systems provide stable power for demanding applications due to their resistance to harmonic distortion & voltage sags.
- Balanced load between phases prevents overloading and improves electrical infrastructure efficiency and durability.
- 3 phase systems provide better power quality, making them appropriate for industrial & large-scale usage that require stability and reliability.