Capacitor banks are mostly utilized in low and medium voltage substations in order to compensate for reactive energy (or power factor) used by electric motors & other loads.
- Capacitor Bank Maintenance Procedure
- Use of PPE
- Equipment Condition
- Electrical Disconnection
- Opening of Equipment
- Capacitor Discharge Process
- Check list
- General Cleaning
- Tightening Electrical Connections
- Component Verification Status
- Component Closure
- Equipment Energization
- Commissioning
- What is inside Capacitor Bank?
- How to select Capacitor Bank Size?
Capacitor banks are used to compensate for reactive energy and avoid paying it to the electrical supply service provider. Additional advantages include
- Reduced voltage drops.
- Reduce energy losses.
- Increase active power transmission capacity in conductors.
However, for them to function well, various variables must be considered in both their design and upkeep, with maintenance occurring at least twice a year & possibly more frequently depending on the working circumstances and climate.
Preventive maintenance tries to identify irregularities that may be interfering with the proper operation of electrical equipment.
In this particular case, predictive maintenance will be performed in order to identify any potential failures and assess the current operating conditions of every component of equipment and the components that make up that equipment.
In order to accomplish this, a work plan is prepared, which includes the following components:
- The identification of the equipment used for compensation
- Checklist,
- General cleaning,
- Tightening connections, and
- Functional test
are all included in this step.
Capacitor Bank Maintenance Procedure
Because capacitor banks store energy, it is necessary to take all of the measures that are recommended by the manufacturer before proceeding with their prevention.
This is the reason why the procedure that is shown here was designed in order to intervene in the maintenance of capacitor banks as:
- Use of PPE
- Equipment Condition
- Electrical Disconnection
- Opening of Equipment
- Capacitor Discharge Process
- Check list
- General Cleaning
- Tightening Electrical Connections
- Component Verification Status
- Component Closure
- Equipment Energization
- Commissioning
Use of PPE
The use of personal protective equipment: to intervene on the equipment, the essential personal protective equipment is employed. This includes a helmet, protective glasses, safety gloves, dust mask, safety shoes, and voltage presence instruments.
Equipment Condition
A summary of the current state of the equipment is displayed, together with an indication of any failures or indications that may be present on the controller of the equipment.
Electrical Disconnection
The electrical disconnection of the compensating equipment is carried out from its main switch, and it is ensured that there is no presence of voltage inside the equipment.
Opening of Equipment
After it has been established that there is no voltage present, the covers of the compensating equipment are opened & removed.
Capacitor Discharge Process
Capacitors are components that store energy for a specific amount of time, and the manufacturer recommends that you wait for their discharge for a period of five minutes before you make any changes to them.
Check list
After the capacitors have been drained, a visual inspection is performed on the internal components of compensation equipment. These components include the controller, fuses, switching sources, reactors or inductors, and capacitors.
General Cleaning
A blower and isopropyl, a dielectric cleaning liquid, are used to remove particles of dust that have accumulated on the equipment. This is the next step in the general cleaning process.
Tightening Electrical Connections
The electrical connections are inspected, and any connections that are found to be loose are then pulled tight.
Component Verification Status
The condition of every part that makes up the compensating equipment is verified. Particularly, the switching source of the equipment, which includes electronic devices such as SCRs and its trip card, is verified.
Component Closure
Putting the protective covers on the equipment. Once all of the components that comprise the equipment have been examined, the protective covers are put on.
Equipment Energization
Once all of those components that were mentioned earlier have been finished, the equipment is next activated, & the nominal capacities of its capacitors as well as their firing sequence are examined.
Commissioning
The process of commissioning involves leaving the equipment in its regular operating mode once the capacity & sequence data of equipment have been validated.
This process is carried out with all of the compensation equipment, and if any of the equipment is discovered to have any observations (or) damaged components, it will be mentioned in the report that pertains to that particular piece of equipment.
Additionally, a new estimate will be generated for the damaged elements, and corrective or scheduled maintenance will be performed in order to return the equipment to its normal state, if necessary, while the same procedure will be followed for the repair.
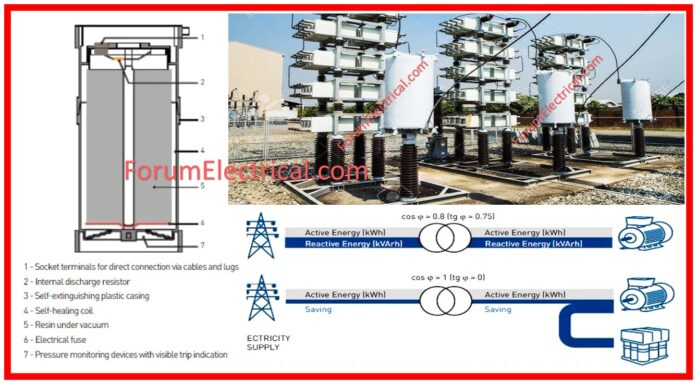
What is inside Capacitor Bank?
A particular type of energy storage system is known as a capacitor bank, which is comprised of many capacitors that are connected in either series (or) parallel to form the system.
The
- Power Factor Lag &
- Phase Shift
an alternating current (AC) power supply can be corrected with the assistance of this technology, which ultimately results in an increase in the electricity transfer efficiency.
How to select Capacitor Bank Size?
The initial step for selecting the suitable capacitor bank is to utilize the power factor adjustment formula & calculate the appropriate size. You must also follow the complete capacitor bank size calculation method, which is addressed in this above link. Following a step-by-step method will ensure you invest in the proper device.