What is a Capacitor Bank ?
A capacitor bank is defined as a combination of numerous capacitors linked in series or parallel with the same rating. Individual capacitors are commonly employed to store electrical energy. As the number of capacitors in a bank increases, so does the amount of energy that can be stored in a single device.
What is the purpose of the capacitor bank ?
Active power is measured in kW or MW (MW). Power should come from a power plant. All electrical power system arrangements address this basic need. In alternating electricity, reactive power is always there. Power is measured in Kilo VAR or Mega VAR.
Inductive load is the principal source of reactive power demand. These inductive loads include electric motors, transformers, transmission and distribution networks, induction furnaces, fluorescent lights, etc. This reactive power must be adequately compensated; otherwise, the ratio of actual load power to total system power (vector sum of active and reactive power) is reduced.
Lower ratios imply a poor electrical power factor of the system. If the system’s power factor is low, the transmission, distribution network, transformers, alternators, and other equipment linked to it require more amperes. So reactive power compensation is important. A capacitor bank is used for reactive power compensation.
There are primarily two categories of equipment that are utilised for the purpose of compensating for reactive power, and they are:
- Static capacitors and
- Synchronous condensers
Static Capacitors :
The capacitor, which is more commonly referred to as a static capacitor, takes in a leading current and neutralises, either partially or entirely, the lagging reactive component of the load current. This results in an increase in the load’s power factor. The capacitors can be connected in either a delta or star configuration for three-phase loads.
In the presence of large inductive loads, such as induction motors and transformers, etc., static capacitors are the capacitors that are installed. They enhance the load circuit power factor, which in turn improves the efficiency of the system or device.
Synchronous Condensers :
Synchronous condensers have the capability to generate reactive power, and that generation of reactive power can be controlled. When compared to static capacitors, synchronous condensers are more expensive but more effective in rectifying the power factor of the system. This is because of the regulating advantage that synchronous condensers provide; nevertheless, this equipment is more costly. Because of this, the usage of synchronous condensers is only appropriate when it comes to the task of regulating the voltage of a very high voltage transmission system.
What are the different types of capacitor bank ?
- Fuse Less,
- Externally Fused and
- Internally Fused
are three types of capacitor banks.
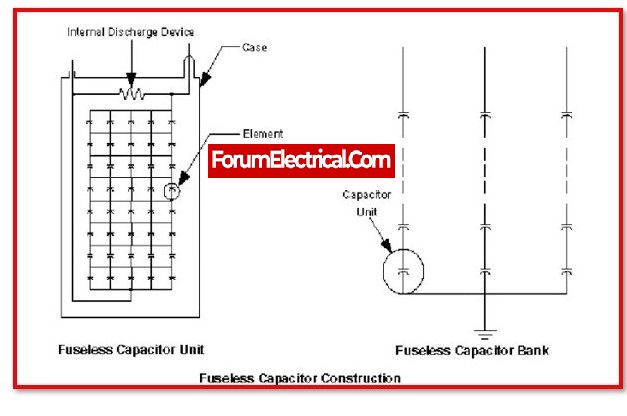
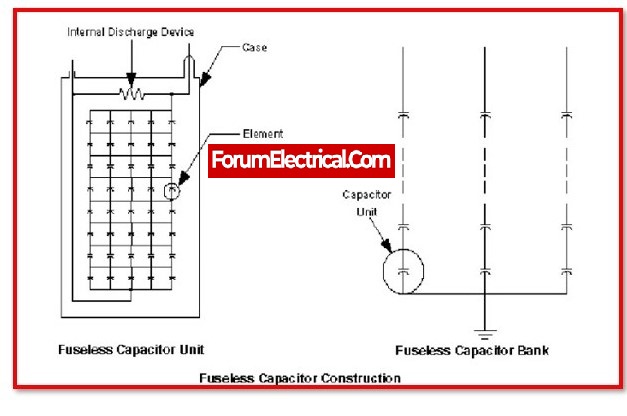
Fuse Less Capacitor Bank:
When working with a fuseless type, the formation of a capacitor string can be accomplished by connecting multiple fuse units in series. Each phase has its own capacitor bank, which is made by connecting these strings together in parallel. Following this step, three phase banks that are virtually identical to one another are connected in the connection of star/delta to produce a complete three-phase bank.
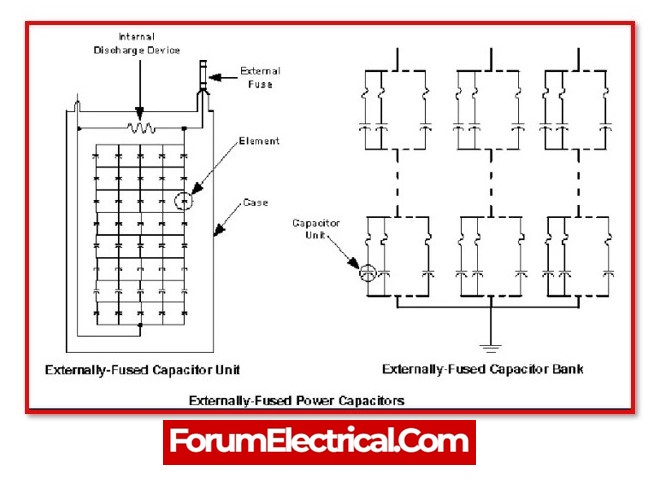
Externally Fused Capacitor Bank :
A form of capacitor known as an externally fused type has the fuse unit for each capacitor unit provided from the outside. In the event that a problem develops in any of the capacitor units, the fuse unit will be harmed. If the faulty capacitor unit can be detached by the fuse unit, then this bank will be able to continue providing service without interruption.
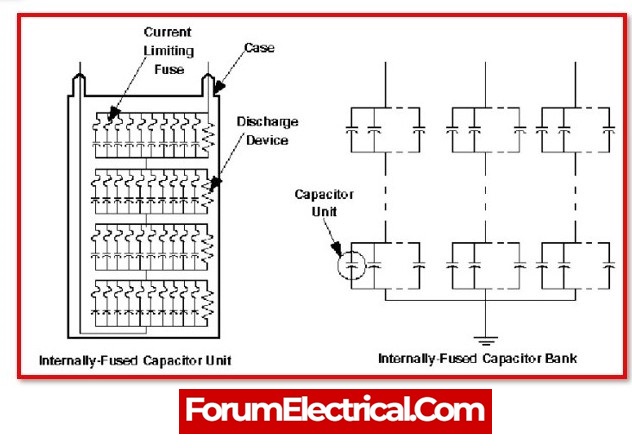
Internally Fused Capacitor Bank :
Internally fused capacitor banks can be designed in a certain way. In its rating, series and parallel components are associated. Each capacitor can be protected by a fuse. In the same enclosure are capacitors and fuses. In this sort of bank, each capacitor element is small. So if a capacitor fails, the bank will not be affected. This capacitor bank can run with one or more broken capacitors.
Capacitor Bank Uses :
- Since most industrial loads are inductive, they require reactive power.
- Parallel capacitor bank provides reactive power.
- Capacitor banks provide local reactive power, reducing line flow.
- A capacitor bank can keep the power factor around unity. Improving power factor reduces voltage-current phase difference.
- Capacitor banks reduce voltage-current phase difference.
- With a power bank, current leads voltage, reducing power factor angle. Power factor improves when power factor angle decreases.
- Substation capacitor bank compensates for reactive power and corrects power factor.