Table of Contents
- Purpose
- Reference
- Scope
- Terminology
- Equipment Required
- Equipment under Test
- Preliminary Checks
- Electrical Checks
- DC Distribution Circuit Breaker Test and Inspection
- Mechanical Tests
- Electrical Testing of Circuit Breakers
- Electrical testing of the Distribution Board
- Placing into Service
- Record Inspection and Test Data
Purpose
The DC distribution board is designed to distribute the DC power delivered by the battery & battery-charger assembly of a system.
These tests are designed to ensure that the board & its components function properly.
Reference
- Single line diagram
- Schematic diagram
- Equipment drawings
Scope
Each working site
Terminology
Not relevant
Equipment Required
- Digital multimeter
- Milliohmmeter for continuity
- 500 V DC megohmmeter
- DC test set power supply
Equipment under Test
All low voltage (LV) DC distribution boards were involved.
Preliminary Checks
- Ensure all distribution board components (e.g., type, ratings, ground fault sensor, voltmeters, voltage monitoring relays, ammeters, circuit breakers) are properly installed and in accordance with the necessary designs.
- Ensure distribution board components are properly marked.
- Prior working on system, avoid touching electrical equipment.
- Verify the main busbar & auxiliary circuits (control, monitoring, alarm, & fault) for continuity.
- Verify the grounding busbar’s continuity & connection to the primary earthing system.
- Ensure panel hinged doors are connected to the frame with earthing braids.
- Check door locks for proper operation.
- Check connections for tightness and reference drawings.
- Open all incomers & load circuit breakers.
Electrical Checks
Testing for continuity between entire Metal parts & Ground
- This test usually requires a milliohmmeter to assess continuity.
Distribution Board (DB) Insulation Resistance (IR) Tests
- It is suggested that these tests be performed before connecting to ensure that all isolating devices are closed.
- If the cables are already connected, disconnect the isolating devices before doing any tests. The downstream circuit will undergo power cable tests.
- Disconnect both the ground sensing device & the control cords.
- Utilizing a 500 V DC megohmmeter, measure insulation resistance after one minute of electrification between:
- Positive and negative busbars with ground.
- Negative and positive busbars with ground.
- Auxiliary circuit & ground.
- Rejoin (or) Reconnect the cables after testing
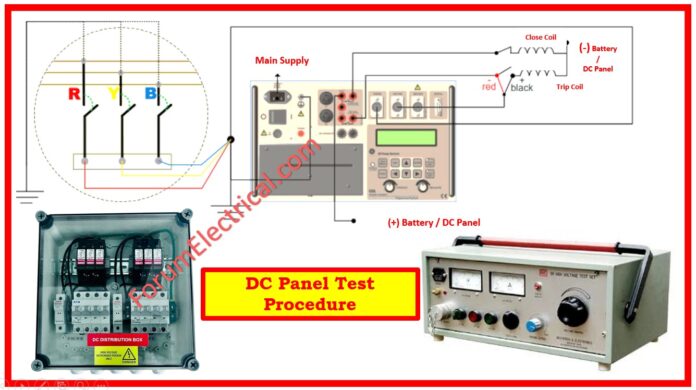
DC Distribution Circuit Breaker Test and Inspection
Circuit breakers perform the following functions, based on the equipment:
- Provides and protects DC motors.
- Inverter supply and protection.
- Protect the DC distribution board, power circuits (batteries and chargers), and auxiliary circuits (monitoring, control, alarm, and fault).
Conformity Checks
Examine the circuit breakers for their presence and compliance with the reference drawings (type, magnetic rating, thermal rating, and label).
Mechanical Tests
- Check the right racking in for the withdrawal circuit breaker, and ensure that it cannot be racked in when closed.
- Circuit breakers cannot be closed unless properly racked in. Circuit breakers cannot be racked out when closed.
- Check closing and opening/tripping operation at no load using manual actuation.
- Press the test pushbutton if applicable.
Electrical Testing of Circuit Breakers
- Magnetic protection causes the circuit breakers to trigger on the short circuits.
- The tripping value must be modified but not checked by providing power.
- Thermal protection used to triggers circuit breaker for tripping at overloads.
- The tripping value must be modified but not checked by providing power.
- Check panel terminal blocks for circuit breaker position & alarms.
Electrical testing of the Distribution Board
Tests for Measurement & Protection Circuits
- Indicators: Use a test set power supply to verify the values displayed on the indicators. Check the output terminal block indications for linked converters.
- Under/Overvoltage Protection: Use a test set power supply to examine the relay operation & adjust to the appropriate rating. The protection information reports must be reviewed up to the distribution board (DB) output terminal block.
Insulation Resistance Tester
- Utilizing a test set power supply, check the relay setup for the specified earth leakage current.
- The information reports must be examined up to the distribution board’s output terminal block.
Energizing
- Connect the battery charger, battery supply cables, or incoming cables from the Main Distribution Board.
- Check for the presence of mechanical guards that prevent inadvertent contact with live parts.
- Open all of the outgoing disconnecting devices.
- Verify for voltage & correct polarities upstream of any disconnecting devices, indicators, and protection by connecting the distribution board to the battery charger or the main distribution board.
- Examine the distribution board alarm information and return it to the output terminal blocks.
Automatic Transfer Switches
- Check the mechanical and/or electrical interlocks.
- Check the correct polarity.
- With both accessible supplies, confirm the functional checks by the existence of voltage, loss of supply, and restoration of supply in manual & automatic modes.
Placing into Service
- Insert the battery into the LVDC distribution board by closing incoming battery circuit breaker (or) second incoming supply from the Main Distribution Board.
- Check that all relevant protective & signaling devices are operational.
- Voltage measurement, polarity check, and voltmeter reading must be performed for each busbar.
- Close all outgoing circuit breakers as needed after testing the corresponding low voltage power lines and polarity.
Record Inspection and Test Data
The outcomes of the checks & measurements obtained during the field test are to be documented.