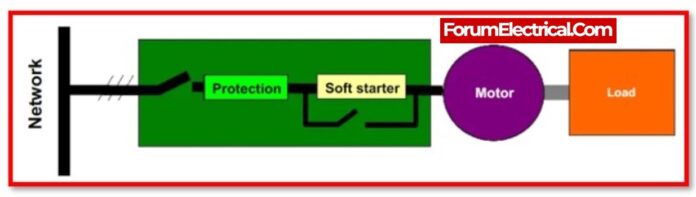
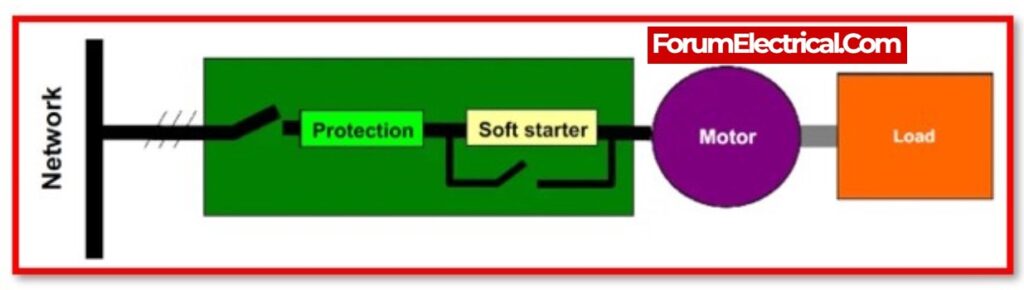
- What is Soft Starter?
- Soft starter operation principle:
- Working of Soft Starter:
- Advantages of the Soft Starters:
- Disadvantages of the Soft Starters:
- Application of the Soft Starters:
- Variable Frequency Drive (VFD):
- Construction of VFD:
- Working of VFD:
- Advantages of VFD:
- Disadvantages of VFD:
- Applications of VFD:
- Difference Between Soft Starters and VFD:
What is Soft Starter?
Soft Starter is a type of motor starter that reduces the starting current or high inrush current by decreasing the applied voltage to the motor.
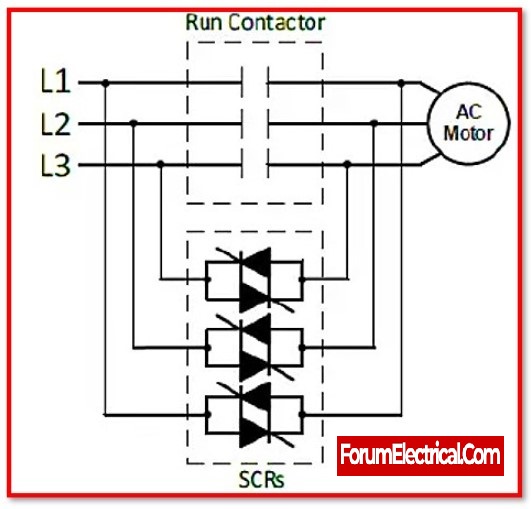
Soft starter operation principle:
A soft starter is made up of three pairs of back-to-back coupled semiconductor devices that regulate the terminal voltage, such as thyristors. These thyristors are alternately switched to lower terminal voltage and inrush current. The motors’ terminal voltage can be regulated by adjusting the firing angles of the thyristors.
Working of Soft Starter:
Soft starter uses semiconductor thyristors to regulate the voltage supply. A pair of back-to-back thyristors is used to control the flow of current in both directions. So, a three-phase soft starter utilizes six thyristors to concurrently reduce voltage on all three phases.
The terminals of the thyristor are the anode, cathode, and gate. Unless a voltage pulse is applied to the gate of the thyristor, current cannot flow. When the gate signal is applied, the thyristor is activated and current begins to flow through it. The quantity of current or voltage permitted by a thyristor is regulated by adjusting the firing angle of the gate signal. Therefore, it reduces the motor’s starting inrush current.
At the starting of the motor’s operation, the firing angle is adjusted to supply a low voltage that is gradually increased. As the voltage reaches the line voltage, the motor’s speed increases gradually and it begins running at its rated speed. In normal operation, a bypass contactor is typically used to supply line voltage directly to the motor.
During the stopping of a motor, the voltage is reduced gradually to decrease the motor’s speed, and the input power source is eventually disconnected.
Since the soft starter only reduces the supply voltage during the motor’s starting and stopping, it cannot change the motor’s speed during normal operation. Therefore, they are applied at a consistent speed.
Advantages of the Soft Starters:
- Mechanical stress on the motor and driving equipment is reduced.
- Power system electromechanical stress is reduced.
- Equipment life has been increased.
- Reduces inrush current during motor start-up.
- There are no harmonics generated.
- When compared to variable frequency drives, they are less expensive.
Disadvantages of the Soft Starters:
- For jerk-free starting, the soft starter can be used to start and stop the motor at a decreased voltage to reduce the starting current.
- It is not permitted to utilise the soft starter for speed regulation.

Application of the Soft Starters:
- Speed and torque control is only necessary during the start/stop phase.
- Reducing the massive starting inrush current of a large motor.
- Normal start-up of mechanical equipment causes torque spikes and stress, which requires a soft start.
- Pumps and blowers are utilised to eliminate pressure surges in piping systems.
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD):
A variable frequency drive (VFD) is a motor starter based on semiconductors. It can start and stop electric motors safely, as well as manage the motor’s speed during operation. It can regulate both the supply voltage and frequency. Since the speed of an induction motor is dependent on the supply frequency, VFD is typically employed to adjust the motor’s speed during operation.
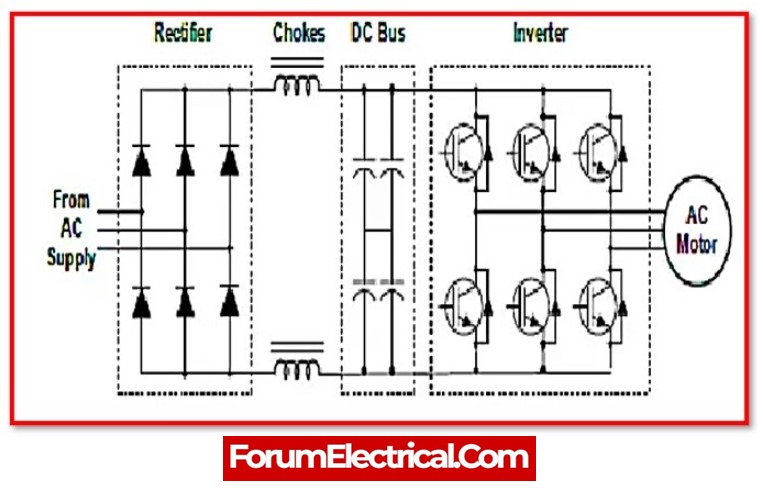
Construction of VFD:

The VFD is divided into three sections.
- Converter Section
- DC Bus
- Inverter Section
1) Converter section:
Six diodes are used in the converter or rectifier portion. The diodes convert the alternating current voltage to direct current voltage. The magnitude of the direct current voltage is;
Vdc = 1.35 X Vrms
2). DC Bus:
There are ripples in the rectified voltage. The capacitor bank filters the alternating current components and generates ripple-free direct current voltage.
3). Inverter Section:
The inverter uses PWM to convert DC voltage to AC voltage. To keep the v/f ratio constant, the inverter regulates both frequency and voltage at the same time.
Working of VFD:
The logic control circuit of the inverter allows varying the output AC voltage’s frequency and voltage. By increasing the frequency, it is possible to boost the motor’s speed from 0 RPM to its rated speed, and sometimes over its rated speed. Therefore, it provides a complete control over the motor’s torque and speed characteristics.The motor’s torque is directly proportional to both the supply current and supply voltage.
VFD has two functions:
- Induction motor soft starting and stopping
- Motor speed regulation based on process requirements
An induction motor’s speed is proportional to its frequency and inversely proportional to the number of poles.
Ns = 120f/p
Advantages of VFD:
- By altering the frequency of the provided voltage, the VFD can alter the speed of the motor while it is in operation. Therefore, it is utilised in situations where the motor speed must be regulated.
- In order to regulate the torque of the motor, it can have complete control over both the voltage and the frequency.
- Traditional motor starts, including DOL starters and soft starters, are incapable of varying the motor’s speed. It can therefore either operate the motor at full speed (full power) or stop the motor. While the VFD can save power usage by running the motor at a predetermined speed, it is programmed to run the motor at a certain speed.
Disadvantages of VFD:
- VFD can cause harmonics in the line, requiring the connection of extra filters.
- Due to the presence of so many circuits and components, the VFD is larger than a soft starter.
- It also impacts the price of the VFD, which is nearly three times that of the soft starter.
Applications of VFD:
- Complete control of the speed is essential.
- The primary purpose of VFD is to save energy.
- Customization control is required.
Difference Between Soft Starters and VFD:
| S.NO | SOFT STARTERS | VFD |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A semiconductor-based motor starter capable of starting and stopping a motor safely. | Semiconductor-based motor starter that can start, stop, and vary the speed of the motor safely. |
| 2 | A contactor is used to bypass the soft starter at full speed. | It is active during the motor’s functioning. |
| 3 | It simply regulates the alternating current voltage with thyristors. | It converts AC to DC and then back to AC at the desired value. |
| 4 | It can only change the voltage of the power supply. | It may change both the voltage and the frequency. |
| 5 | It may change both the voltage and the frequency. | It has a high starting torque. |
| 6 | In the system, no harmonics are generated. | It causes harmonics to be generated in the system. |
| 7 | There are no additional filters required. | Filters are required due to harmonics injection in the line. |
| 8 | It is utilised in applications requiring continuous motor speed. | It is utilised in applications requiring variable motor speed. |
| 9 | It is smaller in size than a VFD. | It has a larger size. |
| 10 | It is less expensive than a VFD. | It has a high cost. |
| 11 | It requires less space. | It requires more space. |
| 12 | It saves less energy. | It saves more energy. |