1). What is Electric Traction?
Electric traction refers to the use of electric power in traction systems (such as railways, trams, and trolleys).
Electric traction refers to the use of electricity to power all of the machines listed above. Nowadays, magnetic traction is further employed for bullet trains. Electric traction systems mostly use direct current motors.
2). What are the criteria for an Ideal Traction System?
The requirements for an optimum traction system are as follows:
- To ensure quick acceleration, the starting tractive effort must be high.
- Track wear should be kept to a minimum.
- Free from pollution.
- Speed control must be simple.
- The equipment must be able to tolerate heavy transient loads.
- Low initial and ongoing costs.
- There must be no interference with the communication wires that run alongside them.
- Braking should be designed so that the brake shoes wear as little as possible.
3) Describe the various Traction Systems.
The various traction systems are:
- Direct steam engine drive,
- Direct internal combustion engine drive,
- Steam electric drive,
- Internal combustion engine electric drive,
- Petrol electric drive,
- Battery electric drive.
4). Classify Electric Traction Supply Systems.
- D.C.(Direct Current) System
- A.C (Alternating Current) System
- Single Phase System
- Three Phase System
- Composite System
- Single Phase AC-DC System
- Single-Three Phase System
5). What are disadvantages of the Battery Electric Drive?
The primary disadvantages of the battery electric drive are the smaller capacity of the batteries, the need for regular charging, and the limited speed range.
6). What are the advantages of Electric Traction?
The advantages of electric traction are:
- High starting torque requires minimal maintenance.
- The most cost-effective and environmentally friendly traction system.
- Great passenger capacity combined with high speed.
- In comparison to other traction systems, this one is highly efficient.
7). Why is Electrical Traction preferable over Steam (or) Internal Combustion Engine Drives?
Because of the strong strain on the rear, engines in IC engine drives will operate at low rpm. If they operate at high RPMs, there is a risk of engine explosion. Because of the lower revs, the starting torque will likely be modest. To address this, electrical traction is used since the motors utilized in electrical drives are capable of generating high starting torque at low RPMs.
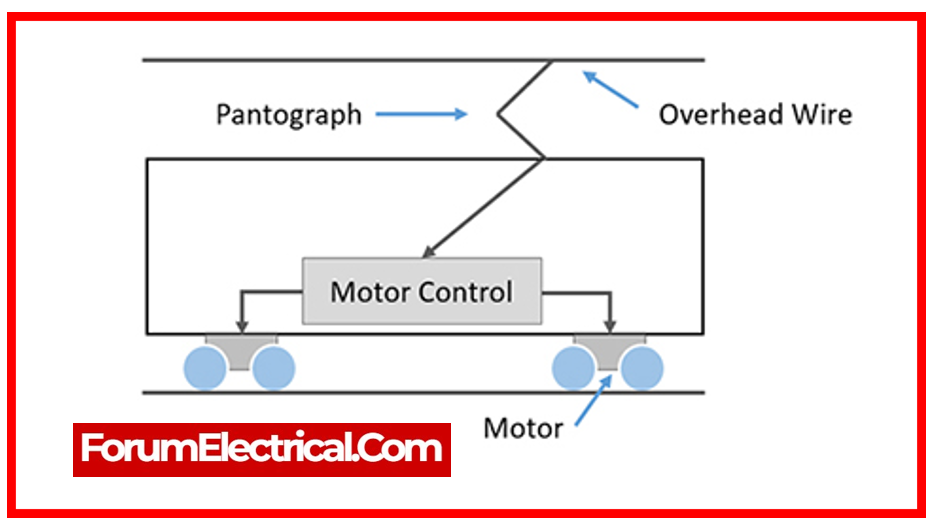
8). What is a MCC (Motor Control Center) & how does it work?
The Motor Control Center (MCC) is where all of the electrical drives are interconnected and regulated. It is used to manage the torque & speed of electrical motors in traction systems.
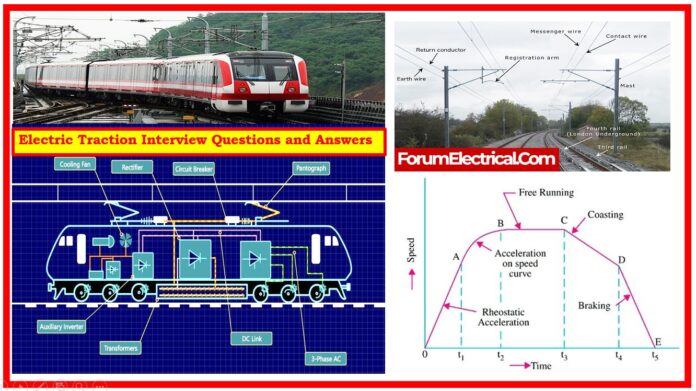
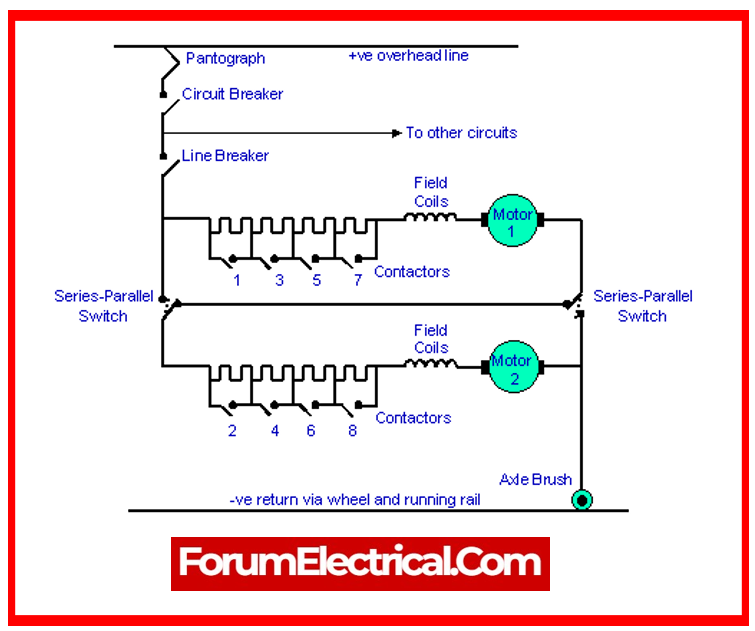
9). What is Pantograph? How does it function?
The pantograph serves as one of the most significant components of electrical traction equipment (electric trains). It is used in electric trains to receive current from overhead lines. It is often referred to as the current collector.
The overhead transmission wires are utilized to supply energy to trains, hence contact is required, and so Pantographs are employed to supply current. The strip will make contact with the wire. As the train begins to run, the pantograph contact remains with the wire.
10). What is Tractive Effort?
Tractive effort refers to the force at outer edges of moving trains’ drive wheels. It is widely known as sum of rolling and tractive forces.
11). What is Traction Voltage, and how can one determine India’s most significant Traction Voltage?
The voltage that passes through overhead lines is referred to as traction voltage. Traction voltage will vary from country to country. In India, the maximum traction voltages are 1.5 KV DC and 25 KV AC.
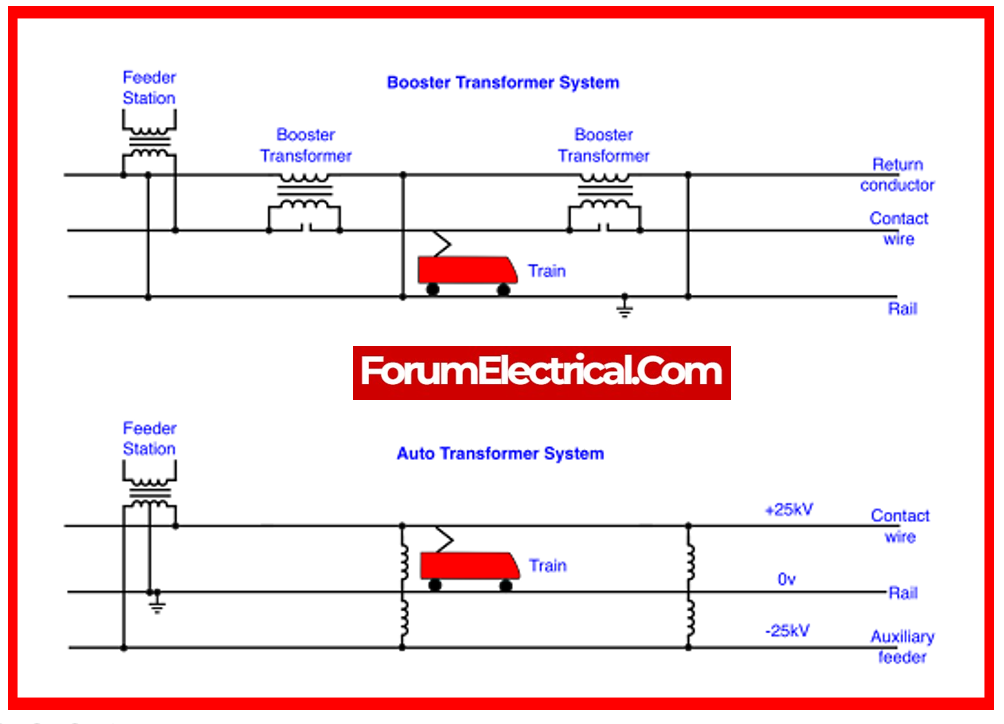
12). What is the Speed-Time Curve?
The curve that connects speed & time is known as the speed-time curve. A speed-time curve will be used to calculate the train’s travel at various time intervals, as well as the acceleration of the motors.
13). What are the basic (electrical) characteristics of an Optimal Traction Motor?
- High starting torque.
- Series speed-torque characteristics.
- Simple speed control.
- Possibility of the regenerative braking.
14). What is the purpose of Traction Motor Control?
- Limit starting current and provide smooth,
- Jerk-free acceleration,
- Both manual & automatic control might be accessible.
15). What do you mean by “Average Speed in Electric Traction?”
The average speed is defined as the mean of the speeds from start to stop, or the distance between the 2 stops divided by the actual period of run.
Average Speed = Distance between stops (km) / Actual time of run (hours)
16). What Type of Braking is typically employed in Electrical Traction?
Regenerative braking is widely utilized in electrical traction as it is the most dependable braking mechanism for electric drives.
17). What is Emergency Braking?
A conventional braking system is a distinct braking device designed to bring a train to a halt as rapidly as feasible. In emergency conditions, passengers can use a separate plunger given in the cabin to stop the trains.
18). What is the reason for Traction Motor Control?
Traction motor control is required for smooth, jerk-free acceleration and to limit beginning current.
19). Which Braking System is utilized on Steam Locomotives?
The vacuum braking method is most commonly employed in steam locomotives since it is far more reliable than steam braking.
20). What are the different methods for controlling Traction Motors?
The traction motor control is primarily used to manage the speed of a dc series motor in traction. The different methods are:
- Field & Thyristor Control,
- Rheostatic Control,
- Buck & Boost control,
- Series parallel control.
21). What are the numerous methods for using Electric Braking?
There are 3 methods for using electric braking:
- Plugging (or) Reverse Current Braking
- Rheostatic Braking.
- Regenerative Braking.
22). Name the Advanced Traction Motor Speed Control Methods.
The most recent methods of speed control for traction motors are:
- Tap changer control.
- Thyristor control.
- Chopper control.
- Microprocessor control.
23). What are the advantages of Microprocessor-Based Control of Traction Motors?
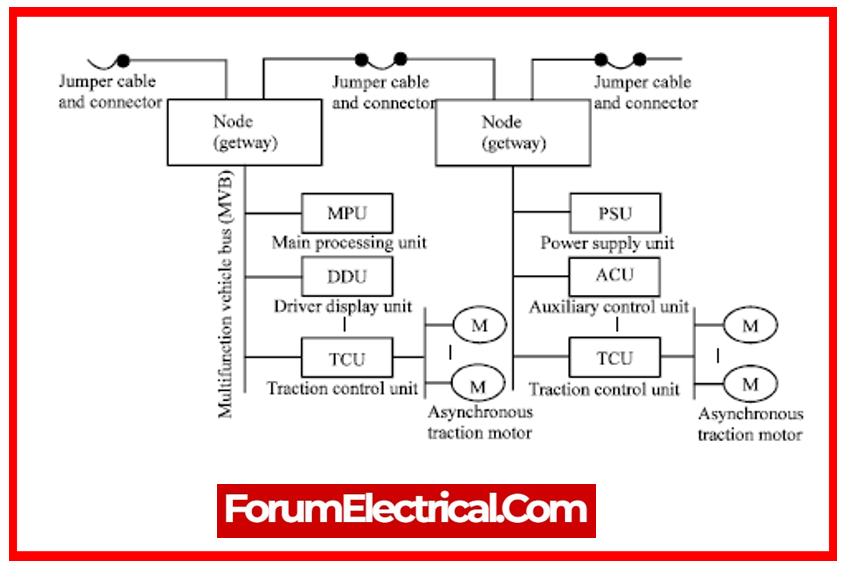
The advantages of microprocessor-based SSDs include:
- Fast response time
- High accuracy.
- Overvoltage and over-speed protection.
- Electronic interlocking.
- Less susceptible to temperature fluctuations and drift.
- The number of components used is minimal.
24). What do you mean by “Scheduled Speed” in Electric Traction?
Schedule speed is the ratio of the distance travelled between two stops to the entire time spent running, including the time spent at each stop.
Schedule Speed = Distance between stops (kms) / Actual time of run (hours) + Stop time (hours).
The schedule speed is consistently lower than the average speed.
The variation is significant between urban and suburban services, but negligible for main line service.
25). What are the disadvantages of the Electric Traction?
- High capital costs.
- Problem with supply failure
- Additional equipment is needed to achieve electric braking and control.
- The current leakage from the distribution mains & the voltage drop in the track must be kept below the permissible limits.
- Electric cars must only travel over a guided route.