- What is the Electrical Testing Tool?
- Different Electrical Testing Tools
- 1). CT-PT Analyzer
- 2). Relay Tester
- 3). Circuit Breaker Analyzer
- 4). Transformer Turn Ratio Tester
- 5). Contact Resistance Tester
- 6). Winding Resistance Tester
- 7). Tan-Delta Tester
- 8). Primary Current Injector
- 9). Voltage Divider
- 10). Insulating Oil Tester
- 11). Dew Point Tester
- 12). Hi-Pot Test Kit (AC & DC)
- 13). High Voltage Insulation Tester
- 14). Earth Resistance Meter
- 15). Electrical Tester
What is the Electrical Testing Tool?
Electrical testing tools are fundamental instruments utilized by electricians, engineers, technicians, & individuals to identify, resolve, maintain, & repair electrical systems and equipment. These instruments are intended to measure different electrical properties precisely and safely.
Different Electrical Testing Tools
15 top essential electrical testing tools are categorized below:
1). CT-PT Analyzer
2). Relay Tester
3). Circuit Breaker Analyzer
4). Transformer Turn Ratio Tester
5). Contact Resistance Tester
6). Winding Resistance Tester
7). Tan-Delta Tester
8). Primary Current Injector
9). Voltage Divider
10). Insulating Oil Tester
11). Dew Point Tester
12). Hi-Pot Test Kit (AC & DC)
13). High Voltage Insulation Tester
14). Earth Resistance Meter
15). Electrical Tester
1). CT-PT Analyzer
Function:
In electrical engineering & power systems, a CT-PT analyzer is essential. The device tests and calibrates current transformers (CTs) & potential transformers (PTs), which are essential to electrical power systems for measurement, protection, and control.
CTs and PTs reduce high voltage & current to instrument and relay levels. To enable reliable power system measurements and protection, they must be carefully calibrated. The CT-PT analyzer performs ratio, polarity, burden, & accuracy tests to aid calibration.
Advantages:
Technicians use the CT-PT analyzer to inject known currents & voltages into transformers and compare the output to the predicted values to find any differences and make modifications during calibration.
The CT-PT analyzer verifies CT and PT performance to ensure electrical power system reliability, safety, and efficiency, contributing to power grid stability and functionality.
Applications:
Advanced CT-PT analyzers have data logging, automated testing, and waveform analysis, improving transformer testing & maintenance efficiency and accuracy.
2). Relay Tester
Function:
A relay tester is specialized for testing relay functionality and performance. Relays are the electromechanical switches that control circuit electricity. Many electrical & electronic systems use them to control high-power equipment using low-power signals.
Relay testers imitate operating circumstances & electrical signals to ensure relays work properly. Applying voltages, currents, & timing patterns to the relay & watching its response is normal.
Advantages:
Engineers, technicians, & quality control professionals designing, manufacturing, and maintaining electrical systems need relay testers. They may check relay performance, find problems, and fix electrical circuit difficulties with relay testers.
Applications:
- Programmable test sequences, data logging, and relay compatibility are common features of modern relay testers.
- Power generation, distribution, automation, transportation, & telecommunications depend on them for electrical system safety, dependability, and efficiency.
3). Circuit Breaker Analyzer
Function:
A circuit breaker analyzer is a complex electrical engineering equipment used to evaluate and maintain circuit breakers. Its main purpose is to test circuit breakers for
- Timing,
- Contact resistance, &
- Mechanical motion.
Opening and shutting times, arc extinction length, and contact resistance give the analyzer significant insights into circuit breaker operational efficiency and condition.
Advantages:
It can test trip units that detect defects and take precautionary action. With dynamic resistance measurement & vibration analysis, the analyzers allow technicians see faults early and avoid them.
Applications:
With safety measures to assure operator & equipment safety during testing, circuit breaker analyzers help maintain electrical network dependability and safety.
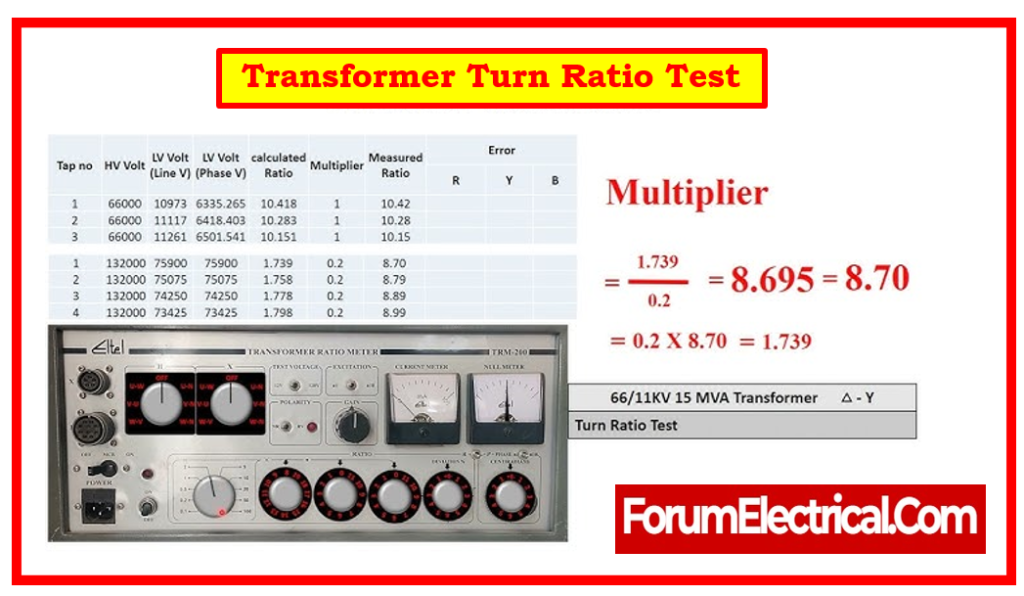
4). Transformer Turn Ratio Tester
Function:
A transformer turn ratio tester is an extremely important instrument for electrical testing that determines the turn ratio between a transformer’s primary and secondary windings. This ratio is essential to ensure that the transformer performs efficiently and produces the desired voltage transformation.
Typically, the tester applies a known voltage to one winding and measures the corresponding voltage in the other winding, allowing the turn ratio to be calculated.
Advantages:
Modern turn ratio testers frequently have advanced features such as
- Automatic detection,
- Digital displays, and
- Data logging capabilities,
Making them invaluable tools for technicians and engineers performing electrical system maintenance and quality control.
5). Contact Resistance Tester
Function:
A contact resistance tester, commonly referred to as a micro-ohmmeter, is an advanced tool that measures the electrical resistance of electrical contacts, joints, and connections
Advantages:
The tester contributes to optimal electrical performance & safety by correctly measuring the resistance of those connections and identifying potential problems such as loose connections or corrosion.
Applications:
It is often used for testing and maintaining high-voltage equipment such
- Circuit Breakers,
- Switches, &
- Busbars.
6). Winding Resistance Tester
Function:
A winding resistance tester is an essential equipment for assessing transformers, motors, & generators. It determines the resistance of each of the windings within these electrical components, allowing employees to identify issues such as short circuits, open circuits, (or) damaged windings.
Advantages:
This tester helps to prevent equipment failures by analyzing winding resistance, as well as the dependability & efficiency of electrical systems.
7). Tan-Delta Tester
Function:
Tan-delta testers used to calculate the tangent of the angle between the voltage & current waveforms in the system, which provides vital information on dielectric losses and insulation quality.
Advantages:
Tan-delta testing helps to prevent insulation failures by detecting irregularities such as moisture infiltration, contamination, or insulation deterioration, ensuring the dependability & safety of electrical infrastructure.
Applications:
Tan-delta testing, also known as dissipation factor testing, is a testing procedure for evaluating the insulation level of high-voltage electrical equipment such
- Transformers,
- Cables, And
- Bushings.
8). Primary Current Injector
Function:
Primary current injector injects large currents into the system being tested, allowing professionals to check the performance and coordination of protection devices, run thermal stability tests, and analyze the overall reliability of the electrical network.
Advantages:
A primary current injector is a powerful tool used to commission, test, and maintain high-current electrical systems that include transformers, switchgear, and safety relays.
Applications:
A primary current injector, with its ability to mimic fault events and overload conditions, is important for the dependability & safety of power distribution systems.
9). Voltage Divider
Function:
A voltage divider is a passive electrical device that divides a voltage into smaller amounts. It is normally made up of a series of resistors that are connected in either series or parallel.
Advantages:
Voltage dividers can be found in a variety of designs and configurations to meet specific voltage ranges & impedance needs, making them useful tools in electronics design & testing.
Applications:
- Voltage dividers are used for a variety of purposes, including signal conditioning, voltage monitoring, and power supply adjustment.
- These devices, which provide exact voltage division ratios, enable accurate voltage scaling & signal processing in the electronic circuits.
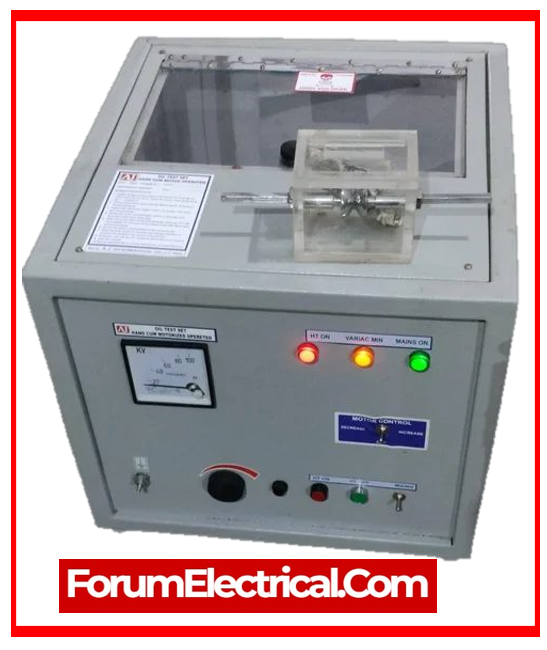
10). Insulating Oil Tester
Function:
Insulating oil testers, which is also known as dielectric oil testers (or) oil BDV (Breakdown Voltage) testers, assess the breakdown voltage of the insulating oils to determine their capacity to endure electrical stress without failure.
Advantages:
Insulating oil testers are important instruments in the electrical industry for determining the dielectric strength of insulating oils.
Applications:
The breakdown voltage allows specialists to determine the quality and compatibility of the insulating oil for application in transformers, circuit breakers, & other high-voltage equipment.

11). Dew Point Tester
Function:
Dew point testers are equipment used to determine the dew point temperature of a gas, usually air or nitrogen. Dew point testing is essential in electrical equipment because it determines the moisture content of insulating gases like sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), which is utilized in
- High-voltage circuit breakers &
- Switchgear.
Advantages:
Dew point testers helps to prevent the production of toxic byproducts caused by moisture penetration, which can weaken insulation and impair the functioning of electrical devices.
12). Hi-Pot Test Kit (AC & DC)
Function:
Hi-Pot (High Potential) test kits, which are available for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) systems, are essential tools for assessing the insulation strength of electrical equipment & components. These tests entail exposing the equipment to high voltage to determine its capacity to survive potential breakdowns (or) insulation failures during operation.
Applications:
Hi-Pot testing is extensively used in
- Manufacture,
- Installation,
- Maintenance, &
- Periodic inspections
for ensuring compliance with safety and reliability standards.
13). High Voltage Insulation Tester
Function:
High voltage insulation testers are devices used to determine the insulation resistance of electrical systems and components. To evaluate resistance, they apply a high voltage through the insulation & measure the current flow that results.
Advantages:
Technicians can detect insulation deterioration, contamination, (or) other problems that could cause electrical failures, breakdowns, or safety issues by testing insulation resistance.
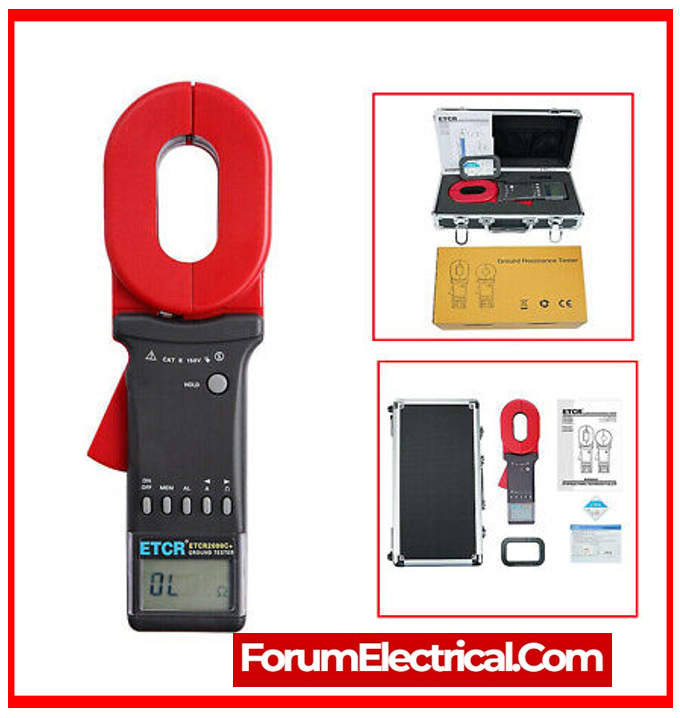
14). Earth Resistance Meter
Function:
Earth resistance meters are tools that measure the resistance of an electrical installation’s grounding system (or) earth electrode. Proper grounding is essential for providing safety, protecting equipment, & allowing fault currents to trip protection devices efficiently.
Earth resistance meters measure the resistance that exists between the grounding electrode & the earth, allowing technicians to evaluate the efficiency of grounding systems.
Advantages:
This test ensures that the resistance remains within permissible limits for electrical safety & system performance.

15). Electrical Tester
Function:
An electrical tester is a vital equipment utilized by electricians & technicians to ensure the safety and performance of electrical systems & components. These testers take several forms, including
- Voltage Testers – Voltage testers detect the existence of electrical current & monitor voltage levels, verifying that circuits are correctly powered.
- Continuity Testers – Continuity testers detect breaks (or) interruptions in the electrical circuits by detecting the presence of a current flow route.
- Multimeter – Multimeters are versatile instruments that can measure voltage, current, & resistance, generating full information on the state of electrical systems.
Advantages:
Electrical testers are important for the integrity & reliability of the electrical installations because of their capacity to identify faults, solve issues and assure compliance with safety requirements.









