1). What is the role of an Electrical Safety Engineer?
An electrical safety engineer is responsible for designing, installing, and maintaining electrical systems to avoid accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
This includes detecting risks, conducting risk assessments, & assuring adherence to safety standards such as NFPA 70E and OSHA regulations.
2). What is NFPA 70E? Why is it important?
The NFPA 70E standard governs workplace electrical safety. It seeks to reduce the possibility of electrical arc flash & shock hazards.
Compliance is critical for protecting workers & lowering the risk of electrical accidents.
3). How do you evaluate Electrical Hazards?
Electrical dangers are evaluated based on the
- Type of electrical equipment,
- Voltage levels,
- Insulation conditions,
- Moisture exposure, &
- Presence of conductive materials.
I would also perform a risk assessment to establish the probability of shock, arc flash, (or) equipment failure.
4). What is an Arc Flash and how may it be prevented?
An arc flash is a dangerous discharge of energy induced by an electrical failure.
It can result in burns, blindness, & even death.
- Proper labeling,
- Equipment maintenance,
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) use, and the
- Installation of protective devices such as circuit breakers
are all examples of preventive measures.
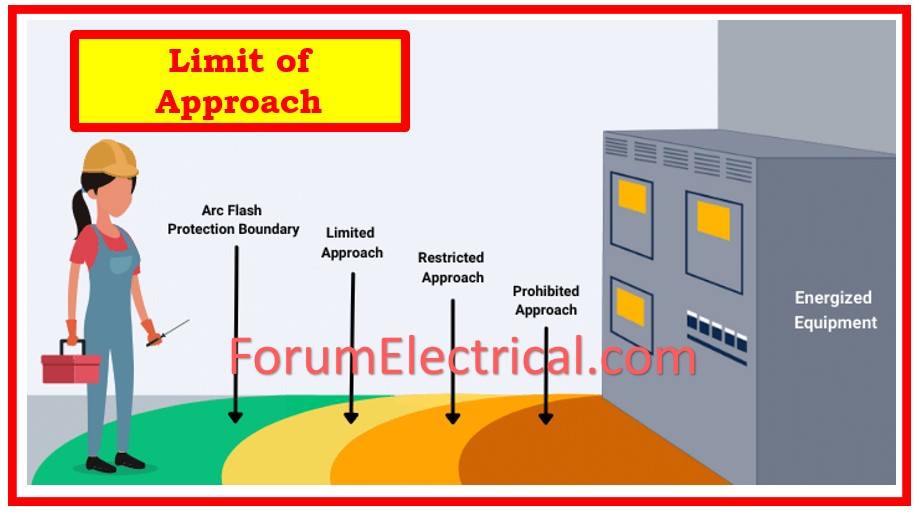
5). Explain the concept of Lockout/Tag out (LOTO) Procedures.
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures make sure that electrical equipment is entirely de-energized before performing maintenance or repairs. It protects machinery from inadvertent startup by locking power sources & labeling them with warnings.
6). What are some important safety precautions when working with high-voltage equipment?
Key safety precautions include wearing suitable PPE (e.g., insulated gloves, face shields), making sure the equipment is grounded, keeping a safe distance from live parts, and following correct isolation and lockout/tagout protocols.
7). What is the difference between Earthing and Grounding?
| Earthing | Grounding |
| Earthing connects the non-current-carrying sections of electrical equipment to the earth for safety. | Grounding connects the current-carrying element of an electrical system to the ground to maintain voltage during faults. |
8). How do you ensure compliance with OSHA standards in electrical safety?
I ensure compliance by staying current with OSHA requirements, conducting frequent safety audits, offering employee training, and ensuring that safety precautions such as PPE use, grounding, and equipment maintenance are implemented.
9). How GFCIs (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters) work?
A GFCI detects ground faults and leakage currents in electrical circuits. When it senses a current difference between the hot & neutral wires, it interrupts the circuit to avoid shock dangers.
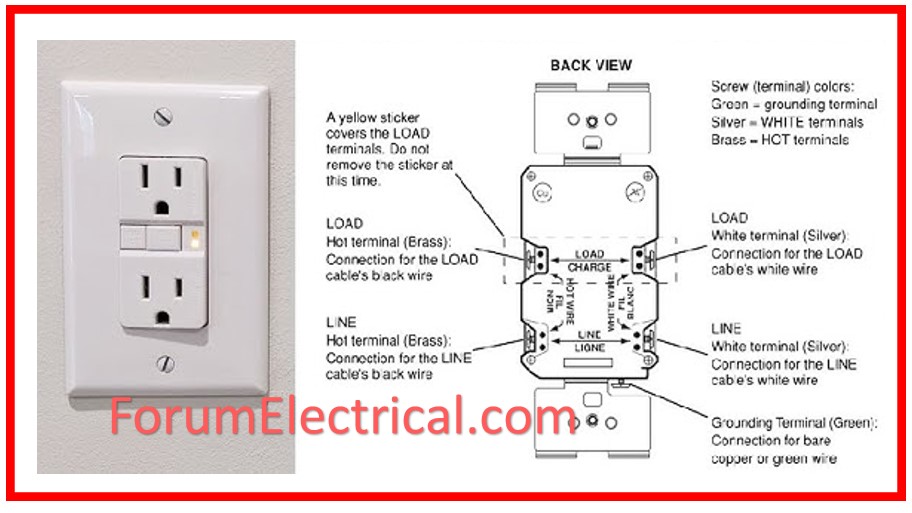
10). What is the significance of Electrical Insulation Testing?
Insulation testing ensures that electrical systems are adequately insulated, which prevents current leakage that might cause equipment damage, electrical shock, or fire dangers.
11). What steps to take if an employee got electrocuted?
First, make sure the power is switched off. Then examine the victim’s condition and, if necessary, perform CPR while promptly phoning for medical aid. I would also chronicle the incident and look into the cause of it.
12). What is the use of a circuit breaker?
When a circuit breaker detects an overload (or) short circuit, it automatically disconnects power to protect the electrical system and avoid fires.
13). What personal protection equipment (PPE) is needed for electrical work?
Depending on the voltage and work conditions, required PPE includes
- Insulated gloves,
- Flame-resistant clothes,
- Hard hats,
- Safety glasses, and
- Arc flash suits.
14). How does one do a safety audit on an electrical installation?
Initially study documents, inspect equipment, check for proper labeling, verify grounding systems, utilize appropriate PPE, and confirm compliance with applicable standards and laws.
15). What are the most prevalent causes of electrical fires, & how may they be prevented?
Common causes include
- Overloaded circuits,
- Defective wiring,
- Poor grounding, and
- Equipment failure.
- Regular maintenance,
- Good installation,
- Avoiding overloads, &
- Employing circuit breakers or fuses
are all examples of preventative measures.
16). Describe how electrical bonding works.
Electrical bonding is the process of joining conductive pieces so that they have the same electrical potential, preventing electric shocks or arcs.
17). What is an ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker), and when is it used?
An ELCB detects earth leakage currents & disconnects electricity to avoid shock dangers. It is used in high-moisture conditions or on sensitive equipment to reduce the risk of electrocution.
18). What procedures would to take to troubleshoot a faulty electrical system?
Initially isolate the circuit and make sure the power is turned off.
Before repairing or replacing broken parts, would physically inspect the system for damage, use a multimeter to test components, and ensure appropriate grounding and connections.
19). What are the most important factors in developing a safe electrical system?
Essential requirements include proper load distribution, adequate grounding, the use of protective devices (such as circuit breakers and fuses), adherence to relevant standards, & ensuring the system is accessible for maintenance.
20). How to stay up to date on electrical safety regulations?
We must stay updated by attending industry conferences, subscribing to safety bulletins, engaging in training sessions, and analyzing regulatory updates from organizations such as OSHA, NFPA, and IEC.
21). What is an RCD, and how does it improve electrical safety?
An RCD is a device that turns off a circuit when it detects an imbalance between the live and neutral wires. This prevents electric shocks and lowers the risk of electrical fires.
22). How would you manage a situation in which an employee does not follow electrical safety procedures?
I would address the problem immediately by halting the dangerous work, emphasizing the significance of safety, and offering extra training as needed.
Continuous non-compliance would be reported to management for disciplinary action.
23). What is the significance of arc-rated PPE?
Arc-rated PPE is intended to protect workers from the thermal risks of arc flashes. It protects against the extreme heat and light created by an arc, lowering the danger of burns or injuries.
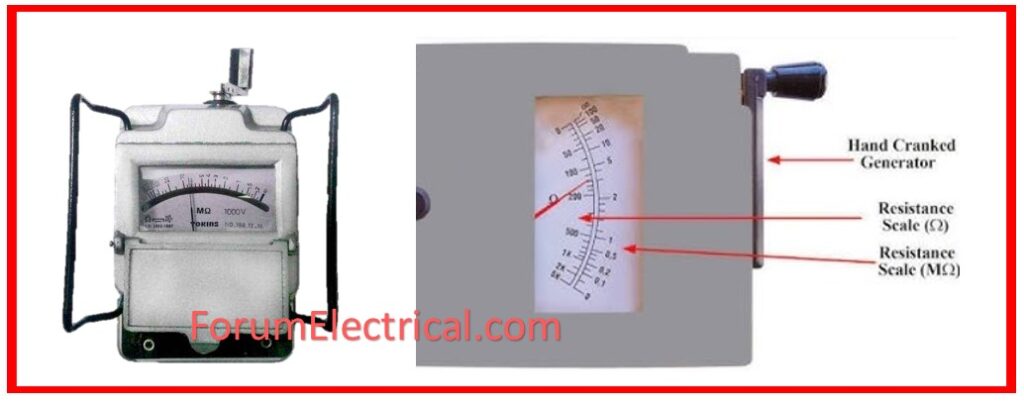
24). What is the use of a Megger in electrical systems?
A Megger measures insulating resistance in electrical systems. It assists in detecting potential insulation failures, avoiding electrical malfunctions, and assuring system safety.
25). Describe the procedure for conducting a risk assessment in an electrical environment.
The process involves
- Identifying potential dangers (e.g., live wires, wetness, high voltage),
- Determining the likelihood of occurrence,
- Estimating the potential impact, and
- Putting in place controls such as grounding, personal protective equipment, and circuit breakers to limit the risks.









