Commissioning oil-immersed shunt reactors is essential for ensuring consistent operation in power systems.
These reactors help to regulate voltage and reactive power, so protecting the grid from over voltages.
- Mechanical Inspections,
- Electrical Testing, &
- Oil Analysis
are all part of the commissioning procedure, which ensures that the reactor fulfills industry standards such as IEC 60076 and IEEE C57.
Following a defined checklist ensures that the reactor runs safely, efficiently, & is ready for operation, reducing risks and increasing equipment lifespan.
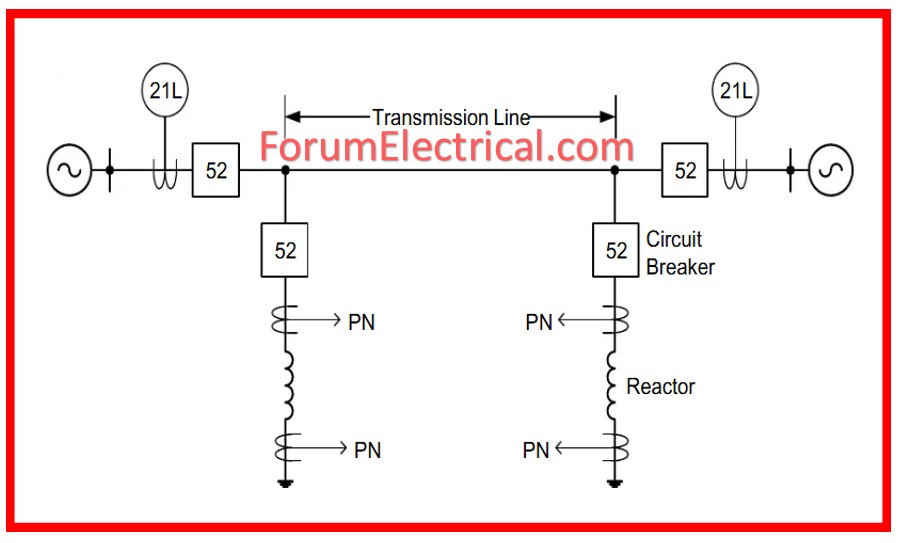
1). Equipment. General Data & Information
Before commissioning, it is essential to obtain all relevant equipment information of shunt reactor.
This involves documenting the substation’s name, panel number, equipment specifications, and serial number.
This documentation verifies that the equipment being commissioned meets the required specifications and installation plans.
Correct identification is also necessary for future use and maintenance.
2). Mechanical Check and Visual Inspection
A thorough mechanical & visual inspection guarantees that the reactor & all of its components are properly installed and in good working order prior to energization.
Key checks include:
Impact Recorder: Inspect the impact recorder for any odd impacts during transportation that may have resulted in internal damage.
Component Installation: Check that all components are installed accordance to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Paint & Structural Integrity: Inspect the reactor for paint quality, rust patches, lifting lugs, weld regions, and secure wheel stoppers.
Nameplate Verification: Confirm that the nameplate information is visible, waterproof, and meets the contract standards.
Grounding: Make that all grounding connections are properly constructed, with at least 2 grounding terminals connected to the main tank, as specified by standards such as IEEE 80 for substation grounding.
Buchholz Relay: After testing, ensure that a two-stage Buchholz relay is properly installed and in service mode.
Valves and Bushing Requirements: Check that valves connecting the tank and radiator are open, and that bushings meet minimum creepage and insulating requirements, using standards such as IEC 60137 for bushings.
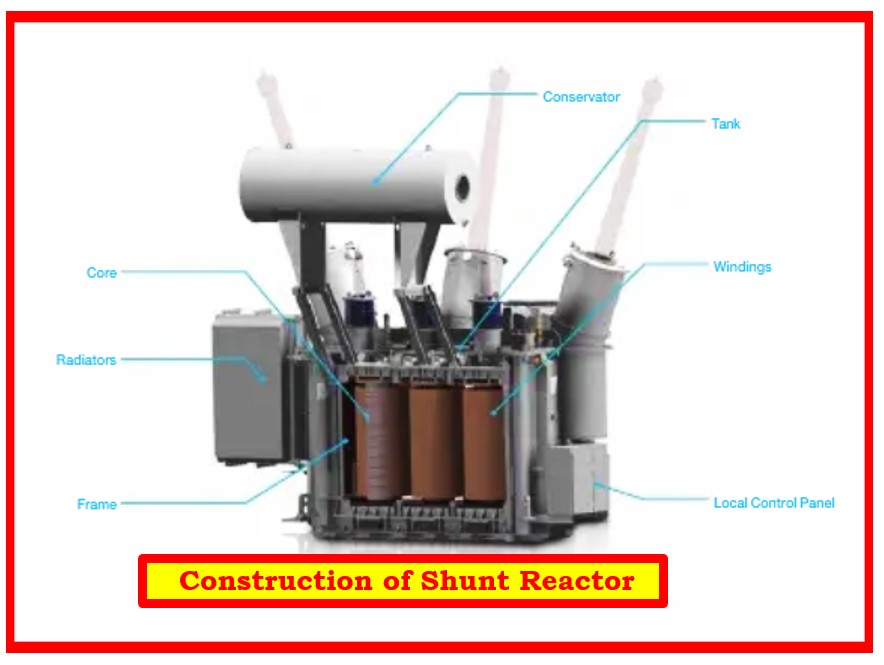
3). Electrical Tests
Before the equipment is turned on, electrical testing must be performed to ensure its integrity and insulation.
Some of the essential tests are:
Insulation Resistance Tests: At 5 kV DC, measure the winding insulation resistance (IR Value) & polarization index (PI), which should be greater than 1.5 according to IEC 60076-3 transformer standards.
Winding Resistance: Measure & record the winding resistance to check that the windings are properly connected and not damaged.
Dissipation Factor Measurement: Use a tan delta test to determine the dissipation factor in insulation system, using standards such as IEC 60247.
Temperature Indicator Calibration: Calibrate the winding temperature monitor to achieve accuracy of ±0.5% of the range (20-160°C). This step is necessary for fan, alarm, & trip settings.
Leakage Test: Perform a pressure test to detect leaks. Apply a pressure at least 35 kPa higher than the typical oil pressure and maintain it for 24 hours, with no oil leaks allowed, according to IEEE C57.12.90 for pressure testing in transformers.
a). Functional Checks
Functional tests are required to ensure that all auxiliary systems & safety devices are operating.
Fan & Pump Functionality: Test the fan motors to confirm the current is within the rated range, and double-check the phase sequence to guarantee appropriate airflow direction toward the radiator.
Current Transformer Testing: Test the bushing CTs’ polarity, insulation resistance, & current ratio, as well as magnetization characteristics, in line with IEC 60044 instrument transformer standards.
Alarm/Trip Devices: Check the functionality of essential alarm and trip devices such as the Buchholz relay, pressure relief devices, oil temperature indicators & winding temperature devices.
b). Oil Tests
The reactor’s oil must be examined before it is turned on to ensure that it has enough insulating characteristics.
Independent laboratory tests must be conducted on parameters such as
Dielectric Strength: This test is critical for determining the oil’s ability to tolerate high voltage without breakdown, as recommended by IEC 60156.
Neutralization Number: This evaluates the acidity of the oil, with lower levels indicating higher quality, according to ASTM D974.
Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detect gas levels in the oil to determine probable internal problems using IEC 60599 standards.
Moisture Content: Check for moisture in the oil, as it can drastically impair insulation. Regarding water content in oil, refer to IEC 60814.
c). Final Inspection & Documentation
After completing all tests and checks, thoroughly document the results. This includes confirming insulation resistance levels, checking control wire requirements, and ensuring that all devices and components operate within the required limits.
Final certification should be based on results that fulfill industry standards, such as IEC 60076 for power transformers & related equipment.
This methodical approach to commissioning assures that the oil-immersed shunt reactor is ready for secure and dependable operation while adhering to international performance, safety, and quality standards.









