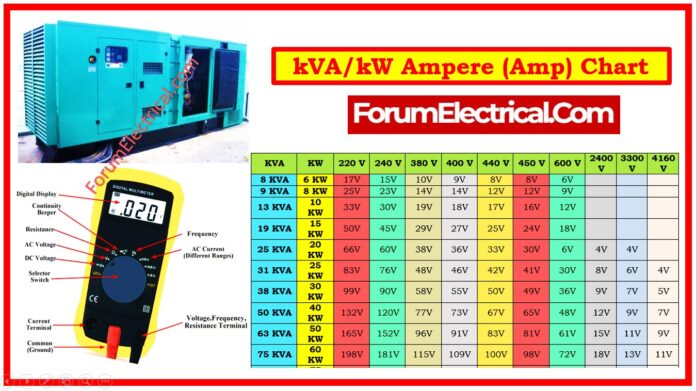
This chart is simply a calculation of how many amps the generator generates when it is running; many factors can raise (or) lower the amount.
KVA/KW Ampere Conversion Chart
This chart calculates a generator’s output amperage depending on its operational power and voltage.
Please keep considering that this table is only an estimate of how many amps a generator produces while in operation and is not an accurate representation owing to different factors that can cause this amount to increase or decrease.
80% Power Factor
| KVA | KW | 220 V | 240 V | 380 V | 400 V | 440 V | 450 V | 600 V | 2400 V | 3300 V | 4160 V |
| 8 KVA | 6 KW | 17V | 15V | 10V | 9V | 8V | 8V | 6V | |||
| 9 KVA | 8 KW | 25V | 23V | 14V | 14V | 12V | 12V | 9V | |||
| 13 KVA | 10 KW | 33V | 30V | 19V | 18V | 17V | 16V | 12V | |||
| 19 KVA | 15 KW | 50V | 45V | 29V | 27V | 25V | 24V | 18V | |||
| 25 KVA | 20 KW | 66V | 60V | 38V | 36V | 33V | 30V | 6V | 4V | 4V | |
| 31 KVA | 25 KW | 83V | 76V | 48V | 46V | 42V | 41V | 30V | 8V | 6V | 4V |
| 38 KVA | 30 KW | 99V | 90V | 58V | 55V | 50V | 49V | 36V | 9V | 7V | 5V |
| 50 KVA | 40 KW | 132V | 120V | 77V | 73V | 67V | 65V | 48V | 12V | 9V | 7V |
| 63 KVA | 50 KW | 165V | 152V | 96V | 91V | 83V | 81V | 61V | 15V | 11V | 9V |
| 75 KVA | 60 KW | 198V | 181V | 115V | 109V | 100V | 98V | 72V | 18V | 13V | 11V |
| 94 KVA | 75 KW | 247V | 226V | 143V | 136V | 123V | 120V | 90V | 23V | 16V | 13V |
| 100 KVA | 80 KW | 264V | 240V | 154V | 146V | 133V | 130V | 96V | 21V | 18V | 14V |
| 125 KVA | 100 KW | 330V | 301V | 192V | 182V | 166V | 162V | 120V | 30V | 22V | 18V |
| 156 KVA | 125 KW | 413V | 375V | 240V | 228V | 208V | 204V | 150V | 38V | 27V | 22V |
| 187 KVA | 150 KW | 495V | 450V | 288V | 273V | 249V | 244V | 180V | 45V | 33V | 26V |
| 219 KVA | 175 KW | 577V | 527V | 335V | 318V | 289V | 283V | 211V | 53V | 38V | 31V |
| 250 KVA | 200 KW | 660V | 601V | 384V | 364V | 332V | 324V | 241V | 60V | 44V | 35V |
| 312 KVA | 250 KW | 825V | 751V | 480V | 455V | 415V | 405V | 300V | 75V | 55V | 43V |
| 375 KVA | 300 KW | 990V | 903V | 576V | 546V | 498V | 487V | 361V | 90V | 66V | 52V |
| 438 KVA | 350 KW | 1155V | 1053V | 672V | 637V | 581V | 568V | 422V | 105V | 77V | 61V |
| 500 KVA | 400 KW | 1320V | 1203V | 770V | 730V | 665V | 650V | 481V | 120V | 88V | 69V |
| 625 KVA | 500 KW | 1650V | 1504V | 960V | 910V | 830V | 810V | 602V | 150V | 109V | 87V |
| 750 KVA | 600 KW | 1980V | 1803V | 1150V | 1090V | 996V | 975V | 721V | 180V | 131V | 104V |
| 875 KVA | 700 KW | 2310V | 2104V | 1344V | 1274V | 1162V | 1136V | 842V | 210V | 153V | 121V |
| 1000 KVA | 800 KW | 2640V | 2405V | 1540V | 1460V | 1330V | 1300V | 962V | 241V | 176V | 139V |
| 1125 KVA | 900 KW | 2970V | 2709V | 1730V | 1640V | 1495V | 1460V | 1082V | 271V | 197V | 156V |
| 1250 KVA | 1000 KW | 3300V | 3009V | 1920V | 1820V | 1660V | 1620V | 1202V | 301V | 218V | 174V |
| 1563 KVA | 1250 KW | 4130V | 3765V | 2400V | 2280V | 2080V | 2040V | 1503V | 376V | 273V | 218V |
| 1875 KVA | 1500 KW | 4950V | 4520V | 2880V | 2730V | 2490V | 2440V | 1805V | 452V | 327V | 261V |
| 2188 KVA | 1750 KW | 5280V | 3350V | 3180V | 2890V | 2830V | 2106V | 528V | 380V | 304V | |
| 2500 KVA | 2000 KW | 6020V | 3840V | 3640V | 3320V | 3240V | 2405V | 602V | 436V | 348V | |
| 2812 KVA | 2250 KW | 6780V | 4320V | 4095V | 3735V | 3645V | 2710V | 678V | 491V |
In simple terms, kW is the amount of power an electrical device generates, and kVA is the amount of current it consumes.
Kilowatts (kW)
In the metric system, one kilowatt is equivalent to 1,000 watts. It refers to the real power generated by a machine, such as an engine (or) a gas generator.
Kilovolt-Ampere (kVA)
This measurement is more commonly used outside of the United States. It shows the apparent power generated, which is the amount of power used by the system.
- In a direct current (DC) system, the 2 numbers are the same.
- In alternating current (AC) systems, the current can become out of phase with the voltage, reducing system efficiency. In such circumstances, you’ll use less electricity than you’re generating.
Phase Amperes Explanation
Generators (sometimes known as gensets or “generator sets”) are classified into two types: single-phase & three-phase devices.
Single-Phase AC Generators
Single-phase AC generators are often utilized when you don’t require a lot of electricity and don’t want a generator that operates constantly. They work between 120 and 240 volts. They’re suitable for domestic use, so if you require a generator for the house, they can deliver efficient and cost-effective power.
To compute the generator’s kVA for a single-phase current, multiply volts by amps and divide by 1000.
To calculate kW, multiply volts x amps by the power factor (PF), which is the ratio of actual power flowing to perceived power, and divide by 1000.
Three-Phase AC Generators
Three-phase currents provide alternating current power and normally run at a much greater voltage, around 480 volts. With single-phase generators, they generate power in three waves, resulting in continuous output. Commercial generators are typically utilized for heavy-duty applications, such as powering industrial & agricultural projects & operations.
To determine the kVA of a 3-phase system generator, multiply volts x amps by 1.73, then divide by 1,000.
To compute kW, multiply volts x amps x 1.73 x PF (the ratio of actual power flowing to perceived power) and divide by 1000.
Click here for kW to Amps Calculator
Click here for kVA to Amps Calculator
Click here for Electrical Calculators