With the help of this calculator, you can determine the resistivity of a component by taking into account its resistance value, length, & cross-sectional area.
What is Resistivity?
A material’s resistivity can be defined as the amount of resistance it can provide to a current dependent on the dimensions of the material. Due to the reason that every type of material has its own resistivity values, this is something that is genuinely inherent to a particular material. In most cases, we determine the resistance R of the material by taking into account its resistivity and dimensions.
With the assistance of our resistivity calculator, you will be able to determine the resistivity of a material, which is a function of the material’s resistance value, length, & cross-sectional area.
Formula
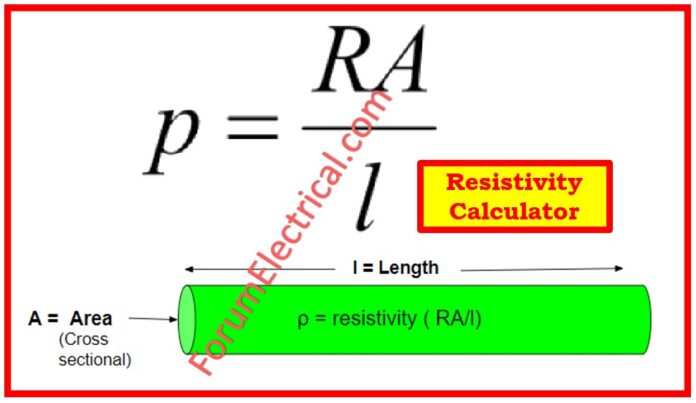
ρ = RA/L
Where
ρ – Resistivity of the material expressed in ohm-meters (Ω-meters)
R – Resistance of the substance is measured in ohms (Ω)
L – Length of the material in (m2)
A – Material’s cross-sectional area expressed in square meters (m2)
Based on the formula, it is possible to determine that the resistivity of a material is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area of the material, whereas its length is inversely related to the resistivity. What this indicates is that a material will have a higher resistivity rating if it has a shorter length or a larger cross-section. At the other end of the spectrum, a material that has a longer length or a smaller cross-section will have a lower resistivity rating. The resistivity of the material is directly proportional to its resistance, which is another component that performs an integral part.
In general, conductors have a low resistivity, whereas insulators have a high resistivity.
Conductivity, which is typically represented by the symbol σ, is the reciprocal of resistivity.
σ = 1/ ρ
Applications of Resistivity Calculator
- Assists in selecting materials with the suitable resistivity for effective power transmission and low energy loss.
- Used to test components such as resistors to ensure they satisfy the required resistivity for performance.
- High resistivity materials generate more heat, which is essential to consider when building heating elements for ovens and toasters.
- In the industrial sector, increases in resistivity over time might indicate corrosion in metal pipes (or) structures.
- Resistivity measurements assist in the identification of distinct layers underground, which is useful for water resource management and oil exploration.
- Required for designing and manufacturing semiconductors, where regulated resistivity is critical for device performance.
Click here for more Electrical Calculators