What distinguishes a cable from a wire? One of the fundamental questions that still has to be explained .
The cable remains to be a single conductor, which is referred to as a wire, if there was no insulation on two conductors.
Cable is a collection of two (or) more insulated conductors, whereas wire is a single conductor.
A wire is typically a single strand or a number of strands of conductive material, such as copper or aluminium, whereas a cable is made up of two (or) more insulated wires enclosed in the jacket. The main difference between the two is that a cable is typically insulated whereas a wire is typically visible.
The post explains in detail about major difference between wire and cable.
What is Wire?
A wire is a single (one) conductor strand (or) a collection of conductor strands that are encased in an insulating jacket to prevent the conductors from creating undesired connections.
Wires are typically used to transmit electrical & telecommunications signals, & they may also support mechanical loads.
Wires can be classified into two types:
- Solid wire and
- Stranded wire.
1). Solid Wire
A solid wire is a lengthy length of a single conductor. Solid wires have low resistance and are therefore suited for usage at higher frequencies. It requires flexibility.
2). Stranded Wire
A stranded wire is made up of numerous thin strands of conductor twisted together.Stranded wires are more flexible and, as a result, last longer.
Furthermore, stranded wires have a higher cross-sectional area than the solid wires have for the same current carrying capacity.
This wire is more flexible and has a longer flex lifespan before getting unusable.
What is Cable?
A cable is often made up of two or more wires that have been connected, twisted, or braided together. They are generally insulated to provide more protection than wires alone.
Cables are mostly used for power transmission as well as the transfer of electrical & telecommunications signals.
Cables can be found in a variety of types, including
- Multi-conductor cable,
- Fiber optic cable,
- Twisted pair cable and
- Coaxial cable
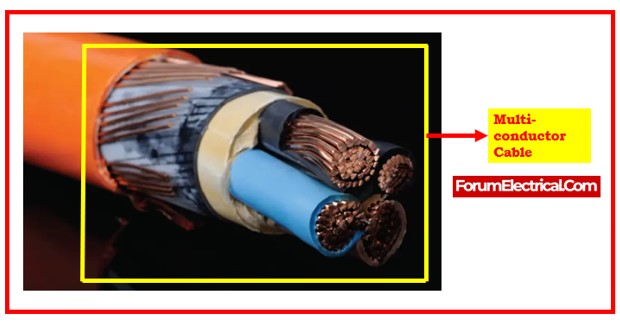
1). Multi-conductor Cable
Multi-conductor cable is a type of cable that has numerous insulated conductors & is used to protect the integrity of the signal by lowering hum, noise, and crosstalk. Although it is frequently used in control applications, this kind of cable is rarely ever employed in signal applications.
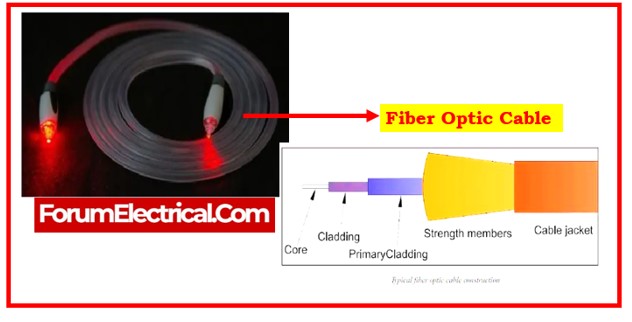
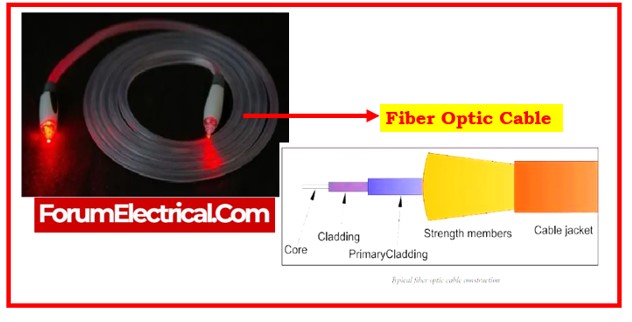
2). Fiber optic Cable
Fiber optic cables use an array of glass threads to carry signals. These cables have a far higher bandwidth than the metal cables, allowing them to transmit more data.
- Plastic fiber,
- Multimode fiber, &
- Single mode fiber
are the three types of fiber optic cable.
Plastic Fiber: Plastic fiber is the largest type of fiber in fiber optic cable and is constructed of plastic. It is commonly utilized in high-end audio communications.
Multi-mode Fiber: Multimode fiber is a type of glass fiber that varies in diameter and is utilized in the data network.
Single mode fiber: Since the fiber is small to see without a microscope, single mode fiber is considered the best fiber cable. This fiber provides the best performance however is extremely difficult to attach due to its size and hardness.
3). Twisted pair Cable
Twisted pairs cable is made up of twisted together pairs of conductors. This cable is designed exclusively for signal transmission. The type of cable was designed in the 1880s specifically for the purpose of connecting up early telephonic systems. Twisting the conductor pairs provides some interference protection to the cable.
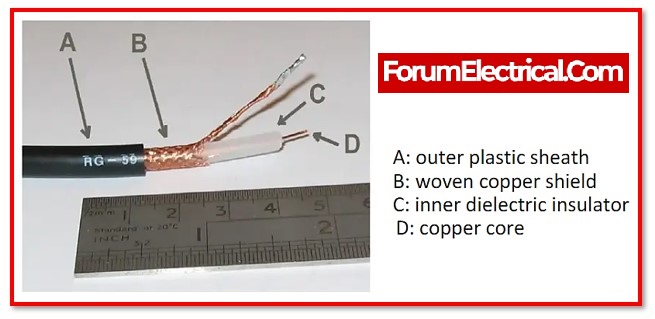
4). Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable is typically used in TV Cable and is composed of an inner solid conductor encircled by a parallel outer foil conductor, shielded by an insulating layer.
The other common cable configuration is coaxial cable. Because the shield carries both the ground and the signal in coaxial cable, the signal on two conductors is not identical.
This arrangement of the line is an unbalanced line as the signal is not identical on both conductors.
Coaxial cable does not possess the same protection to interference as twisted pairs cable, but because coaxial cable is knitted together, the performance may be much more steady than with the twisted pairs cable.
Wires Vs Cables
| Parameters for comparison | Wire | Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements | Several stranded conductors or a solid conductor constitute a wire. | Two (or) more conductors are twisted together and wrapped in insulation to form cables. |
| Characteristic | The jacket is placed over a single conductor that is either insulated or bare. | Two (or) more insulated wires are wrapped in one jacket to form a cable. |
| Types | Solid Wires: Wire conductor with only one strand. Stranded Wires: A conductor made up of many tiny wires that have been bundled or wrapped. | Twisted Pair Cable: Cable with two conductors twisted together. Multi-conductor Cable: Cable with more than a single conductor is known as multi-conductor cable. Coaxial Cable: A cable with two layers. Fiber Optic Cable: A network of optical fiber-based wires is known as fiber optic. |
| Advantages | Ensure Safety & Stability & Versatility | Stronger, more durable, and insulated. |
| Solid wires have low resistance, making them ideal for usage at higher frequencies. The resistance of stranded wire to metal fatigue is higher. | Different types of cables have different type of insulation for protection. | |
| It is strongly advised to utilize an extremely strong cable with superior insulation for long distance use. | It is strongly advised to utilize an extremely strong cable with superior insulation for long distance use. | |
| Disadvantages | Motors, tiny equipment, & house improvement cannot use large diameter wire. | More costly than wire. |
| Applications | To support mechanical loads, transport electrical and telecommunications signals, heat, jewellery, clothing, mesh, components made for automobiles or other industries, pins, needles, and fishhooks, among other things. | Power transmission is needed for transmitting electricity, telecommunications signals, large buildings, and heavy machinery. |