- What is a Vehicle Battery?
- Components of Vehicle Battery
- How the Power is generated by the Battery?
- Functions of a Vehicle Battery
- What is meant by “Cold Cranking Amps”?
- Why does Battery Downs?
- Different Types of Vehicle Battery
- Why do the batteries in vehicles have a voltage of 12 volts?
- How a car battery starts a car?
- What are the 5 functions of a car battery?
- What type of battery is a car battery?
What is a Vehicle Battery?
A battery that can be recharged and provides a motor vehicle with electrical power is referred to as a vehicle or an automobile battery. It is also known as a SLI battery, which stands for starting-lighting-ignition, and its primary function is to turn the ignition on in a motor vehicle.
The primary function of a vehicle battery is to provide the necessary electricity for starting the vehicle. When the engine is turned off, it supplies electricity for short-term usage of devices like the lights, audio, GPS, or windscreen wipers.

It also serves as a surge protector for the computer in the vehicle.
Components of Vehicle Battery
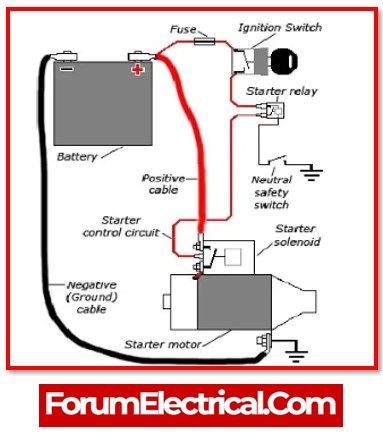
1). Ignition Switch

2). Starting Relay
The starting relay, which is also known as a solenoid, is under the control of the switch. When crank the ignition, a modest electrical current flows to the starting relay via the ignition switch. Because of this, a pair of contacts have been connected.
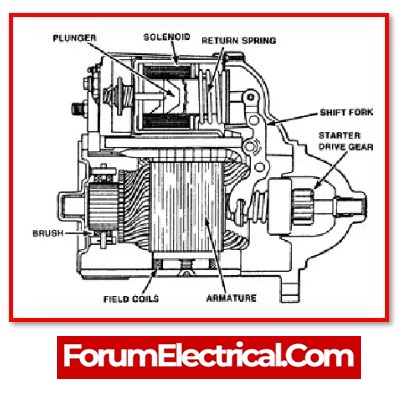
3). Starter Motor
When the contacts come together, the battery transfers electricity to the starter motor. This causes the starter motor to move several gears, which allows the vehicle to be started.
A vehicle’s starting system includes the battery as a component.
How the Power is generated by the Battery?
- Flooded Batteries and
- AGM Batteries
which are the two types of batteries used in vehicles, are powered by lead-acid technology. Plates composed of lead are found inside of a conventional lead-acid automobile battery. These lead plates are interspersed with plates made of other materials, and the whole battery is submerged in an electrolyte solution that is approximately one third sulfuric acid & two-thirds water.
When turn on the ignition, the acid in the liquid electrolyte solution is prompted to react with active material on the plates i.e., active material corresponds to any component in the battery that interacts with the solution to discharge or replenish the battery. A greater amount of electrical current is generated as a result. The current performs a series of reactions as it makes its way through the starting mechanism, which ultimately causes the engine to start turning over.
Functions of a Vehicle Battery
The battery in the vehicle is responsible for a number of important operations; the following are some of the most important functions of a vehicle battery, which may assist recognise its significance.
1). Engine starter
2). Operation of the ignition system
A vehicle’s battery does not simply turn the engine on and get it operating when it’s time to start the vehicle; it also turns on the ignition system. It connects the energy throughout the entire car and activates all of its safety measures. If there is anything wrong with energy system, determining out about it at that point is usually when it will be found. When the engine is turned off, the energy that powers all of the electrical components in the vehicle comes from the battery.
3). Sustainer
If a battery operates, it ensures that the energy system in a vehicle will continue to function sustainably. After starting the vehicle, an alternator will begin (start) to recharge the battery to ensure that everything continues to function normally while driving. In addition, the battery will begin to store chemical energy once again so that it will have enough to start the engine of the vehicle the next time it is needed. The newer types of batteries are equipped with features that not only shield them from corrosive harm for an extended period of time but also stop them from being completely depleted of their stored energy.
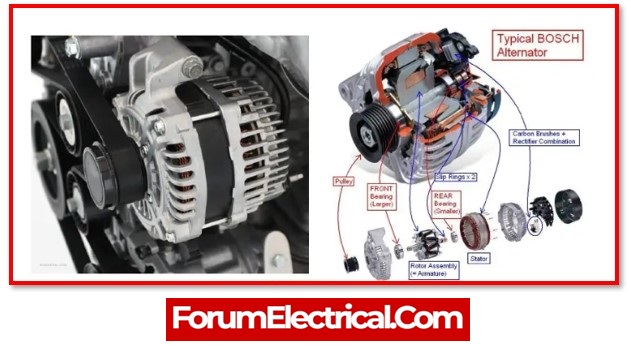
4). Alternator
In its most basic form, the alternator may be regarded as a generator. In order for the starter to be able to turn the engine over, it needs an initial surge of energy, which is supplied by the battery. However, the alternator serves as the component that keeps the electronics functioning and is responsible for charging the battery. Due to the fact that the alternator always maintains a charge on the battery, a vehicle’s battery will not frequently discharge while the vehicle is being driven.
An alternator consists of
- A stator,
- A rotor,
- Diodes,
- A voltage regulator, and
- A cooling fan.
When the vehicle is operating, the alternator is continually working to maintain the flow of energy through the engine and the rest of the vehicle.
In addition to this, a battery is responsible for transferring power to an alternator, which, in case it is operating correctly, is in charge of electric features such as
- The sound system,
- The air conditioning,
- The wipers,
- The headlights, and even
- The airbag system
it is also the component that keeps the automobile going after the engine has been started. Then, in the event that an alternator has any type of failure or overwork, a battery may operate as a backup and allow the machine to continue functioning for some time. Subsequently need to add certain accessories to the vehicle and they need energy, such as additional lights or tools, then will need a battery that is in good condition. This is very important.
5). Voltage regulator
When this happens, other systems in the vehicle might get overworked and create high voltage spikes, which, under normal circumstances, would do the car an extensive amount of damage (they could even catch fire).
However, a contemporary battery has the ability to soak up some of the extra power that may be generated by other components. All of the solid components & the whole electric system are shielded from the possibility of suffering harm as a result of an abnormally high voltage.
It can be seen, a few of the most important tasks of the vehicle, and they are all dependent on this one, rather tiny battery in order to remain operational.
There are many different kinds of batteries, such as ones that can withstand even the worst winters without having trouble starting the engine, but if remain in a warm region, have no concern about possessing one of these specialised batteries or apply standardised batteries for vehicle.
What is meant by “Cold Cranking Amps”?
The amount of power that a battery can give for a period of thirty seconds even when the temperature is below freezing is referred to as the cold cranking amps (CCA). Starting a vehicle on a chilly day or with a larger engine requires a greater amount of power than starting the vehicle on a warm day.
Standard vehicle batteries need to have a high CCA rating if they are to be used in regions that experience temperatures below zero. This is because severely depleted wet cell batteries may solidify at temperatures below zero.
Why does Battery Downs?
A battery will go through thousands of cycles of discharging and charging over the course of its lifetime. The plates get slightly more corroded with each cycle, and the lead gradually loses its quality with time. The number of cold cranking amps produced by a vehicle’s battery drops as its capacity decreases.
A significant number of battery problems may be traced back to the attempt of deep draining, which occurs when the battery is used to power the vehicle’s audio, lights, or other electrical equipment while the engine is turned off. It is possible for the sulphur in the electrolyte solution to adhere to the lead and cause other damage to plates in the battery if a significant portion of the battery’s capacity is depleted by using it in this way for an excessive amount of time. The battery may then be recharged by driving the vehicle.
Different Types of Vehicle Battery
- Standard wet cell batteries and
- Absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries
are the two types of batteries for vehicles that are distributed . Both make use of technology based on lead acid. The requirements of the automobile are different from one another.
1). Standard Wet Cell Batteries
These batteries also known as flooded, conventional, and SLI, which stands for starting, lights, and ignition. These types of conventional batteries may be referred to as vented batteries because they contain vents that enable corrosive gases, steam, & moisture to be released into the air. They feature caps that can be removed so that fluid may be added. Other types of wet cell batteries are closed systems that do not have caps that may be removed.
Service Requirements: It involve carrying out regular tasks such as removing corrosion from the terminals and filling out the fluid with distilled water if the battery has detachable caps. A visual inspection of the battery has to be performed once each year. Before embarking on a road trip, as well as after the summer but before the temperatures start to drop, the battery charge should be checked.
2). Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
These are one of the type of VRLA batteries. VRLA is an abbreviation that means valve-regulated lead-acid. They are also known as dry cell batteries, non-spillable batteries, sealed batteries, and controlled valve batteries. They are referred to be sealed because the caps are not detachable, they do not allow gases to escape, and they do not allow any acid to flow out. They do feature pressure-activated relief valves, but the only time those valves will open is if the battery becomes too hot while it is being charged.
AGM batteries are required in some contemporary vehicles, such as those equipped with start-stop technology. Even after the engine is turned off, these batteries will continue to provide power to the vehicle’s computer and other electrical components.
Standard wet cell batteries lose their charge far more quickly than AGM batteries do. When compared to flooded batteries, they are better able to withstand long periods of non-use as well as multiple cycles of severe discharge and recharge. They have a quick recharge time, but they are quickly destroyed if they are charged over their capacity. Additionally, they function admirably even in severe environments with extremes of temperature.
Service Requirements: It include double-checking the charge before to long car rides and again after the summer, just before the temperatures start to drop.
Wet cell batteries & AGM batteries cannot be switched out for one another; vehicle needs either any one type of battery.
Why do the batteries in vehicles have a voltage of 12 volts?
Ohm’s Law states that the quantity of current that must be present in a circuit is proportional to the voltage, and that if the voltage is doubled, only half as much current is needed. Consider it another way, more current needs cables that are bigger. As a result, the switch to 12 volts resulted in a reduction in the amount of copper that was required to transmit electricity throughout the vehicle.
How a car battery starts a car?
When switch the key in the ignition of the car, a signal is sent to the battery, instructing it to begin the chemical reaction that needs to be occurred. The chemical reaction generates electrical energy, which is subsequently used to power the starting motor, which is responsible for turning the engine over.
What are the 5 functions of a car battery?
5 Key Functions Of the car battery are,
1). Engine starter,
2). Helper to the ignition system
3). Sustainer
4). Alternator
5). Voltage regulator
What type of battery is a car battery?
Six-cell wet cell batteries comprise car batteries. A lead storage battery cell has alternating plates consisting of a lead alloy grid filled with sponge lead (cathode) or coated with lead dioxide (anode). Electrolyte sulfuric acid fills each cell.