Megger is a brand name under which one can find various types of Insulation Tester.
Because this brand is so popular, in this article we often refer to this term as Insulation Tester and Megger value as Insulation Resistance value.
As of to date, there are various other make of Insulation Testers in the market and hence, it is better to refer to it as Insulation Tester rather than Megger.
Let it us now focus the attention on why Megger or Insulation tester has a DC Generator?
Insulation Test is performed to get the insulation resistance (IR). In this test, HV lead of the test kit is connected to the conductor and LV lead is connected to the ground.
Ex: In case of cable, the HV lead will be connected at conductor and LV lead at ground.
The kit delivers high voltage of 250V, 500V, 1000V or 5KV depending on cable voltage rating.
This high voltage as results in leakage current through the insulation. This leakage current is used by the kit to determine various IR values of the connected source.
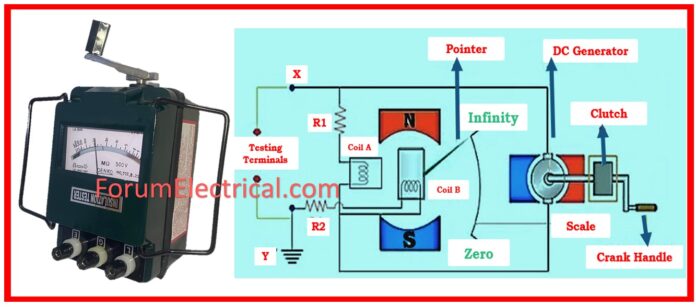
Megger Working Principle
The megger has a DC generator integrated within it. The DC generator may be of the manual type of electronic.
It develops a high direct current voltage.
The positive lead of the megger has its connection with some current carrying part of the circuit.
The negative lead of the megger is connected to the body of the equipment and the positive lead is connected to the outer terminal of the equipment.
Let,
V – Voltage of the DC generator and
R – Insulation Resistance
Then the value of megger or insulation resistance from the equipment under test is,
R = V/I
This test can be done using AC voltage or DC voltage, in order to measure the insulation resistance. How we use DC voltage for the measurement of IR.
Importance of DC Generators in Meggers
A Megger is equipped with a DC generator because Direct Current (DC) is very important in the measurement of insulation resistance.
Here are the key reasons:
1). Elimination of Capacitance Effects
2). Prevention of Reactive Component Influence
3). Polarization & Dielectric Absorption
4). Safety & Compatibility
5). Compact Design & Durability
1). Elimination of Capacitance Effects
Another factor that hampers AC is that it results in capacitive charging currents in the insulation required for resistance measurements. DC overcomes this problem, ensure steady and correct voltage levels.
2). Prevention of Reactive Component Influence
AC makes it somewhat challenging to distinguish more actual resistance from impedance due to the presence of reactance brought in by capacitance and inductance by the introduction of reactance. DC evades this since there is no notion of reactance in the procedure.
3). Polarization & Dielectric Absorption
The insulation materials have polarizing properties as well as dielectric absorption whenever DC is imposed. These effects offer information of the state of the insulation, which AC has been unable to yield conveniently.
4). Safety & Compatibility
HVDC is relatively safer than the AC for the insulation testing since the testing results in leakage currents and can probably damage the insulation.
5). Compact Design & Durability
An independent DC generator that is hand cranked in the older models of Meggers makes the device portable conveniently powering the tests especially in field conditions guaranteeing the most reliable operation under diverse situations.
Therefore, a DC generator in a Megger facilitates accurate, free from interference and safe insulation resistance measurements vital in ensuring electrical equipment reliability.
Why Is DC Voltage Preferred in Megger Testing?
Initially, the current flow mechanism of the insulators must be cleared before we define the concept of its use.
- No current can flow through the insulator when an applied DC voltage across it is below that of the break-over voltage of the insulator.
- Therefore, it will be safe to say that capacitor operates like a low value capacitor.
- The reactance provided by the insulator is very high as a consequence, the amount of current passing through it is extremely low.
- The insulator provides lower reactance when AC is passed through it( Xc=1/2πfc) because of the reason of high frequency.
- Consequently, the current passing through the it is sum of leakage current and current flowing due to lower reactance of insulator.
- It should be noted that these two types of current do not actually reflect the value of insulation resistance through the insulator.
- This is why insulation resistance is measured correctly with the use of DC voltage.
- An ideal insulator becomes very high-reactive when AC voltage is passed through the insulator.
- Therefore the insulator eliminates it and the current has zero amps.
- Regarding the case of DC voltage, the current that flows through the insulator provides the correct measurement of the current & thus the insulation resistance that has been measured is perfect.
Why DC Meggers Are Ideal for Winding Insulation Tests?
DC is employed here because there is need to measure only the resistance of the insulation of the winding.
If we employ the AC to perform the insulation test, we shall be operating in the impedance level as insulation possesses a considerable capacitive reactance insulation.
However, if we are to employ AC in performing the insulation test, the result obtained will be the impedance since the insulation has a very high capacitive reactance.
It may therefore be said that the health of the winding is best measured by the amount of resistance and not impedance. This is the reason only DC is used for the measurement of the insulation resistance only.