- What is Single Phase?
- What is Three Phase?
- Why is 440V used for Three Phase?
- Why 440V in three phases rather than 660V or 690V?
- What is the purpose of 440 volts?
- If a single-phase circuit is 230V, why is a three-phase circuit 440V and not 690V?
- Difference between single-phase & three phase
- Difference between 415V & 440V
What is Single Phase?
An electrical system with only one source of alternating voltage is called a single-phase system.Single-phase uses only two wires, or conductors: a “phase” wire and a “neutral” wire.It is between a phase and the neutral that voltage is measured.
Single Phase Voltage = 230V i.e., Phase to Neutral
Phase VoltageVPH = Line Voltage /√3 = VL/√3
= 400V /√3 ≈ 230V
What is Three Phase?
In an electrical system, the voltage between any two of those three phases is referred to as the three-phase system.In a three-phase supply, there are three supply lines, all of which are phase-shifted by an angle of 120 degrees relative to one another.Consequently, there is a net voltage differential of 440 volts between the two phases, which corresponds to a phase angle of 120 degrees.
Three Phase Voltage = 400V
i.e.,Line to Line (or) Phase to Phase
Line Voltage VL = √3 x Phase Voltage = √3 xVPH
= √3 x 230V = 398V ≈ 400V
Why is 440V used for Three Phase?
When consider 230V single phase voltage, they simply increase it by three for three phase addition, as seen below:
230V + 230V + 230V = 690V
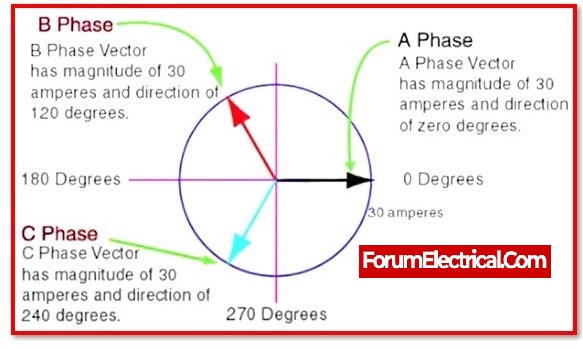
However, this is inapplicable in the case of a three-phase power supply system. Because the EMF produced in three phase systems is a vector (most likely a phasor, which can be simplified by phasor diagrams) quantity with magnitude and direction. The vector difference between two 230V lines is 400V.
In this particular instance, the phasor or vector quantities that have a phase difference.
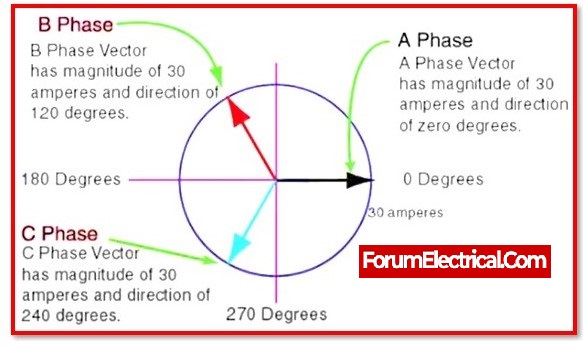
Based on the phasor diagram for a three-supply system, where each line has 230V, the vector difference is about 400V for each phase, i.e., Phase 1& Phase 2, Phase 2 & Phase 3, or Phase 3 & Phase 1.
This is because the phase angle between two phases is 120 degrees, and all three phases change direction with respect to time, and in the case of 230V, the sine wave changes direction 50 times per second due to the frequency of 50Hz.
According to the Rule of Cosine, the voltage between any two phases in a three-phase system is 400V rather than 660 or 690V. This applies only if there are three phases.
[230V2 – 2 x 230V2 x cos (120°)] = 398.37V ≈ 400V
Why 440V in three phases rather than 660V or 690V?
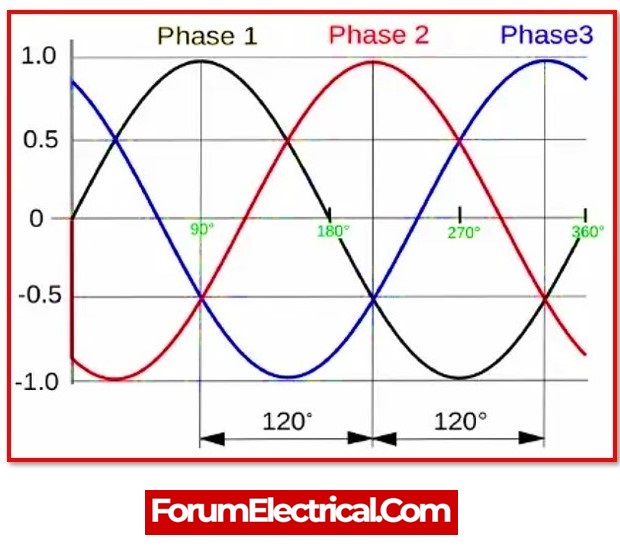
From a different perspective, if draw the sinusoidal waves of three phase power lines that are 120 degrees apart, the graph clearly reveals that circuit only have two Positive (+Ve) values at the same time and the third is Negative (-Ve). They only calculate two of the three cycles because they all change direction with regard to time. In summary, either Phase 1 & 2, Phase 2 &3, or Phase 3 & 1 are positive, whereas Phase 3, Phase 2, or Phase 1 are negative. As a result, two phases of a three-phase system contain 440V rather than 600, 660, or 690V.
What is the purpose of 440 volts?
Using 440 volts for motors results in a reduction in motor load current, which is half the amount of current produced by 230 volts.
According to the formula,
kWloss = I2R/1000
the load current is responsible for the line losses.
If a single-phase circuit is 230V, why is a three-phase circuit 440V and not 690V?
1. Voltage is the potential difference between the two points.
2. A single phase voltage is the voltage between two phases. While the 3-phase is a combination of any two of those three phases.
3. All three phases, i.e., the three wires in the three-phase supply, have the same maximum rms (avg.) value. In other words, if measure the voltage of any of the phases against neutral, it will be 220 or 240 volts. However, when the voltage is measured from one phase to the other, it equals 440.
4. Consider a sin wave with a maximum amplitude of 220 relative to its axis. So, whether in a positive or negative cycle, it can reach a maximum of 220 (+220 or -220).
5. In the case of three phases, the voltage might be applied between two phases rather than one phase and neutral. So, there are three phases, but the voltage between two phases can be calculated. Even though there are three phases, calculate the voltage between any two of them at the same time. And the maximum voltage that received from any two phases is when one is at the top of its positive cycle (i.e., + 220) and the other is at the bottom of its negative cycle (-220).
((+220) -(-220) =440)
And this is the highest value can beachieved by comparing any two points in any of the phases to each other.
Difference between single-phase & three phase
| S.NO | SINGLE PHASE | THREE PHASE |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity flows through a single conductor in a single-phase connection | A three-phase connection is comprised of three different wires that are required for electrical transmission. |
| 2 | The voltage of a single-phase power supply system can reach 230 Volts. | It is capable of carrying a voltage of up to 440 Volts when connected to a three-phase system. |
| 3 | Two wires are needed for single-phase electricity flow. One is the neutral wire and the other a phase. | In a three-phase connection, one neutral wire and three phase wires are needed to make the circuit function. |
| 4 | A single-phase connection has only one phase wire, if something problem occurs with the network, the entire power supply is interrupted. | If something happens to one phase of a three-phase power supply, the other phases will still function. There is no interruption in the power. |
| 5 | It is suitable for light loads such as lighting and heating. | Large industrial motors can be powered by a three-phase supply. |
| 6 | Power distribution in a single-phase supply is inconsistent due to voltage peaks and dips. | The power delivery in three phase supply is always stable and consistent due to three conductors with a 120° phase difference. |
| 7 | The loss in single phase operation is at its maximum. | The three-phase circuit has the minimum amount of loss. |
| 8 | It has a very minimal level of efficiency. | It has its maximum efficiency. |
| 9 | It is not expensive than the three-phase power supply. | It is more expensive than the single-phase supply. |
| 10 | A power supply with a single phase can only transfer a minimum amount of power. | On a three-phase connection, the maximum amount of power is transmitted. |
Difference between 415V & 440V
| S.NO | 415V | 440V |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The RMS voltage from line to line is 415V. | The maximum peak voltage is 440V. |
| 2 | The transformer will be at or around 415v when completely loaded. It also enables to control for supply variations by using the transformer tappings. | To compensate for the transformer’s internal resistance, the nominal voltage is 440V. At full load, a transformer with 5% impedance will drop 5% volts. |