Curie’s Law is a relationship in physics that describes the behavior of magnetic materials at different temperatures. It states that the magnetic moment per unit volume of a material is directly proportional to the temperature. The magnetic moment of a material is a measure of the strength of its magnetization.
Curie’s Law Expression:
Mathematically, Curie’s Law can be expressed as:
M/V = C/T
where:
M – The magnetic moment per unit volume
V – The volume of the material
C – A constant of proportionality known as the Curie constant
T – The temperature of the material
Curie’s Law is based on the idea that the magnetic moments of the atoms or molecules in a material are randomly oriented at high temperatures, but become more aligned at low temperatures. This results in a stronger overall magnetization of the material at low temperatures.
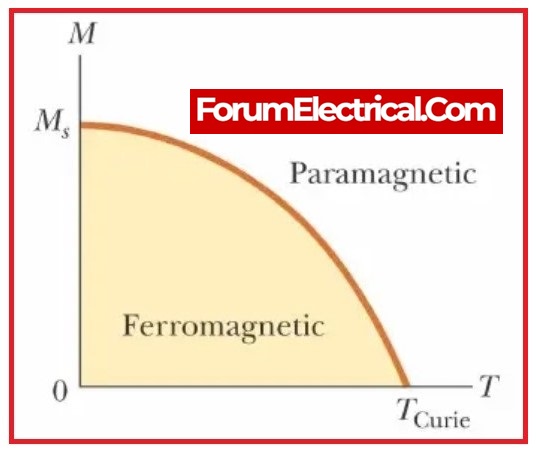
Curie’s Law is useful for predicting the magnetic behavior of materials at different temperatures. It is particularly useful for understanding the behavior of ferromagnetic materials, which are materials that have strong, permanent magnetic moments. Ferromagnetic materials exhibit a phenomenon known as the Curie point, which is the temperature at which they transition from being ferromagnetic to paramagnetic. The Curie point is determined by the Curie constant of the material.
What is the curie symbol?
In the cgs system, the curie i.e., symbol Ci was the unit for radioactive decay. One curie was defined as one gm of pure radium-226 radioactivity, which is equivalent to 3.7 × 1010 decays per second.