The Compensation Theorem is a principle in electrical engineering that allows the response of a linear, two-port network to be determined based on the response of the network to a single input. It states that the response of a two-port network to any two inputs can be determined by measuring the response of the network to a single input and a zero input.
The Compensation Theorem is based on the idea that the response of a linear, two-port network to any two inputs can be represented by a matrix, known as the network’s transfer matrix. The transfer matrix is a mathematical representation of the relationship between the inputs and outputs of the network. According to the Compensation Theorem, the transfer matrix of a two-port network can be determined by measuring the network’s response to a single input and a zero input.
The Compensation Theorem is a useful tool for analyzing and designing electrical circuits and systems, particularly when the circuit or system is symmetrical. It allows engineers to use symmetry to simplify the analysis of the circuit or system, making it easier to understand its behavior and to design it effectively.
The Compensation Theorem is only applicable to linear, two-port networks. It is not applicable to nonlinear networks or to networks with more than two ports.
Where is the compensation theory most commonly used?
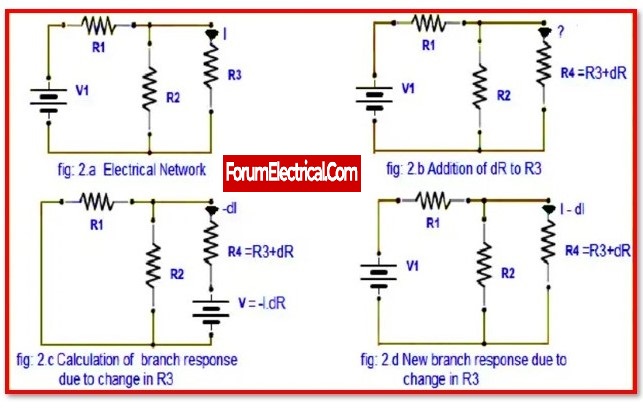
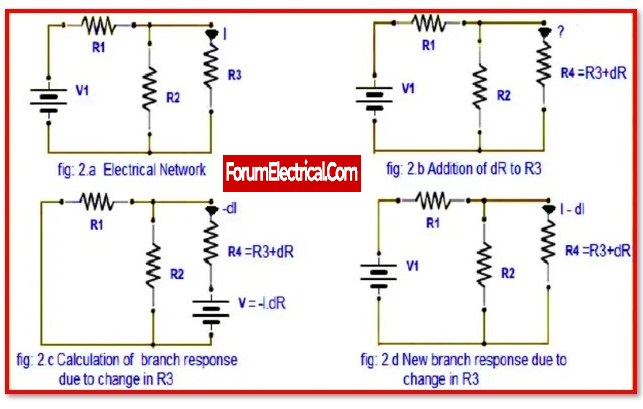
It is highly important in network theory to research or know the effect of change in impedance in one of its branches. As a result, it will have an effect on the related currents and voltages in the circuit or network. As a result, the compensation theorem is used to determine the change in the network.
The compensation theorem is frequently used to calculate the approximate effect of small changes in electrical network elements.
What is the importance of the compensation theorem?
This theorem enables to determine the proper current values in any branch of a network when the network is immediately switched to any given change in one step.