Proper cable sizing is fundamental to the safety & efficiency of electrical systems.
Choosing the appropriate cable size makes sure that electrical installations can withstand the load without overheating or experiencing voltage drops.
This post includes a detailed chart that converts kilowatts (kW) to the proper cable size and ampacity.
This chart allows electricians and engineers to easily calculate the appropriate cable size for various power ratings, guaranteeing compliance with safety requirements and improving performance.
Whether you’re planning a new installation or modifying existing wiring, this kW to cable size & amp chart is a valuable resource for making informed selections.
Check the table of motor kW to cable size chart. The chart is based on both direct online (DOL starter) and star-delta starts (star-delta starter).
The cable sizing chart (cable selection chart) is appropriate for both
- Single-phase and
- Three-phase applications.
Note
It is not recommended to use larger cable sizes.
It is not suggested to use aluminium cable for low-rated motors of up to 1.5kW/2HP.
Importance of Proper Cable Sizing
Selecting the correct cable size in electrical systems is essential for a number of reasons, including:
- Properly sized cables limit the danger of electrical accidents caused by overheating wires and ensure safety.
- Correctly sized cables reduce voltage dips, ensuring that electrical equipment obtains the voltage needed for peak performance.
- Adherence to cable sizing standards & regulations serves as essential for complying with electrical codes and safety rules.
Remember to seek advice from a skilled electrician (or) electrical engineer for complex installations (or) if you are unclear about cable sizing for important applications. You can also check with your chosen manufacturer’s to ensure that cable sizes and applications are compatible.
How do you convert kW to wire size?
A power factor of 0.8 is utilized to calculate the KW. To calculate cable sizing, divide the voltage traveling through the cable by the intended current.
How to Select the Best Electrical Cable for the requirements?
The various types of wiring are as follows.
Cables
Cables are usually utilized for permanent wiring, serving as conduits for transferring electrical power across a building’s infrastructure or via power grids. Cables are typically buried beneath walls, ceilings, and floors, resulting in a seamless and orderly electrical system.
A normal cable will consist of two key components:
- The core and PVC sheathing
- Choosing the correct core size and covering is critical for adapting the cable to certain electrical applications.
| Load (kW) | Voltage (V) | Current (Amps) | Cable Size (mm²) | Cable Type |
| 1 KW | 230 V | 4.35 A | 1.5 mm² | Single-core |
| 2 KW | 230 V | 8.70 A | 2.5 mm² | Single-core |
| 3 KW | 230 V | 13.04 A | 4.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 5 KW | 230 V | 21.74 A | 6.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 10 KW | 230 V | 43.48 A | 10.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 15 KW | 230 V | 65.22 A | 16.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 20 KW | 230 V | 86.96 A | 25.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 30 KW | 230 V | 130.43 A | 35.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 40 KW | 230 V | 173.91 A | 50.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 50 KW | 230 V | 217.39 A | 70.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 60 KW | 230 V | 260.87 A | 95.0 mm² | Single-core |
| 70 KW | 230 V | 304.35 A | 120.0 mm² | Single-core |
Two-core-and-earth cables, commonly referred to as twin-core-and-earth cables, have three core types, each distinguished by the color of its sheathing, which is:
- The living core has been insulated with a brown coating.
- The neutral core has been insulated with a blue sheath, while the earth’s core has no sheathing.
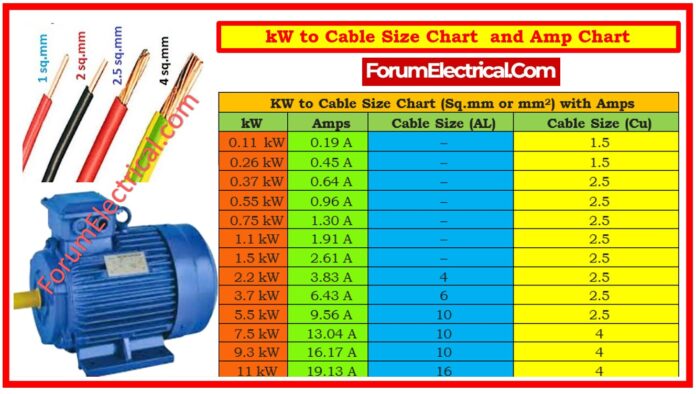
The table below is used as a quick reference for determining the appropriate cable size depending on the electrical power in kilowatts (kW) & the corresponding current in amperes (amps).
| KW to Cable Size Chart (Sq.mm or mm2) with Amps | |||
| kW | Amps | Cable Size (AL) | Cable Size (Cu) |
| 0.11 kW | 0.19 A | – | 1.5 |
| 0.26 kW | 0.45 A | – | 1.5 |
| 0.37 kW | 0.64 A | – | 2.5 |
| 0.55 kW | 0.96 A | – | 2.5 |
| 0.75 kW | 1.30 A | – | 2.5 |
| 1.1 kW | 1.91 A | – | 2.5 |
| 1.5 kW | 2.61 A | – | 2.5 |
| 2.2 kW | 3.83 A | 4 | 2.5 |
| 3.7 kW | 6.43 A | 6 | 2.5 |
| 5.5 kW | 9.56 A | 10 | 2.5 |
| 7.5 kW | 13.04 A | 10 | 4 |
| 9.3 kW | 16.17 A | 10 | 4 |
| 11 kW | 19.13 A | 16 | 4 |
| 15 kW | 26.09 A | 25 | 6 |
| 18.5 kW | 32.17 A | 35 | 10 |
| 22 kW | 38.26 A | 50 | 25 |
| 30 kW | 52.17 A | 70 | 35 |
| 37 kW | 64.35 A | 95 | 50 |
| 45 kW | 78.26 A | 120 | 50 |
| 75 kW | 130.43 A | 150 | 70 |
| 90 kW | 156.52 A | 185 | 95 |
| 110 kW | 191.30 A | 240 | 120 |
| 132 kW | 229.56 A | 300 | 120 |
| 150 kW | 260.86 A | 400 | 150 |
| 175 kW | 304.34 A | 500 | 185 |
| 220 kW | 382.59 A | 500 | 240 |
| 250 kW | 434.76 A | 630 | 300 |
| 280 kW | 486.94 A | 2R x 240 | 300 |
| 310 kW | 539.11 A | 2R x 300 | 400 |
Note
2R represents two run cables.
Electrical Cable Size Calculator
When choosing cables, Use Electrical Cable Sizing Chart to make a better choice. These tables help choose cable sizes for applications. Small cables might melt owing to excessive current flow.
Thus, Cable Sizing Charts determine size and diameter. A smaller diameter resists energy flow more.
The Medium Voltage Cable Sizing is 1KV to 100 kV. Accuracy cutting is needed for their engineered connections. They may explode and injure staff or equipment if not cut properly. The rise in voltage demand prompted Mv Cable Sizing.
We provide the simplest technique to calculate electrical cable size for your application because it is difficult and complicated.
Electrical Cable Size Calculator helps determine the cable size needed to minimize accidents because different applications utilize cables with varied electrical resistance.
- HV – High Voltage Cable Sizing Calculator
- High/Medium Voltage Power Cable Sizing Calculator
- Voltage Drop in Cables: Online Excel Tool
Click here for Electrical Calculators